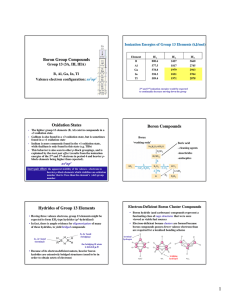
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... ElectronElectron-Deficient Boron Cluster Compounds • There are several basic cluster types: e.g. closo-, nido-, and arachno• Successively smaller clusters are named ...
... ElectronElectron-Deficient Boron Cluster Compounds • There are several basic cluster types: e.g. closo-, nido-, and arachno• Successively smaller clusters are named ...
Chapter 10 Handouts - Bakersfield College
... nonmetals. They are in group 7. •The alkali metals are active metals and have low melting points.They are in group 1. •The alkaline earth metals are less active than the alkali metals. They are in group 2. •The inert gases are inactive nonmetals. They are in group 8 ...
... nonmetals. They are in group 7. •The alkali metals are active metals and have low melting points.They are in group 1. •The alkaline earth metals are less active than the alkali metals. They are in group 2. •The inert gases are inactive nonmetals. They are in group 8 ...
Chapter 10 Handouts_1
... nonmetals. They are in group 7. •The alkali metals are active metals and have low melting points.They are in group 1. •The alkaline earth metals are less active than the alkali metals. They are in group 2. •The inert gases are inactive nonmetals. They are in group 8 ...
... nonmetals. They are in group 7. •The alkali metals are active metals and have low melting points.They are in group 1. •The alkaline earth metals are less active than the alkali metals. They are in group 2. •The inert gases are inactive nonmetals. They are in group 8 ...
Chapter 10_Handouts_6
... •All metals, except mercury, are •Nonmetals may be solid, solid at room temperature. liquid, or gaseous. •Metals have a characteristic metallic luster. ...
... •All metals, except mercury, are •Nonmetals may be solid, solid at room temperature. liquid, or gaseous. •Metals have a characteristic metallic luster. ...
Notes - Organization of Matter
... • For example, in H2O, the number 2 is the subscript for hydrogen and means that there are 2 atoms of hydrogen in the compound of water; since there is no subscript for oxygen it is assumed to be one atom of ...
... • For example, in H2O, the number 2 is the subscript for hydrogen and means that there are 2 atoms of hydrogen in the compound of water; since there is no subscript for oxygen it is assumed to be one atom of ...
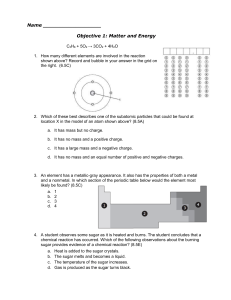
Name Objective 1: Matter and Energy C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
... 5.32 g/cm3; germanium; metalloid 7.87 g/cm3; iron; metal 11.3 g/cm3; lead; metal 13.6 g/cm3; mercury; metal ...
... 5.32 g/cm3; germanium; metalloid 7.87 g/cm3; iron; metal 11.3 g/cm3; lead; metal 13.6 g/cm3; mercury; metal ...
Chapter 1.1 –Chemistry is a Physical Science Chemistry is one of
... Metals are shiny solids at room temperature (except mercury), with characteristic high melting points and densities. Many of the properties of metals, including large atomic radius, low ionization energy, and low electronegativity, are due to the fact that the electrons in the valence shell of a m ...
... Metals are shiny solids at room temperature (except mercury), with characteristic high melting points and densities. Many of the properties of metals, including large atomic radius, low ionization energy, and low electronegativity, are due to the fact that the electrons in the valence shell of a m ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE abbr
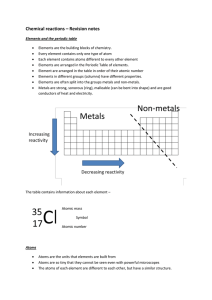
... Left side of the periodic table. Conduct electricity and heat well. Tend to be malleable. Tend to be solid at room temperature. Tend to lose electrons in chemical reactions. ...
... Left side of the periodic table. Conduct electricity and heat well. Tend to be malleable. Tend to be solid at room temperature. Tend to lose electrons in chemical reactions. ...
Made in the Stars Notes
... at room temperature except for mercury, which is a liquid. Non-metal solids are usually brittle (they break easily). Non-metals can be solids, liquids or gases at room temperature. Non-metals usually have low melting and boiling points. They are poor conductors of electricity. The exception is graph ...
... at room temperature except for mercury, which is a liquid. Non-metal solids are usually brittle (they break easily). Non-metals can be solids, liquids or gases at room temperature. Non-metals usually have low melting and boiling points. They are poor conductors of electricity. The exception is graph ...
Chapter 9 - Fayetteville State University
... 4) Solutions: are homogenous mixtures of elements of compounds 5) Atoms: are the ultimate particles of elements 6) Molecules: are made of atoms and form the ultimate particles of gaseous or liquid compounds 7) Periodic Law: States that elements arranged in order of the atomic number share similar ch ...
... 4) Solutions: are homogenous mixtures of elements of compounds 5) Atoms: are the ultimate particles of elements 6) Molecules: are made of atoms and form the ultimate particles of gaseous or liquid compounds 7) Periodic Law: States that elements arranged in order of the atomic number share similar ch ...
Chapter 10 The Periodic Law
... 10-7. The Periodic Table The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev formulated the periodic law about 1869 which states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular intervals. The periodic table is a listing of the eleme ...
... 10-7. The Periodic Table The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev formulated the periodic law about 1869 which states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular intervals. The periodic table is a listing of the eleme ...
Regents questions
... Sample 7.1 Natural gas used in home heating and cooking is odorless. Because natural gas leaks pose the danger of explosion or suffocation, various smelly substances are added to the gas to allow detection of a leak. One such substance is methyl mercaptan, CH3SH. Use Figure 7.6 to predict the lengt ...
... Sample 7.1 Natural gas used in home heating and cooking is odorless. Because natural gas leaks pose the danger of explosion or suffocation, various smelly substances are added to the gas to allow detection of a leak. One such substance is methyl mercaptan, CH3SH. Use Figure 7.6 to predict the lengt ...
CHEM 120 WEEK 11 LECTURES (INORGANIC WEEK 2) Dr. MD
... Contains only metals, apart from boron. Boron is also the only element which does not form a stable trication (B3+) again will have too high a charge density to be stable. Why do the other elements form tri-cations (M3+ )? Soln. √ Because they have the valence electronic configuration ns2np1 and ...
... Contains only metals, apart from boron. Boron is also the only element which does not form a stable trication (B3+) again will have too high a charge density to be stable. Why do the other elements form tri-cations (M3+ )? Soln. √ Because they have the valence electronic configuration ns2np1 and ...
Slide 1
... Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. Metals are shiny. Metals are ductile (can be ...
... Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. Metals are shiny. Metals are ductile (can be ...
General Chemistry First Semester Review General
... - aqueous (aq) is written if a solution is used - pure liquids (not a mixture of something) use (l) - solid: This could refer to a multitude of different substances: metals, flakes, crystals, and precipitates; use (s) - gas: Use (g), these are usually diatomic molecules such as O2, H2, Cl2, etc. - r ...
... - aqueous (aq) is written if a solution is used - pure liquids (not a mixture of something) use (l) - solid: This could refer to a multitude of different substances: metals, flakes, crystals, and precipitates; use (s) - gas: Use (g), these are usually diatomic molecules such as O2, H2, Cl2, etc. - r ...
1) - Kurt Niedenzu
... 32) The increase in atomic radius of each successive element within a group is primarily due to an increase in the number of a) neutrons in the nucleus b) electrons in the outermost shell c) unpaired electrons d) occupied principal energy levels 33) Elements that have properties of both metals and n ...
... 32) The increase in atomic radius of each successive element within a group is primarily due to an increase in the number of a) neutrons in the nucleus b) electrons in the outermost shell c) unpaired electrons d) occupied principal energy levels 33) Elements that have properties of both metals and n ...
Naming Ionic Compounds
... ** this is just like you learned for molecular compounds except you are not worried about the numbers of an element examples: NaCl – sodium chloride CaCl2 – calcium chloride Mg3N2 – magnesium nitride PbO – lead oxide ...
... ** this is just like you learned for molecular compounds except you are not worried about the numbers of an element examples: NaCl – sodium chloride CaCl2 – calcium chloride Mg3N2 – magnesium nitride PbO – lead oxide ...
Topic 4: Classifying Elements What did the early chemists use to
... • NH3(g) à nitrogen trihydride or ammonia • CH4(g) à carbon tetrahydride or methane • H2O2(l) à dihydrogen monoxide or water A MOLECULAR COMPOUND can contain what two combinations of elements? Non-‐metal + ...
... • NH3(g) à nitrogen trihydride or ammonia • CH4(g) à carbon tetrahydride or methane • H2O2(l) à dihydrogen monoxide or water A MOLECULAR COMPOUND can contain what two combinations of elements? Non-‐metal + ...
Chapter 1_chemh
... matter that is present. (volume, mass, etc) ●Intensive properties: do not depend on the amount of matter present. (melting point, boiling point, etc) ●Physical Property: characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of ...
... matter that is present. (volume, mass, etc) ●Intensive properties: do not depend on the amount of matter present. (melting point, boiling point, etc) ●Physical Property: characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of ...
Chemical reactions revision
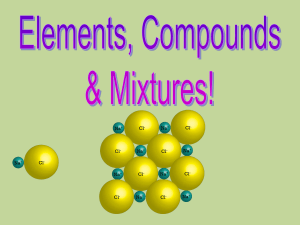
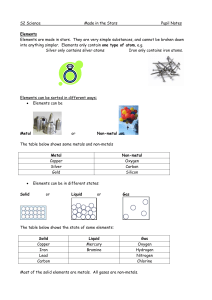
... Elements are the building blocks of chemistry. Every element contains only one type of atom Each element contains atoms different to every other element Elements are arranged in the Periodic Table of elements. Element are arranged in the table in order of their atomic number Elements in different gr ...
... Elements are the building blocks of chemistry. Every element contains only one type of atom Each element contains atoms different to every other element Elements are arranged in the Periodic Table of elements. Element are arranged in the table in order of their atomic number Elements in different gr ...
Chapter 1: Chemistry and You
... are good representation of what to expect on the midterm, but it is not enough to just study from the review. You need to look over your notes, old review sheets, tests and quizzes, homework, etc. Ask questions!!!! You may check your answers online and I am available Tuesday, Wednesday, and Thursday ...
... are good representation of what to expect on the midterm, but it is not enough to just study from the review. You need to look over your notes, old review sheets, tests and quizzes, homework, etc. Ask questions!!!! You may check your answers online and I am available Tuesday, Wednesday, and Thursday ...
Group IV Elements
... molecule with each Si atom bonded to four O. Silane alcohols when dehydrated give polymers, not like the alkenes from carbon. ...
... molecule with each Si atom bonded to four O. Silane alcohols when dehydrated give polymers, not like the alkenes from carbon. ...