Chapter 07
... these form the cytoskeleton, which reinforces the cell’s shape and moves the cell. The components are made of protein. Microtubules are the thickest of the three and microfilaments are the thinnest of them. The intermediate filaments are in the middle. Microtubules, which contain alpha-tubulin and b ...
... these form the cytoskeleton, which reinforces the cell’s shape and moves the cell. The components are made of protein. Microtubules are the thickest of the three and microfilaments are the thinnest of them. The intermediate filaments are in the middle. Microtubules, which contain alpha-tubulin and b ...
The Building Blocks of Life
... -Describe the major organelles that a plant and animal cell don’t have in ...
... -Describe the major organelles that a plant and animal cell don’t have in ...
Lect19.RNA.part2
... Acetylation of histone tails in nucleosomes weakens DNA binding to histone cores, creating “open” chromatin competent for gene transcription. Open chromatin is amenable to transcription factor binding to specific sites on DNA (promoters/ enhancers) Acetylated histones also directly recruit other pro ...
... Acetylation of histone tails in nucleosomes weakens DNA binding to histone cores, creating “open” chromatin competent for gene transcription. Open chromatin is amenable to transcription factor binding to specific sites on DNA (promoters/ enhancers) Acetylated histones also directly recruit other pro ...
Chapter 7 Cells
... respiration. This process makes ATP. ATP is aka adenosine triphosphate. This is cellular energy. ...
... respiration. This process makes ATP. ATP is aka adenosine triphosphate. This is cellular energy. ...
“Stem and Gene Therapy for Cystinosis” – Lay Abstract
... model we developed has dual fluorescence that distinguishes the host cells (Red) from the transplanted cells (green). The host/donor-fused cells in several organs will be easily recognized (yellow) and thus isolated to further study them to determine what kind of genetic and other biological factors ...
... model we developed has dual fluorescence that distinguishes the host cells (Red) from the transplanted cells (green). The host/donor-fused cells in several organs will be easily recognized (yellow) and thus isolated to further study them to determine what kind of genetic and other biological factors ...
Chapter 10
... • Gather and synthesize nutrients – ex. Make the 6 billion nucleotides needed to replicate the DNA. Acquire/synthesize enough amino acids to build all the required proteins to divide the cell, etc… Cells can hang in this subphase for a very long time like certain muscle cells or forever like cardiac ...
... • Gather and synthesize nutrients – ex. Make the 6 billion nucleotides needed to replicate the DNA. Acquire/synthesize enough amino acids to build all the required proteins to divide the cell, etc… Cells can hang in this subphase for a very long time like certain muscle cells or forever like cardiac ...
to the correct answers for the cell
... Chromosomes direct all activities of the cell including HEREDITY, RECIPE FOR PROTEINS, DIRECT ALL MAJOR ACTIVITIES FOR THE CELL. Chromosomes are made of DNA (DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID) The mitochondria are known as the POWERHOUSE of the cell. They provide the cell with ENERGY. Ribosomes are also found i ...
... Chromosomes direct all activities of the cell including HEREDITY, RECIPE FOR PROTEINS, DIRECT ALL MAJOR ACTIVITIES FOR THE CELL. Chromosomes are made of DNA (DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID) The mitochondria are known as the POWERHOUSE of the cell. They provide the cell with ENERGY. Ribosomes are also found i ...
CHAPTER 6 LEARNING OBJECTIVES
... 3. Explain why cell fractionation is a useful technique. A Panoramic View of the Cell 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why there are limits to cell size. 6. Explain the advantages of compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells. The Nucleus and Ribosomes 7. Describe th ...
... 3. Explain why cell fractionation is a useful technique. A Panoramic View of the Cell 4. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 5. Explain why there are limits to cell size. 6. Explain the advantages of compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells. The Nucleus and Ribosomes 7. Describe th ...
MUSINGU BIOLOGY DECEMBER 2013 HOLIDAY ASSIGNMENT
... b) A rapidly respiring cell in comparison to other cells in the same organism? 11. State the two functions of the cell organelle that contains chlorophyll in plants. ...
... b) A rapidly respiring cell in comparison to other cells in the same organism? 11. State the two functions of the cell organelle that contains chlorophyll in plants. ...
Dmca1A encodes voltage-gated calcium channels in
... regulate the entry of calcium into excitable cells. There are three -subunit genes in Drosophila: Dmca1D, Dmca1A, and -1. Previous studies have demonstrated that Dmca1D forms functional calcium channel proteins in Drosophila muscle cells. Dmca1A proteins are expressed in the presynaptic terminals ...
... regulate the entry of calcium into excitable cells. There are three -subunit genes in Drosophila: Dmca1D, Dmca1A, and -1. Previous studies have demonstrated that Dmca1D forms functional calcium channel proteins in Drosophila muscle cells. Dmca1A proteins are expressed in the presynaptic terminals ...
Cell Model Checklist
... Cell Model Checklist Use any interesting materials you may have around your house that are good representations of the cell organelles. For example, plastic wrap may represent the cell membrane which surrounds the cell, or a small AAA battery may represent a mitochondria which produces energy for th ...
... Cell Model Checklist Use any interesting materials you may have around your house that are good representations of the cell organelles. For example, plastic wrap may represent the cell membrane which surrounds the cell, or a small AAA battery may represent a mitochondria which produces energy for th ...
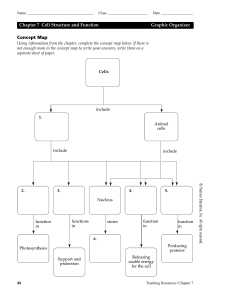
Concept Map Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Graphic
... 15. The fourth, and highest, level of organization in a multicellular organism is a. cell specialization. b. a tissue. c. an organ system. d. an organ. ...
... 15. The fourth, and highest, level of organization in a multicellular organism is a. cell specialization. b. a tissue. c. an organ system. d. an organ. ...
Hybridoma Technology
... synthesis, making the cells dependent on another pathway that needs HGPRT enzyme, which is absent in myeloma cells. • Myeloma cells that do not fuse with B cells will die. • B cells that do not fuse will also die because they lack tumorigenic property of immortal growth. ...
... synthesis, making the cells dependent on another pathway that needs HGPRT enzyme, which is absent in myeloma cells. • Myeloma cells that do not fuse with B cells will die. • B cells that do not fuse will also die because they lack tumorigenic property of immortal growth. ...
Cell Structures - cloudfront.net
... 19. The ____________ theory describes how small prokaryotic cells began to “live” inside larger cells. 20. The ____________ can make up as much as 90% of a plant cell’s volume. ...
... 19. The ____________ theory describes how small prokaryotic cells began to “live” inside larger cells. 20. The ____________ can make up as much as 90% of a plant cell’s volume. ...
cell wall - WordPress.com
... 34. A solar panel collects sunlight and converts it to heat or electrical energy. How is a solar panel similar to chloroplasts? Chloroplasts collect sunlight and convert it to food energy 35. What are cells made of? Cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA (genetic material), and ...
... 34. A solar panel collects sunlight and converts it to heat or electrical energy. How is a solar panel similar to chloroplasts? Chloroplasts collect sunlight and convert it to food energy 35. What are cells made of? Cell membrane, cytoplasm, DNA (genetic material), and ...
Intro to the Cell - Gwinnett County Public Schools
... 1674 - Was the first to see bacteria under a microscope Made many advancements in the field of microscopy by making better microscope lenses and detailed observations ...
... 1674 - Was the first to see bacteria under a microscope Made many advancements in the field of microscopy by making better microscope lenses and detailed observations ...
The Genetic Evolution of H5N1
... Yun-Wei Hsu2 (許芸瑋) and Jen-Ren Wang1,2 (王貞仁) Department of Medical Laboratory Science and Biotechnology, College of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University1; NHRI Tainan Virology Laboratory for Diagnosis and Research, Division of Clinical Research, National Health Research Institutes 2 H5N1 avian i ...
... Yun-Wei Hsu2 (許芸瑋) and Jen-Ren Wang1,2 (王貞仁) Department of Medical Laboratory Science and Biotechnology, College of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University1; NHRI Tainan Virology Laboratory for Diagnosis and Research, Division of Clinical Research, National Health Research Institutes 2 H5N1 avian i ...
Cell membrane Chromatin Nuclear membrane
... http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=9B385B50-541B-447A-89CF2016A3CFC094&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US ...
... http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=9B385B50-541B-447A-89CF2016A3CFC094&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US ...
Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic: prokaryotic – no internal
... not have histone proteins; bacteria and archeae are the only examples. Eukaryotic – have organelles; DNA in linear chromosomes within a nucleus; Key organelles to know functions of: mitochondria, chloroplasts (only organelles that can do chemiosmosis – meaning they make ATP!) of course, you also nee ...
... not have histone proteins; bacteria and archeae are the only examples. Eukaryotic – have organelles; DNA in linear chromosomes within a nucleus; Key organelles to know functions of: mitochondria, chloroplasts (only organelles that can do chemiosmosis – meaning they make ATP!) of course, you also nee ...
Chapter 7.4: The Diversity of Cellular Life
... 1. Made of many cells 2. Cells must communicate with each other 3. Cells throughout an organism can develop in different ways to perform different tasks 4. Large variety of organisms; such as flies, humans, cats ...
... 1. Made of many cells 2. Cells must communicate with each other 3. Cells throughout an organism can develop in different ways to perform different tasks 4. Large variety of organisms; such as flies, humans, cats ...
Structure and Function of the Cell 1: Introduction to the Cell • Cell
... surface. Likewise, waste products must leave through its surface. The larger the cell, the larger the surface area required to maintain it. As a cell grows, its volume increases more rapidly than its surface area does. As a cell grows larger, its surface area becomes too small to maintain life ...
... surface. Likewise, waste products must leave through its surface. The larger the cell, the larger the surface area required to maintain it. As a cell grows, its volume increases more rapidly than its surface area does. As a cell grows larger, its surface area becomes too small to maintain life ...
Cell Transport Definitions Chapter 8
... Isotonic Solution – When the solution concentrations inside and outside the cell are equal. (No net movement of water resulting in a cell that does not change in size) Hypotonic Solution – When the concentration of water is greater outside the cell than inside the cell. This results in a net water g ...
... Isotonic Solution – When the solution concentrations inside and outside the cell are equal. (No net movement of water resulting in a cell that does not change in size) Hypotonic Solution – When the concentration of water is greater outside the cell than inside the cell. This results in a net water g ...
Slide 1
... Microtubules are conveyer belts inside the cells. They move vesicles, granules, organelles like mitochondria, and chromosomes via special attachment proteins. They also serve a cytoskeletal role. Structurally, they are polymers of tubulin which is a globular protein.. The tubulin molecules are the b ...
... Microtubules are conveyer belts inside the cells. They move vesicles, granules, organelles like mitochondria, and chromosomes via special attachment proteins. They also serve a cytoskeletal role. Structurally, they are polymers of tubulin which is a globular protein.. The tubulin molecules are the b ...