Looking Inside Cells (a tiny tour)
... • No! There is a tremendous amount of variety in cells. • Their structure reflects their function! • However… ...
... • No! There is a tremendous amount of variety in cells. • Their structure reflects their function! • However… ...
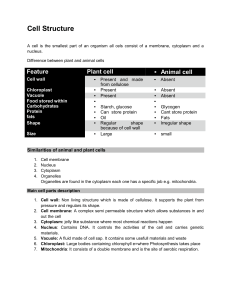
Plant Cell
... The nucleus directs all of the cell‘s activities, including reproduction. Endoplasmic Reticulum This network of passageways carries materials from one part of the cell to another. ...
... The nucleus directs all of the cell‘s activities, including reproduction. Endoplasmic Reticulum This network of passageways carries materials from one part of the cell to another. ...
TPP® Tissue Culture Tubes
... and optimization of suspension cell cultures. Each bioreactor cap has a built-in 0.22 µm hydrophobic membrane to maintain sterility and facilitate gas exchange. Agitation is provided by rocking or shaking in an incubator. In this manner, hundreds of cell cultivations can be performed quickly and eff ...
... and optimization of suspension cell cultures. Each bioreactor cap has a built-in 0.22 µm hydrophobic membrane to maintain sterility and facilitate gas exchange. Agitation is provided by rocking or shaking in an incubator. In this manner, hundreds of cell cultivations can be performed quickly and eff ...
Mary Pilson
... filaments that compose the cytoskeleton. Give an example of how each type of fiber is used in organisms. ...
... filaments that compose the cytoskeleton. Give an example of how each type of fiber is used in organisms. ...
Cells - Cobb Learning
... 12. What organelles that are found in plant and animal cells are also found in bacteria cells?? 13. The cells in many-celled organisms look the same, have the same structure, or are quite different from one another?…..pick one! 14. What is an organism called that is composed of many cells? 15. What ...
... 12. What organelles that are found in plant and animal cells are also found in bacteria cells?? 13. The cells in many-celled organisms look the same, have the same structure, or are quite different from one another?…..pick one! 14. What is an organism called that is composed of many cells? 15. What ...
Activities
... ________ 1. organism that has cells containing a nucleus and other organelles ________ 2. an organelle inside eukaryotic cells where the DNA is located ________ 3. a structure within the cytoplasm of a cell that is enclosed within a membrane and performs a specific job ________ 4. the material insid ...
... ________ 1. organism that has cells containing a nucleus and other organelles ________ 2. an organelle inside eukaryotic cells where the DNA is located ________ 3. a structure within the cytoplasm of a cell that is enclosed within a membrane and performs a specific job ________ 4. the material insid ...
Probing the Expression Patterns of System xc
... Previous work in the lab suggest that System xcexpression patterns change in response to the level of reactive oxygen species ...
... Previous work in the lab suggest that System xcexpression patterns change in response to the level of reactive oxygen species ...
Introduction - An
... A general characteristic of cells is their microscopic size. While there are a few exceptions—the marine alga Acetabularia can be up to 5 centimeters long—a typical eukaryotic cell is 10 to 100 micrometers. Most bacterial cells are only 1 to 10 micrometers in ...
... A general characteristic of cells is their microscopic size. While there are a few exceptions—the marine alga Acetabularia can be up to 5 centimeters long—a typical eukaryotic cell is 10 to 100 micrometers. Most bacterial cells are only 1 to 10 micrometers in ...
Ch 6 Organelles
... a. __________________ May be free or attached b. __________________Site of photosynthesis c. __________________ A double membrane encloses nucleus d. __________________ Stores water in plant cells e. _________________ Contains enzymes, one of which is catalase f. __________________Thickest fiber of ...
... a. __________________ May be free or attached b. __________________Site of photosynthesis c. __________________ A double membrane encloses nucleus d. __________________ Stores water in plant cells e. _________________ Contains enzymes, one of which is catalase f. __________________Thickest fiber of ...
The cell wall
... functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. A cell is the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and cells are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of cells is called cell biology. Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which conta ...
... functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. A cell is the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and cells are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of cells is called cell biology. Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which conta ...
CRCT Jeopardy - Thomas County Schools
... Which statement best describes what happens during meiosis I? ...
... Which statement best describes what happens during meiosis I? ...
PPT - Moti Nissani`s Webpage
... • Single cells, large, complex: SingleCelled Eukaryotes (e.g., paramecium, amoeba) • Complex, many cells: Eukaryotes (maple trees, dogs, fleas) ...
... • Single cells, large, complex: SingleCelled Eukaryotes (e.g., paramecium, amoeba) • Complex, many cells: Eukaryotes (maple trees, dogs, fleas) ...
Unit 03 - fixurscore
... hemoglobin which absorbs oxygen, its shape gives it a high surface area and it is small to fit in capillaries. 6. Nerve cells: they conduct electrical impulses which travel to & from the brain. They are very long and their chemical reactions cause impulses to travel through their fibers. They also h ...
... hemoglobin which absorbs oxygen, its shape gives it a high surface area and it is small to fit in capillaries. 6. Nerve cells: they conduct electrical impulses which travel to & from the brain. They are very long and their chemical reactions cause impulses to travel through their fibers. They also h ...
Stem Cell Research Catholic Social Teaching
... potential to become any type of cell in the body. One of the main characteristics of stem cells is their ability to self-renew or multiply while maintaining the potential to develop into other types of cells. Stem cells can become cells of the blood, heart, bones, skin, muscles, brain etc. There are ...
... potential to become any type of cell in the body. One of the main characteristics of stem cells is their ability to self-renew or multiply while maintaining the potential to develop into other types of cells. Stem cells can become cells of the blood, heart, bones, skin, muscles, brain etc. There are ...
The work of Schleiden and Schwann can be summarized by saying
... rough endoplasmic reticulum smooth endoplasmic reticulum ...
... rough endoplasmic reticulum smooth endoplasmic reticulum ...
Living Systems PowerPoint Notes
... _____________ _____________ that performs a particular function is called a _____________. Muscle tissue, for example, is a tissue that is able to contract. Muscle tissue in ...
... _____________ _____________ that performs a particular function is called a _____________. Muscle tissue, for example, is a tissue that is able to contract. Muscle tissue in ...
Project Cellular Structures and Functions
... Part Two. Create a VENN Diagram using the cell structures in Part One. Label the categories Animal, Both, and Plant. ...
... Part Two. Create a VENN Diagram using the cell structures in Part One. Label the categories Animal, Both, and Plant. ...
Quiz #6
... Q. 6: Which of the following events is NOT associated with prophase of mitosis? A) DNA condensation B) separation of sister chromatids C) duplication of centrosomes D) breakdown of the nuclear envelope E) both, b and d Q. 7: Chromatin consists of which of the following cellular molecule pairs? A) RN ...
... Q. 6: Which of the following events is NOT associated with prophase of mitosis? A) DNA condensation B) separation of sister chromatids C) duplication of centrosomes D) breakdown of the nuclear envelope E) both, b and d Q. 7: Chromatin consists of which of the following cellular molecule pairs? A) RN ...
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A cell, whether it is one part of a larger
... Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A cell, whether it is one part of a larger organism or is a single organism, undergoes a cell cycle. ...
... Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A cell, whether it is one part of a larger organism or is a single organism, undergoes a cell cycle. ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.