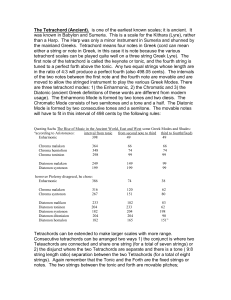
Intervals Perfect Intervals
... Intervals An Interval is the distance between two notes. In level one we learned to name intervals by number: ...
... Intervals An Interval is the distance between two notes. In level one we learned to name intervals by number: ...
Strähle construction

Strähle's construction is a geometric method for determining the lengths for a series of vibrating strings with uniform diameters and tensions to sound pitches in a specific rational tempered musical tuning. It was first published in the 1743 Proceedings of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences by Swedish master organ maker Daniel Stråhle (1700–1746). The Academy's secretary Jacob Faggot appended a miscalculated set of pitches to the article, and these figures were reproduced by Friedrich Wilhelm Marpurg in Versuch über die musikalische Temperatur in 1776. Several German textbooks published about 1800 reported that the mistake was first identified by Christlieb Benedikt Funk in 1779, but the construction itself appears to have received little notice until the middle of the twentieth century when tuning theorist J. Murray Barbour presented it as a good method for approximating equal temperament and similar exponentials of small roots, and generalized its underlying mathematical principles.It has become known as a device for building fretted musical instruments through articles by mathematicians Ian Stewart and Isaac Jacob Schoenberg, and is praised by them as a unique and remarkably elegant solution developed by an unschooled craftsman.The name ""Strähle"" used in recent English language works appears to be due to a transcription error in Marpurg's text, where the old-fashioned diacritic raised ""e"" was substituted for the raised ring.