daughter DNA interphase volume binary fission G1 nucleus cell
... During interphase, there are three stages. During the __________ phase, the cell grows. During the ___________ phase, the genetic material (DNA) of the cell is copied. During the ____________ phase, the cell prepares for division. ...
... During interphase, there are three stages. During the __________ phase, the cell grows. During the ___________ phase, the genetic material (DNA) of the cell is copied. During the ____________ phase, the cell prepares for division. ...
Cell Review
... 9. Distinguish between active and passive transport (all three types). Provide examples to support your explanation. 10. Distinguish between endocytosis and exocytosis. Give examples of types of cells or organisms that use these processes. 11. Describe the different phases of the cell cycle. What is ...
... 9. Distinguish between active and passive transport (all three types). Provide examples to support your explanation. 10. Distinguish between endocytosis and exocytosis. Give examples of types of cells or organisms that use these processes. 11. Describe the different phases of the cell cycle. What is ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Answer each question as you view the videos and explore the interactives in this lesson. Explore the Gallery of Cells image to see the variety of specialized cells that exist in organisms. (Click on the image and zoom in to see larger.) 1. What can you infer about function from the structure of any ...
... Answer each question as you view the videos and explore the interactives in this lesson. Explore the Gallery of Cells image to see the variety of specialized cells that exist in organisms. (Click on the image and zoom in to see larger.) 1. What can you infer about function from the structure of any ...
Cell membrane – boundary that separates the interior of
... Cytoplasm – the cytosol (gel like substance) and organelles; cytosol: 70% of the cell volume, made of water, salts, and organic molecules ...
... Cytoplasm – the cytosol (gel like substance) and organelles; cytosol: 70% of the cell volume, made of water, salts, and organic molecules ...
Quest study guide#1
... 1. How are the cells of unicellular organisms different than the cells of multicellular organisms? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. ...
... 1. How are the cells of unicellular organisms different than the cells of multicellular organisms? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. ...
Label a Plant Cell (Up to 16yrs old / GCSE)
... The structure in plant cells that contains chlorophyll and in which photosynthesis takes place ...
... The structure in plant cells that contains chlorophyll and in which photosynthesis takes place ...
cells: The living units
... important, before ‘cell theory’ which includes all these discoveries, people accepted the theory of spontaneous generation ...
... important, before ‘cell theory’ which includes all these discoveries, people accepted the theory of spontaneous generation ...
Biology Microbes / Classification 2012 – 2013 #4
... Bacterial anatomy A. Cell Wall = not like that of a plant 1. Gram + have typical cell wall - stain purple 2. Gram - have an extra lipid layer ...
... Bacterial anatomy A. Cell Wall = not like that of a plant 1. Gram + have typical cell wall - stain purple 2. Gram - have an extra lipid layer ...
Cell Study Guide
... 3. You will need to be able to identify the different parts of an animal cell: Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria Vacuole 4. You will need to be able to identify how plant cells DIFFER from animal cells. 5. You will need to be able to discuss how cells are organized: 1 Cell ...
... 3. You will need to be able to identify the different parts of an animal cell: Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Mitochondria Vacuole 4. You will need to be able to identify how plant cells DIFFER from animal cells. 5. You will need to be able to discuss how cells are organized: 1 Cell ...
Cell Organelle Crossword Puzzle
... Material inside the cell membrane- not including the nucleus ...
... Material inside the cell membrane- not including the nucleus ...
What to know Chap 11
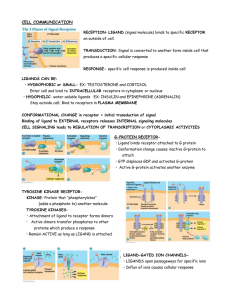
... TYROSINE KINASE RECEPTORKINASE- Protein that “phosphorylates” (adds a phosphate to) another molecule TYROSINE KINASES: • Attachment of ligand to receptor forms dimers • Active dimers transfer phosphates to other proteins which produce a response • Remain ACTIVE as long as LIGAND is attached ...
... TYROSINE KINASE RECEPTORKINASE- Protein that “phosphorylates” (adds a phosphate to) another molecule TYROSINE KINASES: • Attachment of ligand to receptor forms dimers • Active dimers transfer phosphates to other proteins which produce a response • Remain ACTIVE as long as LIGAND is attached ...
Diversity of Cell Structure and Function
... or other characteristics of each type of cell help this type of cell to accomplish its function. Cell Type and How These Characteristics Help This Type of Cell ...
... or other characteristics of each type of cell help this type of cell to accomplish its function. Cell Type and How These Characteristics Help This Type of Cell ...
Chapter 5
... A special protein that transports Na+ ions and K+ up their concentration gradients ...
... A special protein that transports Na+ ions and K+ up their concentration gradients ...
Chpt 6 - San Diego Unified School District
... b. Rough ER 2. Golgi apparatus 3. Lysosome 4. Vacuoles a. food vacuole b. contractile vacuole c. central vacuole (plants) D. Mitochondrion E. Chloroplast (plants) III. Cytoskeleton A. Cilia B. Flagella IV. Extracellular components A. Cell wall (plants) Study Tips: Know … the differences between prok ...
... b. Rough ER 2. Golgi apparatus 3. Lysosome 4. Vacuoles a. food vacuole b. contractile vacuole c. central vacuole (plants) D. Mitochondrion E. Chloroplast (plants) III. Cytoskeleton A. Cilia B. Flagella IV. Extracellular components A. Cell wall (plants) Study Tips: Know … the differences between prok ...
Northeast High School GHSGT Junior Academy
... The modern tenets of the Cell Theory include: 1. All known living things are made up of cells. 2. The cell is structural & functional unit of all living things. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells by division. (Spontaneous Generation does not occur). 4. Cells contains hereditary information wh ...
... The modern tenets of the Cell Theory include: 1. All known living things are made up of cells. 2. The cell is structural & functional unit of all living things. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells by division. (Spontaneous Generation does not occur). 4. Cells contains hereditary information wh ...
Oct. 5, 2015 Cells - AP Biology Study Guide
... 11. Describe the structure and functions of the three types of cell junctions. 12. List the properties possessed by all living things. Practice Questions 1. Discuss each of the following, writing a paragraph or two for each one: a) the structure and role of the cell membrane b) the formation of cell ...
... 11. Describe the structure and functions of the three types of cell junctions. 12. List the properties possessed by all living things. Practice Questions 1. Discuss each of the following, writing a paragraph or two for each one: a) the structure and role of the cell membrane b) the formation of cell ...
Onion Root Cell Virtual Lab
... percent into a decimal (divide the percent by 100) and multiply it by 24 hours (that’s the total length of the cell cycle). Which phase is the longest phase of the cell cycle? How many hours is it? Interphase is not part of mitosis, which is the longest phase of mitosis? Draw a pie graph of the cell ...
... percent into a decimal (divide the percent by 100) and multiply it by 24 hours (that’s the total length of the cell cycle). Which phase is the longest phase of the cell cycle? How many hours is it? Interphase is not part of mitosis, which is the longest phase of mitosis? Draw a pie graph of the cell ...
Cell Theory PPT
... Matthias Schleiden- (German, around 1830’s) a Botanist, concluded that all plants were made up of cells. Theodor Schwann- (German, worked during the same time as Schleiden), studied animal cells. Concluded that animals were made up of cells. Rudolf Virchow- (1858) concluded that all new cells ...
... Matthias Schleiden- (German, around 1830’s) a Botanist, concluded that all plants were made up of cells. Theodor Schwann- (German, worked during the same time as Schleiden), studied animal cells. Concluded that animals were made up of cells. Rudolf Virchow- (1858) concluded that all new cells ...