Apoptosis (programmed cell death) plays many important roles in
... Strategy to find mutations that block apoptosis: take advantage of mutations in engulfment genes, specifically, ced-1 apoptosis ...
... Strategy to find mutations that block apoptosis: take advantage of mutations in engulfment genes, specifically, ced-1 apoptosis ...
•Eukaryotic cells are about 1000 times larger than bacteria cells and
... In cell biology, a mitochondrion is a membrane-enclosed organelle, found in most eukaryotic cells.Mitochondria are sometimes described as "cellular power plants," because they convert NADH and NADPH into energy in the form of ATP via the process of oxidative phosphorylation. A typical eukaryotic cel ...
... In cell biology, a mitochondrion is a membrane-enclosed organelle, found in most eukaryotic cells.Mitochondria are sometimes described as "cellular power plants," because they convert NADH and NADPH into energy in the form of ATP via the process of oxidative phosphorylation. A typical eukaryotic cel ...
Outline for Cell structure and membranes
... A. enzymes are proteins, so they are made of amino acids and have complex three-dimensional structure B. enzymes are biological catalysts. They lower the "activation energy" needed to start a reaction, so they make the reactions go faster. Enzymes control every chemical reaction that takes place ins ...
... A. enzymes are proteins, so they are made of amino acids and have complex three-dimensional structure B. enzymes are biological catalysts. They lower the "activation energy" needed to start a reaction, so they make the reactions go faster. Enzymes control every chemical reaction that takes place ins ...
6.2 workbook - Fetal Development
... Embryonic development takes place during the first eight weeks after fertilization. During this time, the embryo develops. Its cells divide constantly, and tissues and organs form. During the first week, the single fertilized cell, the zygote, develops into a mass of many cells. This mass of cells t ...
... Embryonic development takes place during the first eight weeks after fertilization. During this time, the embryo develops. Its cells divide constantly, and tissues and organs form. During the first week, the single fertilized cell, the zygote, develops into a mass of many cells. This mass of cells t ...
Slide 1
... -PS Reactants are the Products of CR -CR Reactants are the Products of PS -CR makes energy (ATP) -PS uses energy (ATP) ...
... -PS Reactants are the Products of CR -CR Reactants are the Products of PS -CR makes energy (ATP) -PS uses energy (ATP) ...
Week_9
... • A BS functions under the supervision of a telecommunication switch called Mobile Switching Center (MSC) and connected to it through wired line. • It is the MSC which connects the entire mobile system with PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network). • Figure 3 illustrates a communication path ...
... • A BS functions under the supervision of a telecommunication switch called Mobile Switching Center (MSC) and connected to it through wired line. • It is the MSC which connects the entire mobile system with PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network). • Figure 3 illustrates a communication path ...
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
... • Movement against the concentration gradient • Requires ATP (energy) and a specific transporter protein for each substance • Group translocation – Occurs only in prokaryotes – Substance being transported is altered during transport (often phosphorylation) – Membrane is impermeable to the new produc ...
... • Movement against the concentration gradient • Requires ATP (energy) and a specific transporter protein for each substance • Group translocation – Occurs only in prokaryotes – Substance being transported is altered during transport (often phosphorylation) – Membrane is impermeable to the new produc ...
Topic 3 revision notes - Mr Cartlidge`s Saigon Science Blog
... Plants become turgid, but do not burst because of their tough cell wall; Animal cells will burst, because they have no cell wall; The reverse happens when plant and animal cells are placed in a concentrated sugar or salt solutions. This is because there is a higher concentration of water molec ...
... Plants become turgid, but do not burst because of their tough cell wall; Animal cells will burst, because they have no cell wall; The reverse happens when plant and animal cells are placed in a concentrated sugar or salt solutions. This is because there is a higher concentration of water molec ...
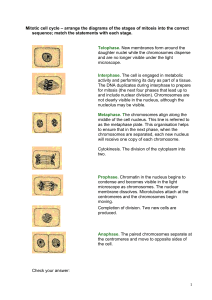
Mitotic cell cycle – arrange the diagrams of the stages of mitosis into
... activity and performing its duty as part of a tissue. The DNA duplicates during interphase to prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Chromosomes are not clearly visible in the nucleus, although the nucleolus may be visible. Metaphase. The chromosomes ...
... activity and performing its duty as part of a tissue. The DNA duplicates during interphase to prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Chromosomes are not clearly visible in the nucleus, although the nucleolus may be visible. Metaphase. The chromosomes ...
Slide ()
... PTH effects on bone. PTH binds to osteoblast parathyroid hormone receptor 1 (PTHR1), stimulating the cell surface expression of RANKL, which binds to RANK, a cell surface protein on osteoclast precursors. Binding of RANKL to RANK activates osteoclast gene transcription and the differentiation into a ...
... PTH effects on bone. PTH binds to osteoblast parathyroid hormone receptor 1 (PTHR1), stimulating the cell surface expression of RANKL, which binds to RANK, a cell surface protein on osteoclast precursors. Binding of RANKL to RANK activates osteoclast gene transcription and the differentiation into a ...
PAPER TITLE: Animal Diversity: Non Chordates
... discusses the fundamental processes that enable cells to grow, move and communicate and will cover topics such as cell architecture, cell chemistry, cell division, functions and cell cycle. Students will also learn current molecular biological techniques that are used to study cell biology. Laborato ...
... discusses the fundamental processes that enable cells to grow, move and communicate and will cover topics such as cell architecture, cell chemistry, cell division, functions and cell cycle. Students will also learn current molecular biological techniques that are used to study cell biology. Laborato ...
Chapter 3 Innate Immunity
... particular patterns, such receptors of the host are called pattern recognition receptors (PRR) - The patterns found on pathogens are called pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMP) ...
... particular patterns, such receptors of the host are called pattern recognition receptors (PRR) - The patterns found on pathogens are called pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMP) ...
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... • These cells are larger and more complex. • They contain many structures and membranes, and are highly specialized. • They contain a nucleus in which their genetic material is separated from the rest of the cell. • Some are single celled and other are multicellular. • Plants, animals, fungi are euk ...
... • These cells are larger and more complex. • They contain many structures and membranes, and are highly specialized. • They contain a nucleus in which their genetic material is separated from the rest of the cell. • Some are single celled and other are multicellular. • Plants, animals, fungi are euk ...
Chapter 20 Multi cellular Algae Kingdom Plantae
... • Can be put in Kingdom Protista but they do share more in common with plants because they reproduce with alternation or generation. Page 437 copy the Chlamydomonas Reproduction of Chlamydomonas: Life cycle: • Most of its life cycle is in the haploid stage • As long as conditions are good, it will r ...
... • Can be put in Kingdom Protista but they do share more in common with plants because they reproduce with alternation or generation. Page 437 copy the Chlamydomonas Reproduction of Chlamydomonas: Life cycle: • Most of its life cycle is in the haploid stage • As long as conditions are good, it will r ...
Eric H. Davidson
... advances in DNA-sequencing technology to examine the genomic sequences near genes. Coupled with data on when genes were being turned on, and in what cells, during the early development of sea urchins, they showed how the sequences near many genes have a regulatory role. This approach rapidly led to ...
... advances in DNA-sequencing technology to examine the genomic sequences near genes. Coupled with data on when genes were being turned on, and in what cells, during the early development of sea urchins, they showed how the sequences near many genes have a regulatory role. This approach rapidly led to ...
Investigating Cell Types
... Paramecium is a group of single-celled eukaryotes, which are commonly studied as a representative of the ciliate group, as they are covered with cilia (small hairs) which allow the cells to move with a synchronous motion (like a caterpillar) at speeds of approximately 12 body lengths per second. The ...
... Paramecium is a group of single-celled eukaryotes, which are commonly studied as a representative of the ciliate group, as they are covered with cilia (small hairs) which allow the cells to move with a synchronous motion (like a caterpillar) at speeds of approximately 12 body lengths per second. The ...
Chapter 3 Section 1
... Anything that can live on its own is called an organism. If a single cell is living on its own, it is called unicellular. Most unicellular organisms require a microscope to see them. Humans have many cells and are called a multicellular organism. This means that humans can only exist as a group of c ...
... Anything that can live on its own is called an organism. If a single cell is living on its own, it is called unicellular. Most unicellular organisms require a microscope to see them. Humans have many cells and are called a multicellular organism. This means that humans can only exist as a group of c ...
Epicel Skin Grafts - University of Rhode Island
... backing of petrolatum gauze. Enough skin can be grown to heal the whole wound from a biopsy (of the patient’s own healthy skin) the size of a postage stamp. The cells within the epidermis of the skin sample are separated and grown by a process called “tissue culture”, which involves feeding the cell ...
... backing of petrolatum gauze. Enough skin can be grown to heal the whole wound from a biopsy (of the patient’s own healthy skin) the size of a postage stamp. The cells within the epidermis of the skin sample are separated and grown by a process called “tissue culture”, which involves feeding the cell ...
Introduction: plant cell wall proteins
... the plasma membrane and then processed for release to the cell wall and/or as extracellular secretions. The expression of AGP genes is then considered along with the localization patterns of various AGPs; these data highlight the involvement of AGPs in plant development. Whereas AGPs are likely to h ...
... the plasma membrane and then processed for release to the cell wall and/or as extracellular secretions. The expression of AGP genes is then considered along with the localization patterns of various AGPs; these data highlight the involvement of AGPs in plant development. Whereas AGPs are likely to h ...
CHAPTER 8 NOTES
... 2) Why is osmosis important? 3) How do molecules move against their concentration gradient? CELL COMMUNICATION To coordinate their activities cells must communicate. Cell use Signal Molecules- (something that is produced and released by one cell to send a message to another)- to communicate. Example ...
... 2) Why is osmosis important? 3) How do molecules move against their concentration gradient? CELL COMMUNICATION To coordinate their activities cells must communicate. Cell use Signal Molecules- (something that is produced and released by one cell to send a message to another)- to communicate. Example ...
Cell Test Review
... Answer 5 – 40 • Uni - the cone cell carries out all of the life processes of the organism. • Multi – Cell are specialized to only carry our specific functions. They rely on either specialized cell in the same organism to ...
... Answer 5 – 40 • Uni - the cone cell carries out all of the life processes of the organism. • Multi – Cell are specialized to only carry our specific functions. They rely on either specialized cell in the same organism to ...
The Incredible Edible Cell Model
... #2 Create a 3-D cell model It can be out of any nonfood material like paper Mache, styrene, clay, cardboard, etc…. #3 Author a PowerPoint slide show on cell biology. It must have at least 10 slides but no more ...
... #2 Create a 3-D cell model It can be out of any nonfood material like paper Mache, styrene, clay, cardboard, etc…. #3 Author a PowerPoint slide show on cell biology. It must have at least 10 slides but no more ...
Mineral Nutrition in Plants II - Western Washington University
... No one can look at the plants growing on a bank or on the borders of a thick wood, and doubt that the young stems and leaves place themselves so that the leaves may be well illuminated...they are extremely heliotropic; and this probably serves...as a guide (for) the buried seeds through fissures in ...
... No one can look at the plants growing on a bank or on the borders of a thick wood, and doubt that the young stems and leaves place themselves so that the leaves may be well illuminated...they are extremely heliotropic; and this probably serves...as a guide (for) the buried seeds through fissures in ...
Phytoplankton Cell Model Building: Expanded Teaching Notes The
... o Describe that these phytoplankton are eukaryotic cells, but another important group of photosynthesizers in the ocean are prokaryotic cells Explain that the students are going to build a model of the phytoplankton. They will build either a coccolithophore, diatom, or dinoflagellate. Depending on r ...
... o Describe that these phytoplankton are eukaryotic cells, but another important group of photosynthesizers in the ocean are prokaryotic cells Explain that the students are going to build a model of the phytoplankton. They will build either a coccolithophore, diatom, or dinoflagellate. Depending on r ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.