Diffusion and Cell Size Introduction
... relationship between cell size and the diffusion of substances across the cell membrane. Diffusion is the spontaneous movement of a substance from high to low concentration. It is how many substances naturally move from where there is more to where there less: such as the smell of perfume moving acr ...
... relationship between cell size and the diffusion of substances across the cell membrane. Diffusion is the spontaneous movement of a substance from high to low concentration. It is how many substances naturally move from where there is more to where there less: such as the smell of perfume moving acr ...
Mohsin Abstract - Professional Heart Daily
... Rationale: Cortical bone derived stem cells (CBSCs) are known to have improved growth kinetics and myocardial repair properties that are superior to other known stem cell types used. Salutary effects of CBSCs in large are mediated by paracrine secretion. Since exosomes represent an active component ...
... Rationale: Cortical bone derived stem cells (CBSCs) are known to have improved growth kinetics and myocardial repair properties that are superior to other known stem cell types used. Salutary effects of CBSCs in large are mediated by paracrine secretion. Since exosomes represent an active component ...
Oncogenic Role of eIF-5A2 in the Development
... genomic hybridization and amplification of 3q26 is one of the most frequent alterations (3– 6). Amplification of 3q26 has been also frequently detected in lung cancer (7), esophageal cancer (8), prostate cancer (9), breast cancer (10), and nasopharyngeal cancer (11). These studies suggest that 3q26 ...
... genomic hybridization and amplification of 3q26 is one of the most frequent alterations (3– 6). Amplification of 3q26 has been also frequently detected in lung cancer (7), esophageal cancer (8), prostate cancer (9), breast cancer (10), and nasopharyngeal cancer (11). These studies suggest that 3q26 ...
This is Jeopardy
... and it was placed in a solution with a salt concentration of 20%, in which direction would the net movement of water be ? ...
... and it was placed in a solution with a salt concentration of 20%, in which direction would the net movement of water be ? ...
Passive Transport
... Passive Transport: 2. Facilitated Diffusion A 2. Facilitated diffusion: diffusion of specific particles through transport proteins(protein channels/carriers) found in the membrane a. Transport Proteins are specific – they “select” only certain molecules to cross the membrane b.Transports larger or ...
... Passive Transport: 2. Facilitated Diffusion A 2. Facilitated diffusion: diffusion of specific particles through transport proteins(protein channels/carriers) found in the membrane a. Transport Proteins are specific – they “select” only certain molecules to cross the membrane b.Transports larger or ...
Transport Within Cells
... Living things have 2 types of transportation that are important to each cell: 1) Getting nutrients and gasses to the cell and waste away from the cell 2) Getting nutrients and gasses into the cell and waste out of the cell. Transport- Getting nutrients to the Cell: It is important for living things ...
... Living things have 2 types of transportation that are important to each cell: 1) Getting nutrients and gasses to the cell and waste away from the cell 2) Getting nutrients and gasses into the cell and waste out of the cell. Transport- Getting nutrients to the Cell: It is important for living things ...
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
... Sexual Reproduction Haploid Cell Chromosomes are not located in pairs. Only have half of the number of chromosomes as a body cell. These cells are called sex cells. – In humans, sex cells have 23 chromosomes. ...
... Sexual Reproduction Haploid Cell Chromosomes are not located in pairs. Only have half of the number of chromosomes as a body cell. These cells are called sex cells. – In humans, sex cells have 23 chromosomes. ...
Cloning
... What do scientists use to create a clone animal? They use the genes of the first animal so they both have the same DNA. ...
... What do scientists use to create a clone animal? They use the genes of the first animal so they both have the same DNA. ...
Structure and Function of the Lysosomes of Human
... living cell. Whether the specific activities of other lysosomal enzymes are influenced by medium pH is under investigation and the results will be reported elsewhere. The consequences of an increase in medium pH on the morphology of cultured human fibroblasts are compatible with a severe inhibition ...
... living cell. Whether the specific activities of other lysosomal enzymes are influenced by medium pH is under investigation and the results will be reported elsewhere. The consequences of an increase in medium pH on the morphology of cultured human fibroblasts are compatible with a severe inhibition ...
7th District Science Curriculum Guide 0609
... Students will be able to… 1. Identify the three components of the cell theory. 2. Identify the microscope as one of the inventions that led to the discovery of the cell. 3. Recognize the major scientists whose work on cells led to the discovery of the cell theory. 4. Draw and label the major organel ...
... Students will be able to… 1. Identify the three components of the cell theory. 2. Identify the microscope as one of the inventions that led to the discovery of the cell. 3. Recognize the major scientists whose work on cells led to the discovery of the cell theory. 4. Draw and label the major organel ...
osmosis
... Water moves from high to low concentrations. •Water moves freely through pores. •Solute (green) too large to move across. ...
... Water moves from high to low concentrations. •Water moves freely through pores. •Solute (green) too large to move across. ...
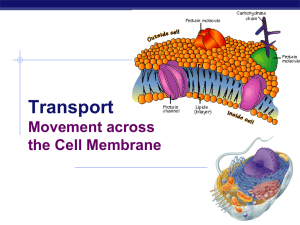
Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane
... Membrane Carbohydrates Play a key role in cell-cell recognition ability of a cell to distinguish neighboring cells from another important in organ & tissue development basis for rejection of foreign cells by immune system ...
... Membrane Carbohydrates Play a key role in cell-cell recognition ability of a cell to distinguish neighboring cells from another important in organ & tissue development basis for rejection of foreign cells by immune system ...
Biology 11 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Explain how unicellular organisms differ from multicellular organisms with respect to how they perform their life processes. Describe how cells are arranged into increasingly complex levels of cellular organization in multicellular organisms - tissues; organs; organ systems Explain why it is necessa ...
... Explain how unicellular organisms differ from multicellular organisms with respect to how they perform their life processes. Describe how cells are arranged into increasingly complex levels of cellular organization in multicellular organisms - tissues; organs; organ systems Explain why it is necessa ...
SBI3U - Hwdsb
... Write out the chemical equations for lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation. How many ATP are produced using lactic acid fermentation or alcoholic fermentation? How do these numbers compare to the number of ATPs produced using aerobic cellular respiration? ...
... Write out the chemical equations for lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation. How many ATP are produced using lactic acid fermentation or alcoholic fermentation? How do these numbers compare to the number of ATPs produced using aerobic cellular respiration? ...
Morphological Plasticity of the Mitotic Apparatus in
... and developmentalprograms expressed in each cell. A great deal of evidence strongly favors the first conclusion, but other data indicate that the second is important as well, at least in certain cell types. Numerous investigators have proposed that space constraints are responsible for oblique or de ...
... and developmentalprograms expressed in each cell. A great deal of evidence strongly favors the first conclusion, but other data indicate that the second is important as well, at least in certain cell types. Numerous investigators have proposed that space constraints are responsible for oblique or de ...
Development of differentiation assay in neuroblastoma to elucidate
... overall survival of only 50%. Amplification of MYCN and overexpression of its coded protein is associated with rapid tumour progression and poor outcome. Induction of terminal differentiation is a very promising approach to neuroblastoma treatment. However, there’s no golden standard to asses neurob ...
... overall survival of only 50%. Amplification of MYCN and overexpression of its coded protein is associated with rapid tumour progression and poor outcome. Induction of terminal differentiation is a very promising approach to neuroblastoma treatment. However, there’s no golden standard to asses neurob ...
Lindner et al (2008) patent application
... Escherichia coli as model organism for aging research Aging: Reduced metabolism Decreased offspring production Increased chance of death Reduced fitness as function of time ...
... Escherichia coli as model organism for aging research Aging: Reduced metabolism Decreased offspring production Increased chance of death Reduced fitness as function of time ...
Active Transport
... against the concentration gradient. The direction of movement of the substance is from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration. - Active transport usually involves the use of specialized carrier proteins embedded in the cell membrane that function as pumps. ...
... against the concentration gradient. The direction of movement of the substance is from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration. - Active transport usually involves the use of specialized carrier proteins embedded in the cell membrane that function as pumps. ...
Abstract
... and between disrupted and non-disrupted discs is also not fully understood. The hypothesis of this dissertation, is that IVDD is initiated by micro-damage to disc tissues, followed by cellular attempts to repair which are impeded by some degree of tissue hypoxia, leading to synthesis of an ‘‘inferio ...
... and between disrupted and non-disrupted discs is also not fully understood. The hypothesis of this dissertation, is that IVDD is initiated by micro-damage to disc tissues, followed by cellular attempts to repair which are impeded by some degree of tissue hypoxia, leading to synthesis of an ‘‘inferio ...
Synthetic Chloroplasts - BLI-Research-in-Synthetic-Biology
... dependent on the bacteria within their cells • This is because the amoebae no longer produced a protein that was required for survival, because the bacteria were providing that protein • So if the bacteria were removed, the amoebae’s nucleoli were damaged, because the amoebae could no longer produce ...
... dependent on the bacteria within their cells • This is because the amoebae no longer produced a protein that was required for survival, because the bacteria were providing that protein • So if the bacteria were removed, the amoebae’s nucleoli were damaged, because the amoebae could no longer produce ...
CELL PARTS Chapter 4
... with the plasma membrane. This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve cells communicate with one another. ...
... with the plasma membrane. This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve cells communicate with one another. ...
Section 8.1
... Chromosomes are visible during cell reproduction only Chromatin – the same material in between cell divisions (uncoiled) Each chromosome is made of 2 parts: A single DNA molecule tightly coiled ...
... Chromosomes are visible during cell reproduction only Chromatin – the same material in between cell divisions (uncoiled) Each chromosome is made of 2 parts: A single DNA molecule tightly coiled ...
The Inhibitory Effect of Compound 48/80 on the Formation of Giant
... The Inhibitory Effect of Compound 48/80 on the Formation of Giant Cells Induced by Herpesvirus Hominis (Accepted I9 November I97o) Formation of giant cells is characteristic of the cytopathic effect of herpesvirus hominis on cultured rabbit kidney cells. Giant cells are the result of the fusion of m ...
... The Inhibitory Effect of Compound 48/80 on the Formation of Giant Cells Induced by Herpesvirus Hominis (Accepted I9 November I97o) Formation of giant cells is characteristic of the cytopathic effect of herpesvirus hominis on cultured rabbit kidney cells. Giant cells are the result of the fusion of m ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.