
Monitoring the activity of G protein-coupled receptors
... Figure 1. Schematic presentation of cAMP Glo™ Assay. Ligand binding to its cognate G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) triggers dissociation of the heterotrimeric G (Gαβγ) protein to Gα and Gβγ complex and exchanges GDP for Gα-GTP. The Gα-GTP interacts with adenylate cyclase (AC), resulting in either ...
... Figure 1. Schematic presentation of cAMP Glo™ Assay. Ligand binding to its cognate G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) triggers dissociation of the heterotrimeric G (Gαβγ) protein to Gα and Gβγ complex and exchanges GDP for Gα-GTP. The Gα-GTP interacts with adenylate cyclase (AC), resulting in either ...
Regulation of hepatic metabolism by AMPK - HAL
... by phosphorylation of the carbohydrate response element binding protein (ChREBP), reducing its DNA binding capacity and nuclear translocation, and down-regulating sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) gene expression and stability probably through SIRT1-dependent deacetylation [1, ...
... by phosphorylation of the carbohydrate response element binding protein (ChREBP), reducing its DNA binding capacity and nuclear translocation, and down-regulating sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) gene expression and stability probably through SIRT1-dependent deacetylation [1, ...
Peptide microarrays for detailed, high-throughput
... reagent consumption were reduced considerably. PKA was shown to phosphorylate many peptides containing known PKA phosphorylation sites as well as some new substrates. Data in table 1 shows that staurosporine is a full ATP competitive inhibitor whereas AMP-PNP has a different inhibition mechanism. ...
... reagent consumption were reduced considerably. PKA was shown to phosphorylate many peptides containing known PKA phosphorylation sites as well as some new substrates. Data in table 1 shows that staurosporine is a full ATP competitive inhibitor whereas AMP-PNP has a different inhibition mechanism. ...
Rational design_substrate specificity
... - Comparison with the homologous enzymes if available 2) Predict the critical loops or residues interacting with a target substrate (cf: TIM barrel fold) 3) Mutagenesis to determine the critical loops or residues If the critical loops or residues are confirmed, go to the next step Otherwise, go to t ...
... - Comparison with the homologous enzymes if available 2) Predict the critical loops or residues interacting with a target substrate (cf: TIM barrel fold) 3) Mutagenesis to determine the critical loops or residues If the critical loops or residues are confirmed, go to the next step Otherwise, go to t ...
Enzymes
... • This enzyme has an active site for fructose-6-phosphate molecules to bind with another phosphate group • It has an allosteric site for ATP molecules, the inhibitor • When the cell consumes a lot of ATP the level of ATP in the cell falls • No ATP binds to the allosteric site of phosphofructokinase ...
... • This enzyme has an active site for fructose-6-phosphate molecules to bind with another phosphate group • It has an allosteric site for ATP molecules, the inhibitor • When the cell consumes a lot of ATP the level of ATP in the cell falls • No ATP binds to the allosteric site of phosphofructokinase ...
The Photosynthetic Dark Reactions Do Not Operate
... Phosphorylation of the enzyme increases its activity. At night, the phosphate group is removed by a phosphatase enzyme and the enzyme activity decreases (Figure 3) (Bennett 1979). The mechanism by which the kinase and phosphatase enzymes are regulated is uncertain. In view of the fact that the Calvi ...
... Phosphorylation of the enzyme increases its activity. At night, the phosphate group is removed by a phosphatase enzyme and the enzyme activity decreases (Figure 3) (Bennett 1979). The mechanism by which the kinase and phosphatase enzymes are regulated is uncertain. In view of the fact that the Calvi ...
Gene Section MST1R (Macrophage stimulating 1 receptor) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2B and renal papillary carcinoma - results in activation of oncogenic capacity and triggers a strong metastatic activity of RON. Expression of these RON mutants causes cellular accumulation of b-catenin via inhibition of its association with the axin/GSK complex and ...
... Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2B and renal papillary carcinoma - results in activation of oncogenic capacity and triggers a strong metastatic activity of RON. Expression of these RON mutants causes cellular accumulation of b-catenin via inhibition of its association with the axin/GSK complex and ...
Enzymes - Hartismere
... • An enzyme that functions within the cell in which it was produced. • Majority of enzymes fall within this category. • Intracellular enzymes are not as effective as extracellular. (Extracellular enzymes are up to 25% more efficient in breaking down the substrate) ...
... • An enzyme that functions within the cell in which it was produced. • Majority of enzymes fall within this category. • Intracellular enzymes are not as effective as extracellular. (Extracellular enzymes are up to 25% more efficient in breaking down the substrate) ...
Document
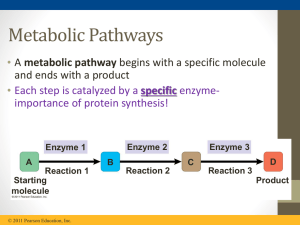
... respiration, the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen) • Anabolic pathways consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones (synthesis of protein from amino acids) ...
... respiration, the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen) • Anabolic pathways consume energy to build complex molecules from simpler ones (synthesis of protein from amino acids) ...
Ch7 Enzymes II: Coenzymes, Regulation, Abzymes, and Ribozymes
... • Vitamins and coenzymes – Coenzyme: an organic or organometallic molecule that assists an enzyme. – Vitamins: a group of relatively small, organic molecules essential in small amounts in the diet for proper growth and development. • Water-soluble: B2, B1, B6,B12, C • Fat-soluble: A, D, E, K1 ...
... • Vitamins and coenzymes – Coenzyme: an organic or organometallic molecule that assists an enzyme. – Vitamins: a group of relatively small, organic molecules essential in small amounts in the diet for proper growth and development. • Water-soluble: B2, B1, B6,B12, C • Fat-soluble: A, D, E, K1 ...
Chymotrypsin is a Serine Protease
... • Correct positioning of two reacting groups (in model reactions or at enzyme active sites): (1) Reduces their degrees of freedom (2) Results in a large loss of entropy (3) The relative enhanced concentration of substrates (“effective molarity”) predicts the rate acceleration expected due to this ef ...
... • Correct positioning of two reacting groups (in model reactions or at enzyme active sites): (1) Reduces their degrees of freedom (2) Results in a large loss of entropy (3) The relative enhanced concentration of substrates (“effective molarity”) predicts the rate acceleration expected due to this ef ...
PowerPoint Template
... For a given hormone, different receptors can exist on the same or on different cells. Thus, the same hormone can trigger very distinct reactions in different tissues. An example of such a phenomenon is adrenaline, which can initiate, on the one hand, a cAMP-mediated signal transduction and, on the ...
... For a given hormone, different receptors can exist on the same or on different cells. Thus, the same hormone can trigger very distinct reactions in different tissues. An example of such a phenomenon is adrenaline, which can initiate, on the one hand, a cAMP-mediated signal transduction and, on the ...
enz resp photo test marker
... Explain the effect of pH on enzyme activity. enzymes have an optimal pH; lower activity above and below optimum pH / graph showing this; too acidic / basic pH can denature enzyme; change shape of active site / tertiary structure altered; substrate cannot bind to active site / enzyme-substrate comple ...
... Explain the effect of pH on enzyme activity. enzymes have an optimal pH; lower activity above and below optimum pH / graph showing this; too acidic / basic pH can denature enzyme; change shape of active site / tertiary structure altered; substrate cannot bind to active site / enzyme-substrate comple ...
Decreased
... windshield washer fluid, etc.) is metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase to formaldehyde and formic acid. Leads to metabolic acidosis and optic neuritis (from formate) that can cause blindness. • Treatment: Infuse EtOH to keep blood concentration at 100-200 mg/dL (legally intoxicated) for long enough ...
... windshield washer fluid, etc.) is metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase to formaldehyde and formic acid. Leads to metabolic acidosis and optic neuritis (from formate) that can cause blindness. • Treatment: Infuse EtOH to keep blood concentration at 100-200 mg/dL (legally intoxicated) for long enough ...
Three-Dimensional Structure of Adenosylcobinamide Kinase
... the corrin ring and the subsequent attachment of GMP to form the product adenosylcobinamide-GDP. The kinase activity is believed to be associated with a P-loop motif, whereas the transferase activity proceeds at a different site on the enzyme via a guanylyl intermediate. The enzyme was crystallized ...
... the corrin ring and the subsequent attachment of GMP to form the product adenosylcobinamide-GDP. The kinase activity is believed to be associated with a P-loop motif, whereas the transferase activity proceeds at a different site on the enzyme via a guanylyl intermediate. The enzyme was crystallized ...
Anti-ZAP-70 [pTyrpTyr315/319]Phosphospecific Antibody
... and 319 within zeta chain-associated protein 70 for T cell development. J. Exp. Med. 194(4): 507-518. Wu, J., et al. (1997) The Vav binding site (Y315) in ZAP-70 is critical for antigen receptor-mediated signal transduction. J. Exp. Med. 185(10): 1877-1882. Kong, G., et al. (1996) Distinct tyrosine ...
... and 319 within zeta chain-associated protein 70 for T cell development. J. Exp. Med. 194(4): 507-518. Wu, J., et al. (1997) The Vav binding site (Y315) in ZAP-70 is critical for antigen receptor-mediated signal transduction. J. Exp. Med. 185(10): 1877-1882. Kong, G., et al. (1996) Distinct tyrosine ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Urea is one of the major breakdown products of proteins and one of the main ingredients of urine. The enzyme urease enhances the rate of urea hydrolysis at pH 8 and 20oC by a factor of 1014. If a given quantity of urease can completely hydrolyze a given quantity of urea in 5 minutes, how long, in ye ...
... Urea is one of the major breakdown products of proteins and one of the main ingredients of urine. The enzyme urease enhances the rate of urea hydrolysis at pH 8 and 20oC by a factor of 1014. If a given quantity of urease can completely hydrolyze a given quantity of urea in 5 minutes, how long, in ye ...
Enzymes - Land of Mayo
... fever makes us weak, but are more effective against bacteria ► Fevers do not allow bacterial cell division because their enzymes for cell division do not work correctly or at all at the higher temperature ► At elevated body temperatures, cell division do not work or makes “leaky” cell walls ...
... fever makes us weak, but are more effective against bacteria ► Fevers do not allow bacterial cell division because their enzymes for cell division do not work correctly or at all at the higher temperature ► At elevated body temperatures, cell division do not work or makes “leaky” cell walls ...
Enzyme Kinetics
... 0.2 units/mg or ml protein upon which purification may increase to 10 units/mg or ml protein. One unit would be formation of one μmol product per minute at a specific pH and temperature with a substrate concentration much greater than the value of Km. ...
... 0.2 units/mg or ml protein upon which purification may increase to 10 units/mg or ml protein. One unit would be formation of one μmol product per minute at a specific pH and temperature with a substrate concentration much greater than the value of Km. ...
Ultrasensitivity

In molecular biology, ultrasensitivity describes an output response that is more sensitive to stimulus change than the hyperbolic Michaelis-Menten response. Ultrasensitivity is one of the biochemical switches in the cell cycle and has been implicated in a number of important cellular events, including exiting G2 cell cycle arrests in Xenopus laevis oocytes, a stage to which the cell or organism would not want to return.Ultrasensitivity is a cellular system which triggers entry into a different cellular state. Ultrasensitivity gives a small response to first input signal, but an increase in the input signal produces higher and higher levels of output. This acts to filter out noise, as small stimuli and threshold concentrations of the stimulus (input signal) is necessary for the trigger which allows the system to get activated quickly. Ultrasensitive responses are represented by sigmoidal graphs, which resemble cooperativity. Quantification of ultrasensitivity is often approximated by the Hill equation (biochemistry):Response= Stimulus^n/(EC50^n+Stimulus^n)Where Hill's coefficient (n) may represent quantitative measure of ultrasensitive response.
















![Anti-ZAP-70 [pTyrpTyr315/319]Phosphospecific Antibody](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007988667_1-98a23e7ab9217d5db62ad8a049eacb7d-300x300.png)





