8TH Grade Fourth Marking Period Test
... b. List the three major steps of the cell cycle and state what happens in each step. c. How are the results of mitosis and meiosis different? (hint: How many cells are produced during each process? What types of cells are produced in each process?) 3. In your own words, explain how the energy in fos ...
... b. List the three major steps of the cell cycle and state what happens in each step. c. How are the results of mitosis and meiosis different? (hint: How many cells are produced during each process? What types of cells are produced in each process?) 3. In your own words, explain how the energy in fos ...
Biology Review
... A. I am one of the first to see the cell structure for cell division. B. I invented the first simple light microscopes in the 1700s. C. I created the system of binomial nomenclature using Latin. D. I coined the term “cells” by looking at cork in the microscope. E. I supported the idea of biogenesis ...
... A. I am one of the first to see the cell structure for cell division. B. I invented the first simple light microscopes in the 1700s. C. I created the system of binomial nomenclature using Latin. D. I coined the term “cells” by looking at cork in the microscope. E. I supported the idea of biogenesis ...
Xavier Cancer Study - Xavier University of Louisiana
... natural compounds from dietetic plants and herbs and is completely non-toxic to normal cells, but exclusively kills cancer cells. It is completely effective only in combination and not individually because by including them in this mixture we have made them active at bioavailable levels, that is lev ...
... natural compounds from dietetic plants and herbs and is completely non-toxic to normal cells, but exclusively kills cancer cells. It is completely effective only in combination and not individually because by including them in this mixture we have made them active at bioavailable levels, that is lev ...
identification and characterization of genes regulated by aqsr, a luxr
... mobility shift assays (EMSA) with purified AqsR was performed to know direct binding of AqsR to the promoter region . Results. (1) 353 genes were differentially expressed during the stationary phase of wild type cells compared to that of aqsR mutant. AqsR appears to be a very important regulator bec ...
... mobility shift assays (EMSA) with purified AqsR was performed to know direct binding of AqsR to the promoter region . Results. (1) 353 genes were differentially expressed during the stationary phase of wild type cells compared to that of aqsR mutant. AqsR appears to be a very important regulator bec ...
Lab Science Name
... when scraping the inside of your cheek. Only a few cells are needed. The end of the toothpick will have several cheek cells stuck to it even though you may see nothing but a drop of saliva. 3. Stir the water on the slide with the end of the toothpick to mix the cheek cells with the water. Dispose th ...
... when scraping the inside of your cheek. Only a few cells are needed. The end of the toothpick will have several cheek cells stuck to it even though you may see nothing but a drop of saliva. 3. Stir the water on the slide with the end of the toothpick to mix the cheek cells with the water. Dispose th ...
MICB 201- Learning Objectives
... Incomplete cell division – In some prokaryotes, a significant fraction of cells never completely separate after symmetric cell division. Therefore, chains/filaments or clumps of cells result depending on the orientations of the division planes. If they only divide on one plane you get a chain. If t ...
... Incomplete cell division – In some prokaryotes, a significant fraction of cells never completely separate after symmetric cell division. Therefore, chains/filaments or clumps of cells result depending on the orientations of the division planes. If they only divide on one plane you get a chain. If t ...
No Slide Title - Washington State University
... •More complex functions, AOI….. Design generation •Schematic using the cells •Higher level description language (VHDL, Verilog) All cells have identical heights Widths of the cells may vary Standard cell design can be combined with other layout methodologies ...
... •More complex functions, AOI….. Design generation •Schematic using the cells •Higher level description language (VHDL, Verilog) All cells have identical heights Widths of the cells may vary Standard cell design can be combined with other layout methodologies ...
Comparative Analysis of Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotic
... published papers [1,2,3]. We used the expression profiles of seven time series experiments; three experiments from S.cerevisiae, three from H.sapiens, and one from A.thaliana. Periodically expressed genes within the cell cycles were extracted as cell cycle regulated genes, by applying Fourier Analys ...
... published papers [1,2,3]. We used the expression profiles of seven time series experiments; three experiments from S.cerevisiae, three from H.sapiens, and one from A.thaliana. Periodically expressed genes within the cell cycles were extracted as cell cycle regulated genes, by applying Fourier Analys ...
Cells - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... maintain the cell, respond to changes in the environment, and to divide into 2 cells. The cell’s instructions are coded in the DNA, which is the main part of chromosomes. A chromosome is composed of a single DNA molecule plus the proteins that support it and control it. Most eukaryotes have a small ...
... maintain the cell, respond to changes in the environment, and to divide into 2 cells. The cell’s instructions are coded in the DNA, which is the main part of chromosomes. A chromosome is composed of a single DNA molecule plus the proteins that support it and control it. Most eukaryotes have a small ...
Cells
... maintain the cell, respond to changes in the environment, and to divide into 2 cells. The cell’s instructions are coded in the DNA, which is the main part of chromosomes. A chromosome is composed of a single DNA molecule plus the proteins that support it and control it. Most eukaryotes have a small ...
... maintain the cell, respond to changes in the environment, and to divide into 2 cells. The cell’s instructions are coded in the DNA, which is the main part of chromosomes. A chromosome is composed of a single DNA molecule plus the proteins that support it and control it. Most eukaryotes have a small ...
Chapter 02
... A Generalized Cell Although the human body is composed of more than 200 different types of cells, each performing a different function, all cells possess certain unifying characteristics and thus can be described in general terms. Every cell is surrounded by a bilipid plasma membrane, possesses org ...
... A Generalized Cell Although the human body is composed of more than 200 different types of cells, each performing a different function, all cells possess certain unifying characteristics and thus can be described in general terms. Every cell is surrounded by a bilipid plasma membrane, possesses org ...
From Cells to Tissues: Cell Junctions
... Cell Junctions are Dynamic Structures When they were originally discovered cell junctions were considered to be relatively static structures. This was likely because they appeared to have a consistent, unchanging structure when viewed with the electron microscope. New techniques have revealed that p ...
... Cell Junctions are Dynamic Structures When they were originally discovered cell junctions were considered to be relatively static structures. This was likely because they appeared to have a consistent, unchanging structure when viewed with the electron microscope. New techniques have revealed that p ...
Protist Jeopardy
... two different organisms exist in a Relationship, where each one benefits from the other ...
... two different organisms exist in a Relationship, where each one benefits from the other ...
Biology 11th Class 2015-16
... contraction; skeletal system and its functions; joints; disorders of muscular and skeletal system myasthenia gravis, tetany, muscular dystrophy, arthritis, osteoporosis, gout. Chapter-21: Neural Control and Coordination Neuron and nerves; Nervous system in humans - central nervous system; peripheral ...
... contraction; skeletal system and its functions; joints; disorders of muscular and skeletal system myasthenia gravis, tetany, muscular dystrophy, arthritis, osteoporosis, gout. Chapter-21: Neural Control and Coordination Neuron and nerves; Nervous system in humans - central nervous system; peripheral ...
Document
... The cells of multicellular organisms may differentiate and become adapted for specific functions. Tissues are aggregations of similar cells; organs are aggregations of tissues performing specific physiological functions. Organs are organised into organ systems, which work together to form organisms. ...
... The cells of multicellular organisms may differentiate and become adapted for specific functions. Tissues are aggregations of similar cells; organs are aggregations of tissues performing specific physiological functions. Organs are organised into organ systems, which work together to form organisms. ...
3.2 Cell Structures
... processes of life without any help from other cells. • A biofilm is a thin layer of bacteria that sticks to a surface. Cells in a biofilm are all alike, but they may play different roles, such as taking in nutrients or making the “glue” that sticks the biofilm to the surface. The sticky plaque that ...
... processes of life without any help from other cells. • A biofilm is a thin layer of bacteria that sticks to a surface. Cells in a biofilm are all alike, but they may play different roles, such as taking in nutrients or making the “glue” that sticks the biofilm to the surface. The sticky plaque that ...
Lab 4. Cell Structure: What Type of Cell Is on the Unknown Slides?
... scientific theories that have developed over time. These theories combine different types of evidence to support a big idea that explains some aspect of life or the natural world. One of the major theories that scientists rely on when studying living things is the cell theory. This theory includes t ...
... scientific theories that have developed over time. These theories combine different types of evidence to support a big idea that explains some aspect of life or the natural world. One of the major theories that scientists rely on when studying living things is the cell theory. This theory includes t ...
Additional Biology B2 Core Knowledge
... The double-helix shapes DNA structure found in many cells, including human cells. The gel-like substance which holds all of a cells contents. Where two things both increase at the same ratio to each other. A molecule containing the genetic code. A special type of telescope for looking at objects sma ...
... The double-helix shapes DNA structure found in many cells, including human cells. The gel-like substance which holds all of a cells contents. Where two things both increase at the same ratio to each other. A molecule containing the genetic code. A special type of telescope for looking at objects sma ...
Passive and Active Transport
... difference between concentrations across a membrane, for cellular transport to occur. • No energy is needed because the particles are already in motion. ...
... difference between concentrations across a membrane, for cellular transport to occur. • No energy is needed because the particles are already in motion. ...
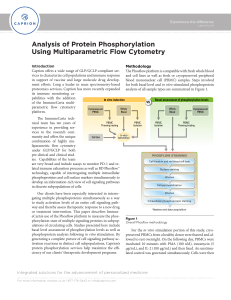
Analysis of Protein Phosphorylation Using Multiparametric Flow
... cells detects the basal level of protein phosphorylation. Assessment of basal levels leads to an understanding of the complex phosphorylation equilibrium that exists in vivo. By contrast, phosphorylation analysis done on the same clinical specimens following in vitro stimulation with PMA, ionomycin ...
... cells detects the basal level of protein phosphorylation. Assessment of basal levels leads to an understanding of the complex phosphorylation equilibrium that exists in vivo. By contrast, phosphorylation analysis done on the same clinical specimens following in vitro stimulation with PMA, ionomycin ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.