Origins of Heredity
... •It is hypothesized that this RNA started to evolve inside cell-like structures made of proteins, amino acids, and lipids •Then the RNA started to direct the cell ...
... •It is hypothesized that this RNA started to evolve inside cell-like structures made of proteins, amino acids, and lipids •Then the RNA started to direct the cell ...
Inside the Cell - Riverdale Middle School
... (enzymes) Breaks down old cell parts and recycles them ...
... (enzymes) Breaks down old cell parts and recycles them ...
Structures and Functions of Living things
... • New cells are produced from existing cells – Living things begin life as a single cell. This cell divides into two cells. Each new cell also divides into two cells. After a certain point, the cells being to specialize and take on different functions. – Cell division is what causes you or any other ...
... • New cells are produced from existing cells – Living things begin life as a single cell. This cell divides into two cells. Each new cell also divides into two cells. After a certain point, the cells being to specialize and take on different functions. – Cell division is what causes you or any other ...
Data Supplement
... following a given BT549 cell transiently transfected with FAPP1-PH-GFP and treated with either DMSO (vehicle control) or Pik93 (250 nM) over 60 min show that the PI(4)P reporter construct is redistributed to the cytoplasm in cells treated with Pik93 at the 30 min mark. This same effect is not observ ...
... following a given BT549 cell transiently transfected with FAPP1-PH-GFP and treated with either DMSO (vehicle control) or Pik93 (250 nM) over 60 min show that the PI(4)P reporter construct is redistributed to the cytoplasm in cells treated with Pik93 at the 30 min mark. This same effect is not observ ...
IB Biology Topic 2 - Cells Revision Sheet What is understood by the
... What causes the cell cycle & division to go wrong and cause 1° and 2° tumors in cancer? Use the terms cyclins, mutagens, oncogenes and metastasis Cancer is caused by cells losing control of the cell cycle. Cyclins, which normally can halt the cell cycle, can no longer do so, and for this reason, the ...
... What causes the cell cycle & division to go wrong and cause 1° and 2° tumors in cancer? Use the terms cyclins, mutagens, oncogenes and metastasis Cancer is caused by cells losing control of the cell cycle. Cyclins, which normally can halt the cell cycle, can no longer do so, and for this reason, the ...
4.1 The Function of the Nucleus Within the Cell
... Genes are small segments of DNA located on a chromosome. Genes store the information needed to produces proteins. Each chromosome can carry thousands of genes. ...
... Genes are small segments of DNA located on a chromosome. Genes store the information needed to produces proteins. Each chromosome can carry thousands of genes. ...
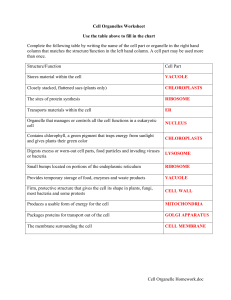
Cell Organelle Homework.doc Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria ...
... Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria ...
Macromolecules and Cells – Study Guide
... H) smallest part of an organism that can carry on all life processes ...
... H) smallest part of an organism that can carry on all life processes ...
Horticulture
... • 8 millionths of a mm thick (it would take 12,500 of them stacked to = the thickness of a piece of paper!!!!!!!) ...
... • 8 millionths of a mm thick (it would take 12,500 of them stacked to = the thickness of a piece of paper!!!!!!!) ...
Proteins relevant for Stem Cell Research - Bio
... box 2, belongs to a diverse family of structurally-related transcription factors whose primary structure contains a 79-residue DNA-binding domain, called high mobility group (HMG) box. It plays an essential role in maintaining the pluripotency of embryonic stem cells (ESC) and determination of cell ...
... box 2, belongs to a diverse family of structurally-related transcription factors whose primary structure contains a 79-residue DNA-binding domain, called high mobility group (HMG) box. It plays an essential role in maintaining the pluripotency of embryonic stem cells (ESC) and determination of cell ...
structure and function of the cell
... Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism. ...
... Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism. ...
BIOLOGY CHAPTER 10
... take up positions on opposite sides of the nucleus. Metaphase: The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. Each chromosome is connected to a spindle fiber at its centromere. Anaphase: The sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes and are moved apart. Telophase: The chromosome ...
... take up positions on opposite sides of the nucleus. Metaphase: The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. Each chromosome is connected to a spindle fiber at its centromere. Anaphase: The sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes and are moved apart. Telophase: The chromosome ...
Cell Notes
... i. Consists of 3 main statements about ALL living things. 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of living things. 3. All cells come from existing cells. e. Cell size i. Most cells are too small to be seen with the naked eye ii. Some cells, like the yolk of a ...
... i. Consists of 3 main statements about ALL living things. 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of living things. 3. All cells come from existing cells. e. Cell size i. Most cells are too small to be seen with the naked eye ii. Some cells, like the yolk of a ...
PowerPointi esitlus
... Applications of single-cell RNA-seq Analysis of rare cell types – circulating tumor cells, CTCs; cells from human embryo; transient adult stem cells Understanding evolution and diversity - individual cells vary in morphology, size, developmental origin, functional properties Characterise transcript ...
... Applications of single-cell RNA-seq Analysis of rare cell types – circulating tumor cells, CTCs; cells from human embryo; transient adult stem cells Understanding evolution and diversity - individual cells vary in morphology, size, developmental origin, functional properties Characterise transcript ...
7.2 Cell Structure 196-207
... 21. Nearly all of the mitochondria in your cells were inherited from your mother. 22. Both chloroplasts and mitochondria lack genetic information in the form of DNA. ...
... 21. Nearly all of the mitochondria in your cells were inherited from your mother. 22. Both chloroplasts and mitochondria lack genetic information in the form of DNA. ...
Slkjflsjdklfjsldjf
... Parkinson's disease2 (PD) is a very common neurodegenerative disorder that affects more than 2% of the population over 65 years of age. PD is caused by a progressive degeneration and loss of dopamine3 (DA)-producing neurons, which leads to tremor4, rigidity, and hypokinesia (abnormally decreased mob ...
... Parkinson's disease2 (PD) is a very common neurodegenerative disorder that affects more than 2% of the population over 65 years of age. PD is caused by a progressive degeneration and loss of dopamine3 (DA)-producing neurons, which leads to tremor4, rigidity, and hypokinesia (abnormally decreased mob ...
UNIT 1 LESSON 4 Specialised cells
... The ova is the cell with the largest volume in the human body. Its function is to produce new offspring. Introduce the discussion by showing the pupils a hen’s egg , crack it and show the contents. Point out the cell membrane which holds the contents of the egg together, the nucleus which is fertili ...
... The ova is the cell with the largest volume in the human body. Its function is to produce new offspring. Introduce the discussion by showing the pupils a hen’s egg , crack it and show the contents. Point out the cell membrane which holds the contents of the egg together, the nucleus which is fertili ...
CHAPTER 3 CELLS unit of life
... Lysosomes destroy foreign cells with an enzyme called lysozyme. They also aid in destroying our older cells. The nucleus contain the genetic material, DNA, that is in long strands called chromosomes. Humans have our genes contained in 23 different chromosomes (haploid number). We have a pair of each ...
... Lysosomes destroy foreign cells with an enzyme called lysozyme. They also aid in destroying our older cells. The nucleus contain the genetic material, DNA, that is in long strands called chromosomes. Humans have our genes contained in 23 different chromosomes (haploid number). We have a pair of each ...
DNA & RNA
... Cloning • Clones are genetically identical organisms • Natural Clones are: – Bacteria that underwent binary fission – Organisms that reproduce through asexual reproduction – Identical twins ...
... Cloning • Clones are genetically identical organisms • Natural Clones are: – Bacteria that underwent binary fission – Organisms that reproduce through asexual reproduction – Identical twins ...
what know about protists cells and human body
... • Cytoplasm - a gel-like material inside the cell; it contains water and nutrients for the cell • Nucleus - directs the activity of a cell; it contains chromosomes with the DNA • Nuclear Membrane -separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm • Mitochondria - break down food and release energy to the cel ...
... • Cytoplasm - a gel-like material inside the cell; it contains water and nutrients for the cell • Nucleus - directs the activity of a cell; it contains chromosomes with the DNA • Nuclear Membrane -separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm • Mitochondria - break down food and release energy to the cel ...
Cells!
... Name_______________________________ Period _____________ Date ____________ PART III Go to the Cell Comparison Tutorial www.omatclasses.com/cellcomparisons/html/cell_comparisons.html Click on Animal vs. Plant Cell 15. Complete the Venn Diagram and make a copy of the correct answers here. Animal Cell ...
... Name_______________________________ Period _____________ Date ____________ PART III Go to the Cell Comparison Tutorial www.omatclasses.com/cellcomparisons/html/cell_comparisons.html Click on Animal vs. Plant Cell 15. Complete the Venn Diagram and make a copy of the correct answers here. Animal Cell ...
Test Review Sheet - Lyndhurst School District
... Word Banks: Be able to label the parts of the cell (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm). Be able to label the parts of the cell membrane (lipids, proteins, carbohydrates). Be able to identify if a cell is in a hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic solution based on what happens to it. Be able to identif ...
... Word Banks: Be able to label the parts of the cell (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm). Be able to label the parts of the cell membrane (lipids, proteins, carbohydrates). Be able to identify if a cell is in a hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic solution based on what happens to it. Be able to identif ...
MSc / BSc positions in Systems Biology of Gene Regulation
... What defines the identity of a cell? How is the same genetic code used to build more than 200 different cell types with distinct physiological and morphological properties? These fundamental questions drive our enthusiasm for understanding how information processing is regulated at the level of chro ...
... What defines the identity of a cell? How is the same genetic code used to build more than 200 different cell types with distinct physiological and morphological properties? These fundamental questions drive our enthusiasm for understanding how information processing is regulated at the level of chro ...
Cell Unit Test Study Guide
... cell membrane and fuses with the cell membrane thus releasing the particle 5. When does fermentation occur? a. When oxygen is not available for cellular respiration to occur to make energy 6. What does fermentation produce? a. Lactic acid 7. What occurs during binary fission? a. A type of cell divi ...
... cell membrane and fuses with the cell membrane thus releasing the particle 5. When does fermentation occur? a. When oxygen is not available for cellular respiration to occur to make energy 6. What does fermentation produce? a. Lactic acid 7. What occurs during binary fission? a. A type of cell divi ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.