Definitions of Cell Structures and Their Functions Instructions for
... -Cell wall: Non-living structure surrounding plant cell; provides shape and support -Cell membrane: Enclosed the cell, controlling the inward and outward flow of materials -Chloroplasts: Contain chlorophyll, used by plants to make food -Cytoplasm: Jelly-like material where chemical processes take pl ...
... -Cell wall: Non-living structure surrounding plant cell; provides shape and support -Cell membrane: Enclosed the cell, controlling the inward and outward flow of materials -Chloroplasts: Contain chlorophyll, used by plants to make food -Cytoplasm: Jelly-like material where chemical processes take pl ...
Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Lab
... 5. In what ways are the cells of onion epidermis and Elodea similar?____________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 6. In what ways are the cells of onion epidermis and Elodea DIFFERENT? _______________________ __________________________ ...
... 5. In what ways are the cells of onion epidermis and Elodea similar?____________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 6. In what ways are the cells of onion epidermis and Elodea DIFFERENT? _______________________ __________________________ ...
Cell Organelles - Bath.k12.ky.us
... Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) A system of folded membranes that transport ...
... Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) A system of folded membranes that transport ...
Unit B: Cell structure
... • Nuclear pores: allow mRNA out of nucleus, nucleotides, nutrients & enzymes in. They are made from protein. • Chromatin: Protein & DNA; form chromosomes when cell divides. • Nucleolus:contains rRNA and Ribosomal proteins. ...
... • Nuclear pores: allow mRNA out of nucleus, nucleotides, nutrients & enzymes in. They are made from protein. • Chromatin: Protein & DNA; form chromosomes when cell divides. • Nucleolus:contains rRNA and Ribosomal proteins. ...
Postassessment Study Guide
... Cells: • Describe how cells, tissues, organs and organ systems are related • Be able to identify a plant and animal cell • Know the jobs/roles of each cell organelle • Know the differences between plant and animal cells ...
... Cells: • Describe how cells, tissues, organs and organ systems are related • Be able to identify a plant and animal cell • Know the jobs/roles of each cell organelle • Know the differences between plant and animal cells ...
Biology- ch. 7
... • Cell wall - support and protect (plant, fungus & bacteria cells) • Cytoplasm – “cell gel” material inside of the cell membrane. Most ...
... • Cell wall - support and protect (plant, fungus & bacteria cells) • Cytoplasm – “cell gel” material inside of the cell membrane. Most ...
Label a Plant Cell (Up to 16yrs old / GCSE)
... The structure in plant cells that contains chlorophyll and in which photosynthesis takes place ...
... The structure in plant cells that contains chlorophyll and in which photosynthesis takes place ...
Notes Chapter 10 Lesson 1 The Basics of a Cell
... Single Celled Organism- Living things that are made up of only ONE Cell Multi-celled Organism- Describes organisms that are composed of different kinds of specialized cells ...
... Single Celled Organism- Living things that are made up of only ONE Cell Multi-celled Organism- Describes organisms that are composed of different kinds of specialized cells ...
UNICELLULAR MULTICELLULAR
... MADE OF CELL(S) Ingest-surrounds and engulfs other organisms and moves them into the REPRODUCE vacuoles Digest-enzymes move into the GROW AND REPAIR vacuole in order to break down food into nutrients that can be used INGEST by the cell Reproduce-binary fission-divides DIGEST into two cells that are ...
... MADE OF CELL(S) Ingest-surrounds and engulfs other organisms and moves them into the REPRODUCE vacuoles Digest-enzymes move into the GROW AND REPAIR vacuole in order to break down food into nutrients that can be used INGEST by the cell Reproduce-binary fission-divides DIGEST into two cells that are ...
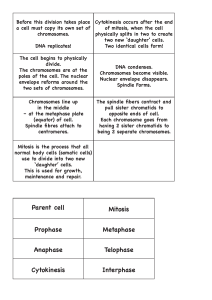
Parent cell Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
... DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at the poles of the cell. The nuclear envelope reforms around the two sets of chromosomes. Chromosomes line up in the middle – at the metaphase plate (equator) of cell. centromeres. ...
... DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at the poles of the cell. The nuclear envelope reforms around the two sets of chromosomes. Chromosomes line up in the middle – at the metaphase plate (equator) of cell. centromeres. ...
Organic Compounds= most compounds containing carbon… make
... (ATP), can also offer structure and support (Cellulose & chitin) Cell walls, cytoskeleton ,mitochondr ia, chloroplasts primarily ...
... (ATP), can also offer structure and support (Cellulose & chitin) Cell walls, cytoskeleton ,mitochondr ia, chloroplasts primarily ...
MICRONUCLEUS FORMATION AND CELL PROLIFERATION IN A
... Background: A better understanding of the underlying mechanisms of DNA repair after lowand high-LET radiations is needed to improve the outcome of clinical radiotherapy making e.g. use of high-LET new particle beams like carbon ions. To date, however, our knowledge regarding the importance of DNA DS ...
... Background: A better understanding of the underlying mechanisms of DNA repair after lowand high-LET radiations is needed to improve the outcome of clinical radiotherapy making e.g. use of high-LET new particle beams like carbon ions. To date, however, our knowledge regarding the importance of DNA DS ...
Complete the following table to fully describe the various organelles
... To process lipids and proteins and ‘package’ them for exocytosis ...
... To process lipids and proteins and ‘package’ them for exocytosis ...
Notes Outline: How Cells Divide (4
... How Eukaryotic Cells Divide A. Introduction Eukaryotic cells carry far more DNA than bacteria ________________________________________________________________________ Chromosomes: ________________________________________________________________________ A typical human cell contains 46 chro ...
... How Eukaryotic Cells Divide A. Introduction Eukaryotic cells carry far more DNA than bacteria ________________________________________________________________________ Chromosomes: ________________________________________________________________________ A typical human cell contains 46 chro ...
Lecture 6
... - tubulins 2. Support “scaffolding” all cells would otherwise form a sphere 3. Provide the “machinery” for cellular movement - cilia and flagella made of microtubules - also used to move organelles and chromosomes within cells ...
... - tubulins 2. Support “scaffolding” all cells would otherwise form a sphere 3. Provide the “machinery” for cellular movement - cilia and flagella made of microtubules - also used to move organelles and chromosomes within cells ...
Lecture 6
... - tubulins 2. Support “scaffolding” all cells would otherwise form a sphere 3. Provide the “machinery” for cellular movement - cilia and flagella made of microtubules - also used to move organelles and chromosomes within cells ...
... - tubulins 2. Support “scaffolding” all cells would otherwise form a sphere 3. Provide the “machinery” for cellular movement - cilia and flagella made of microtubules - also used to move organelles and chromosomes within cells ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).