Cells - Steven Lin`s Websites
... Image Courtesy of http://www.cnas.missouristate.edu/labimages/Biology/Bio122/images/Week%208%20Images/Liver%20cells.JPG ...
... Image Courtesy of http://www.cnas.missouristate.edu/labimages/Biology/Bio122/images/Week%208%20Images/Liver%20cells.JPG ...
Edexcel AS/A level Biology
... Two main factors affect whether an individual will develop a form of cancer: Genetics: some people are more likely than others to experience a mutation which results in cancer, and some people are born with a mutation which gives them a very high risk of developing particular cancers. ● Environment: ...
... Two main factors affect whether an individual will develop a form of cancer: Genetics: some people are more likely than others to experience a mutation which results in cancer, and some people are born with a mutation which gives them a very high risk of developing particular cancers. ● Environment: ...
Cell Coloring
... 1. Color the cell membrane LIGHT RED on the animal & plant cell. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier made up of lipids & some proteins. Its function is to protect the cell, as well as allow certain substances in & out. 2. Shade the cytoplasm LIGHT YELLOW in the animal cell. This is the mat ...
... 1. Color the cell membrane LIGHT RED on the animal & plant cell. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier made up of lipids & some proteins. Its function is to protect the cell, as well as allow certain substances in & out. 2. Shade the cytoplasm LIGHT YELLOW in the animal cell. This is the mat ...
Planet Earth and Its Environment A 5000-million year
... A year later (1839) Schwann published a book on plant and animal cells, listing three main conclusions, two of which are still accepted today as the basis for the cell theory: 1. The cell is the unit of structure of all living things 2. The cell exists as a distinct entity and as a building block in ...
... A year later (1839) Schwann published a book on plant and animal cells, listing three main conclusions, two of which are still accepted today as the basis for the cell theory: 1. The cell is the unit of structure of all living things 2. The cell exists as a distinct entity and as a building block in ...
Pengantar Biokimia Pertemuan 1
... organisms and viruses are ideally suited for the elucidation of many metabolic pathways and regulatory mechanisms. 6. Physiology, which investigates life processes at the tissue and organism levels. 7. Cell biology, which describes the biochemical division of labor within a cell. 8. Genetics, which ...
... organisms and viruses are ideally suited for the elucidation of many metabolic pathways and regulatory mechanisms. 6. Physiology, which investigates life processes at the tissue and organism levels. 7. Cell biology, which describes the biochemical division of labor within a cell. 8. Genetics, which ...
Exam 1-8thED.doc
... A) plant cells B) animal cells C) chloroplasts D) prokaryotic cells E) all of the above 58) How does a cell rid itself of defective or malfunctioning organelles? A) Ribosomes play a significant role in the removal of malfunctioning parts by absorbing the parts. B) Lysosomes assist in the removal of ...
... A) plant cells B) animal cells C) chloroplasts D) prokaryotic cells E) all of the above 58) How does a cell rid itself of defective or malfunctioning organelles? A) Ribosomes play a significant role in the removal of malfunctioning parts by absorbing the parts. B) Lysosomes assist in the removal of ...
Environ-X - NanoServices
... pollution comprehensive management and photodynamic therapy. Actually, photocatalytic sterilization is supposed to constantly work between bacteria and titanium dioxide instead of simple surface reaction as photocatalytic degradation. As the active hydroxyl radical cannot longtime exist and cannot e ...
... pollution comprehensive management and photodynamic therapy. Actually, photocatalytic sterilization is supposed to constantly work between bacteria and titanium dioxide instead of simple surface reaction as photocatalytic degradation. As the active hydroxyl radical cannot longtime exist and cannot e ...
Cell Exploration - Core Concepts: Biology
... mechanisms maintain homeostasis. [Clarification Statement: Examples of investigations could include heart rate response to exercise, stomate response to moisture and temperature, and root development in response to water levels.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the cellular process ...
... mechanisms maintain homeostasis. [Clarification Statement: Examples of investigations could include heart rate response to exercise, stomate response to moisture and temperature, and root development in response to water levels.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the cellular process ...
Chapter 3 Cells, Tissues, and Organ Systems
... *animal – outer layer; cholesterol *selectively permeable ...
... *animal – outer layer; cholesterol *selectively permeable ...
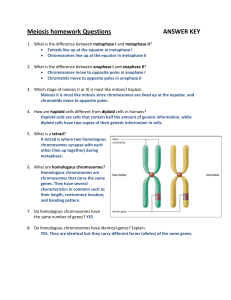
Meiosis homework Questions ANSWER KEY
... Spermatogensis occurs in males, even division produces four gametes 13. A muscle cell of a mouse contains 22 chromosomes. Based on this information, how many chromosomes are there in the following types of mouse cells? a. Daughter muscle cell formed from mitosis 22 chromosomes b. Egg cell 22 chrom ...
... Spermatogensis occurs in males, even division produces four gametes 13. A muscle cell of a mouse contains 22 chromosomes. Based on this information, how many chromosomes are there in the following types of mouse cells? a. Daughter muscle cell formed from mitosis 22 chromosomes b. Egg cell 22 chrom ...
CELLS
... • Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) • Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division) ...
... • Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) • Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division) ...
Lecture 6 eukaryote
... sphingolipids, and sterol, all of which contribute to strength of membrane – Fatty acids attach to glycerol by ester linkage ...
... sphingolipids, and sterol, all of which contribute to strength of membrane – Fatty acids attach to glycerol by ester linkage ...
Bio10lab1 0710
... specialized tasks such as moving, feeding and reproducing. Despite their minute size, cells are amazingly complex and often very beautiful. There are two general types of cells: • Prokaryotic cells o Lack a nucleus, but they do contain DNA o Also lack other organelles, such as mitochondria, chloropl ...
... specialized tasks such as moving, feeding and reproducing. Despite their minute size, cells are amazingly complex and often very beautiful. There are two general types of cells: • Prokaryotic cells o Lack a nucleus, but they do contain DNA o Also lack other organelles, such as mitochondria, chloropl ...
green = key features - mr. welling` s school page
... Evolution of mitosis • A possible progression of mechanisms intermediate between binary fission & mitosis seen in modern organisms ...
... Evolution of mitosis • A possible progression of mechanisms intermediate between binary fission & mitosis seen in modern organisms ...
PLASMOLYZED CELLS
... Name:________________________ Per._____ PLASMOLYZED CELLS Pre-lab Discussion: Diffusion of water molecules across a cell’s outer membrane form areas of high water concentration to areas low water concentration is called osmosis. This movement of water may be harmful to cells. It can result in cell w ...
... Name:________________________ Per._____ PLASMOLYZED CELLS Pre-lab Discussion: Diffusion of water molecules across a cell’s outer membrane form areas of high water concentration to areas low water concentration is called osmosis. This movement of water may be harmful to cells. It can result in cell w ...
Asexual reproduction
... Red blood cells: 120 days Stomach lining cells: 2 days Skin cells: 20 days You need mitosis and cell division to replace these cells. In your body about 3 billion cells die every minutes. ADJH- H. Aucoin ...
... Red blood cells: 120 days Stomach lining cells: 2 days Skin cells: 20 days You need mitosis and cell division to replace these cells. In your body about 3 billion cells die every minutes. ADJH- H. Aucoin ...
The Role of Patched in Basal Cell Carcinoma
... - This inhibition is relieved with the binding of the ligand Sonic ...
... - This inhibition is relieved with the binding of the ligand Sonic ...
Animal Cell Glossary
... Which type of cell forms a protective layer for your body? a. nerve cell b. skin cell c. muscle cell d. fat cell Which of the following is an organ? a. stomach b. muscle tissue c. nerve tissue d. blood tissue What is the smallest unit of life in all living things called? a. an atom b. a molecule c. ...
... Which type of cell forms a protective layer for your body? a. nerve cell b. skin cell c. muscle cell d. fat cell Which of the following is an organ? a. stomach b. muscle tissue c. nerve tissue d. blood tissue What is the smallest unit of life in all living things called? a. an atom b. a molecule c. ...
Plant vs. Animal Cell Compariset
... observe the key differences between the two types of cells. Students will also gain a thorough understanding of why certain organelles are found only in plant cells, animal cells, or both, based on their cell functions. ...
... observe the key differences between the two types of cells. Students will also gain a thorough understanding of why certain organelles are found only in plant cells, animal cells, or both, based on their cell functions. ...
Bio 101 Cumulative FINAL Homework Prof. Fournier
... The daughter cells will pass on only half of the genetic information they received from the original cell. The daughter cells will each produce offspring that will have the same genetic information as the original cell. The daughter cells will each undergo the same mutations as the original cell aft ...
... The daughter cells will pass on only half of the genetic information they received from the original cell. The daughter cells will each produce offspring that will have the same genetic information as the original cell. The daughter cells will each undergo the same mutations as the original cell aft ...
Chapter 12: Nervous Tissue - WKC Anatomy and Physiology
... 1. the inactivation gate is open. 2. the activation gate is closed. 3. the channel is permeable to Na+. a) b) c) d) e) ...
... 1. the inactivation gate is open. 2. the activation gate is closed. 3. the channel is permeable to Na+. a) b) c) d) e) ...
The Fundamental Units of Life Classwork Name: 7th Grade PSI 1
... 11. The liver is an organ that is responsible for detoxification. This means that it breaks down toxins in the body. Explain which organelle is important for the function of the liver. ...
... 11. The liver is an organ that is responsible for detoxification. This means that it breaks down toxins in the body. Explain which organelle is important for the function of the liver. ...
The Fundamental Units of Life Classwork Name: 7th Grade PSI
... 11. The liver is an organ that is responsible for detoxification. This means that it breaks down toxins in the body. Explain which organelle is important for the function of the liver. ...
... 11. The liver is an organ that is responsible for detoxification. This means that it breaks down toxins in the body. Explain which organelle is important for the function of the liver. ...
CELL DIVISION: BINARY FISSION AND MITOSIS The Cell Cycle
... features in their cell division processes. Replication of the DNA must occur. Segregation of the "original" and its "replica" follow. Cytokinesis ends the cell division process. Whether the cell was eukaryotic or prokaryotic, these basic events must occur. Cytokinesis is the process where one cell s ...
... features in their cell division processes. Replication of the DNA must occur. Segregation of the "original" and its "replica" follow. Cytokinesis ends the cell division process. Whether the cell was eukaryotic or prokaryotic, these basic events must occur. Cytokinesis is the process where one cell s ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.