Cell Type and Form - Southmoreland School District
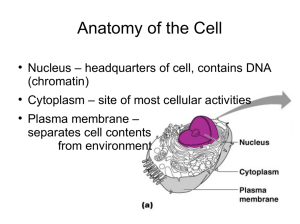
... respiration produces the energy carrier ATP. The distinctive organelle of a eukaryotic cell, consisting of a membranous envelope in which the chromosomes reside Membrane surrounding the cytoplasm that consists of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins; functions to regulate the entrance and e ...
... respiration produces the energy carrier ATP. The distinctive organelle of a eukaryotic cell, consisting of a membranous envelope in which the chromosomes reside Membrane surrounding the cytoplasm that consists of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins; functions to regulate the entrance and e ...
The Cell Theory and the Microscope
... Schleiden (mid 1800’s) later concluded that plants and animals were made up of cells. This information was used to develop the CELL THEORY. I’m cuter… ...
... Schleiden (mid 1800’s) later concluded that plants and animals were made up of cells. This information was used to develop the CELL THEORY. I’m cuter… ...
3.1 Study Guide
... MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. In a phrase, tell what each scientist did to help develop the cell theory. Scientist ...
... MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. In a phrase, tell what each scientist did to help develop the cell theory. Scientist ...
231_study guide
... MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. In a phrase, tell what each scientist did to help develop the cell theory. Scientist ...
... MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. In a phrase, tell what each scientist did to help develop the cell theory. Scientist ...
Mitosis Lab Activity: 1. Diagram a cell in interphase, prophase
... 5. Calculate the time a cell spends in each phase. Consider that it takes, on average, 24 hours (or 1,440 minutes) for onion root tip cells to complete the cell cycle. You can calculate the amou ...
... 5. Calculate the time a cell spends in each phase. Consider that it takes, on average, 24 hours (or 1,440 minutes) for onion root tip cells to complete the cell cycle. You can calculate the amou ...
Graphic organiser
... This resource was originally developed by Z. Davies and has been adapted for EAL Nexus. ...
... This resource was originally developed by Z. Davies and has been adapted for EAL Nexus. ...
2.5 Growth and repair – Further questions and answers Q1. Bk Ch2
... Most of your body cells have 46 chromosomes. If all of these body cells contain the same genetic information, coding for the same instructions, explain how it is that cells in different tissues of the body are different from one another. ...
... Most of your body cells have 46 chromosomes. If all of these body cells contain the same genetic information, coding for the same instructions, explain how it is that cells in different tissues of the body are different from one another. ...
In vitro study of host
... Host-microbe interactions are important field of research aiming to elucidate signaling and its role in health and disease. Our research was designed to study the signaling involving various human cell lines and human opportunistic Gram-negative bacterial pathogen P. aeruginosa that causes wide spec ...
... Host-microbe interactions are important field of research aiming to elucidate signaling and its role in health and disease. Our research was designed to study the signaling involving various human cell lines and human opportunistic Gram-negative bacterial pathogen P. aeruginosa that causes wide spec ...
File - Timber Wolves
... ***If it does not have these characteristics, then it is _____________ What are the three things 1) ____________ (all energy used by life comes from the _______) every organism needs in 2) ____________ order to live? (C 10) 3) ____________ to live What is a cell? (C 11) The _______________ unit of a ...
... ***If it does not have these characteristics, then it is _____________ What are the three things 1) ____________ (all energy used by life comes from the _______) every organism needs in 2) ____________ order to live? (C 10) 3) ____________ to live What is a cell? (C 11) The _______________ unit of a ...
Stem cells Before we discuss human cloning we need to talk about
... cells. These are special cells that can turn into any cell in the body. A stem cell can be made to grow into a skin cell, a heart muscle cell, a white blood cell etc. The most common source of human stem cells used in scientific research is the human embryo. Experiments using stem cells from human e ...
... cells. These are special cells that can turn into any cell in the body. A stem cell can be made to grow into a skin cell, a heart muscle cell, a white blood cell etc. The most common source of human stem cells used in scientific research is the human embryo. Experiments using stem cells from human e ...
The Need for Cell Division
... the ribosomes, telling them to make melanin • The melanin blocks sunlight, preventing sunlight from damaging cells below ...
... the ribosomes, telling them to make melanin • The melanin blocks sunlight, preventing sunlight from damaging cells below ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... Noncoding RNAs play multiple roles in controlling gene expression. A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism. Cancer results from genetic changes that affect cell cycle control. ...
... Noncoding RNAs play multiple roles in controlling gene expression. A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism. Cancer results from genetic changes that affect cell cycle control. ...
Discover Cell Cycle Video
... 8. Where do the chromosomes line up during metaphase? 9. What happens to the twin chromatids in anaphase? 10. During telophase spindle fibers ____________ nuclear membrane ____________, and ___________________ unwind. 11. What phase does the cell divide? 12. What is the process of splitting into 2 c ...
... 8. Where do the chromosomes line up during metaphase? 9. What happens to the twin chromatids in anaphase? 10. During telophase spindle fibers ____________ nuclear membrane ____________, and ___________________ unwind. 11. What phase does the cell divide? 12. What is the process of splitting into 2 c ...
Development of the Cell Theory
... explore the newly discovered microscopic world. They examined drops of blood, scrapings from their own teeth, and other small things. Cells weren't discovered until the m scop improved. 1665, Ro ert Hooker cut a thin slice of cor an 00 ed ...
... explore the newly discovered microscopic world. They examined drops of blood, scrapings from their own teeth, and other small things. Cells weren't discovered until the m scop improved. 1665, Ro ert Hooker cut a thin slice of cor an 00 ed ...
Life Science 2014 Trimester Exam- Study Guide Be able understand
... Understand the difference between eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells Know the difference between plant and animal cells Know the organization of an organism from cells to organisms Know the structure and function of parts of the microscope Know what microscope we use in class Understand the diff ...
... Understand the difference between eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells Know the difference between plant and animal cells Know the organization of an organism from cells to organisms Know the structure and function of parts of the microscope Know what microscope we use in class Understand the diff ...
Cells ( Think of the analogy of the factory) Cell parts are called
... chlorophyll ( green pigment) ...
... chlorophyll ( green pigment) ...
3 The cell as the basic unit of life
... (d) Mitochondria. Respiration occurs in mitochondria to release energy. ...
... (d) Mitochondria. Respiration occurs in mitochondria to release energy. ...
Cells - Denton ISD
... out of it. •If cells grow too large they would not be able to supply their own needs, and growth would come to a stop. ...
... out of it. •If cells grow too large they would not be able to supply their own needs, and growth would come to a stop. ...
The Cell Theory Timeline Project
... • Be sure to include the scientists pictures. • Use the legal size colored paper. • A rubric is attached to make sure you know what is expected. ...
... • Be sure to include the scientists pictures. • Use the legal size colored paper. • A rubric is attached to make sure you know what is expected. ...
Bone Formation Cell Lines
... To generate large numbers of osteocyte-like cells in order to produce sufficient quantities of osteocytes for study. To generate large numbers of cells of a homogeneous stage of osteogenic differentiation. To study osteocyte secretion of sclerostin, such as screening for sclerostin antagonists. To i ...
... To generate large numbers of osteocyte-like cells in order to produce sufficient quantities of osteocytes for study. To generate large numbers of cells of a homogeneous stage of osteogenic differentiation. To study osteocyte secretion of sclerostin, such as screening for sclerostin antagonists. To i ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.