Biology: Cell Unit Review
... Cell Structure • Form follows function: Shapes evolve to allow cells to perform their function. • Sizes range from nm to 2 m in length, but average cells are 10 – 50 mm. • Surface-area-to-volume ratio limits size. – Volume increases more quickly. – Cells’ need for nutrient intake & waste disposal d ...
... Cell Structure • Form follows function: Shapes evolve to allow cells to perform their function. • Sizes range from nm to 2 m in length, but average cells are 10 – 50 mm. • Surface-area-to-volume ratio limits size. – Volume increases more quickly. – Cells’ need for nutrient intake & waste disposal d ...
Cellular Chemical Reactions
... 93% of the human body is made up of Oxygen, Carbon, and Hydrogen. The four main types of large molecules are Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids. All of theses large molecules contain Carbon atoms and are made up of smaller parts called subunits. An important property of Lipids is tha ...
... 93% of the human body is made up of Oxygen, Carbon, and Hydrogen. The four main types of large molecules are Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids. All of theses large molecules contain Carbon atoms and are made up of smaller parts called subunits. An important property of Lipids is tha ...
CELLS UNIT 1 Learning Targets - Milton
... Draw/create a bacteria, plant, and animal cell and place the appropriate organelles in each cell type. Name the four cell structures in common to all cell types. Describe Anton Van Leeuwen hoek’s contribution to cellular biology. List the three principles of the cell theory. Describe the function of ...
... Draw/create a bacteria, plant, and animal cell and place the appropriate organelles in each cell type. Name the four cell structures in common to all cell types. Describe Anton Van Leeuwen hoek’s contribution to cellular biology. List the three principles of the cell theory. Describe the function of ...
Cells
... 1. Every organism is composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the smallest unit that has the properties of life. 3. The continuity of life arises directly from the growth and division of single cells. ...
... 1. Every organism is composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the smallest unit that has the properties of life. 3. The continuity of life arises directly from the growth and division of single cells. ...
Unit 2 Overview
... 2. Understand the relative sizes of different cells. 3. Understand that the shape (structure) of a cell is directly related to its function & be able to give examples. 4. Identify the structure and function of the different organelles found in eukaryotic cells. 5. Understand the difference & similar ...
... 2. Understand the relative sizes of different cells. 3. Understand that the shape (structure) of a cell is directly related to its function & be able to give examples. 4. Identify the structure and function of the different organelles found in eukaryotic cells. 5. Understand the difference & similar ...
Matthew Keirle Office: 25-115 Phone: 752
... Cell Theory • Every living organism is made of one or more cells • The smallest organisms are made of single cells while multicellular organisms are made of many cells • All cells arise from pre-existing cells ...
... Cell Theory • Every living organism is made of one or more cells • The smallest organisms are made of single cells while multicellular organisms are made of many cells • All cells arise from pre-existing cells ...
Supplementary Figure 4
... Supplementary figure 4. Aortic ring assays. a: overview of the culture. Scale bar, 0.5cm. b: quantification of cell movement. The distance of cell movement (pixel/2h1/2) was measured for each cell filmed (n=6 control, 8 Netrin-1, 16 Netrin-1/UNC5B-Fc). The mean±s.e.m. of all cells for each treatment ...
... Supplementary figure 4. Aortic ring assays. a: overview of the culture. Scale bar, 0.5cm. b: quantification of cell movement. The distance of cell movement (pixel/2h1/2) was measured for each cell filmed (n=6 control, 8 Netrin-1, 16 Netrin-1/UNC5B-Fc). The mean±s.e.m. of all cells for each treatment ...
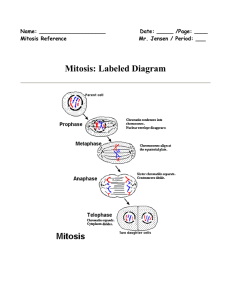
Mitosis - Mahopac Voyagers!
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
Actin filaments
... It is a dynamic structure that maintains cell shape, protects the cell, enables cellular motion (using structures such as flagella, cilia and lamellipodia), and plays important roles in both intracellular transport (the movement of vesicles and organelles, for example) and cellular division. ...
... It is a dynamic structure that maintains cell shape, protects the cell, enables cellular motion (using structures such as flagella, cilia and lamellipodia), and plays important roles in both intracellular transport (the movement of vesicles and organelles, for example) and cellular division. ...
File
... 12. Organelles that make proteins are called ______________________. 13.Proteins are made of ______________________. ...
... 12. Organelles that make proteins are called ______________________. 13.Proteins are made of ______________________. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Endoplasmic Reticulum- consists of membranous tubules, and sacs, called cisternae. • Smooth ER- lacks ribosomes. Functions lipid synthesis, detoxification, and storing calcium ions. • Rough ER- has ribosomes on surface. Continuous with the nuclear envelope. Synthesizes glycoproteins and other sec ...
... • Endoplasmic Reticulum- consists of membranous tubules, and sacs, called cisternae. • Smooth ER- lacks ribosomes. Functions lipid synthesis, detoxification, and storing calcium ions. • Rough ER- has ribosomes on surface. Continuous with the nuclear envelope. Synthesizes glycoproteins and other sec ...
What the Cell? - Effingham County Schools
... form a cell can use (ATP) during the process of cellular respiration. • Contain own ‘Mitochondrial DNA’ ...
... form a cell can use (ATP) during the process of cellular respiration. • Contain own ‘Mitochondrial DNA’ ...
Cell Structure and Function - Crossword
... 13. Undigested materials removed from cell membrane 14. Large fluid filled space found in plant cells for storage and digestion. 15. Specialized structure in cell with particular function. 16.Thin rod-like structure composed of DNA and protein and found in nucleus. 17. Structures reponsible for cell ...
... 13. Undigested materials removed from cell membrane 14. Large fluid filled space found in plant cells for storage and digestion. 15. Specialized structure in cell with particular function. 16.Thin rod-like structure composed of DNA and protein and found in nucleus. 17. Structures reponsible for cell ...
Name_____________________ Anat/phys chapter 3 part 2 quiz 10
... rRNA= ribosomal RNA. It attaches to the mRNA and translates it. It reads the messages and gives a site for the tRNA to bind the amino acids tRNA= transfer RNA. It brings the amino acids to the peptide chain. ...
... rRNA= ribosomal RNA. It attaches to the mRNA and translates it. It reads the messages and gives a site for the tRNA to bind the amino acids tRNA= transfer RNA. It brings the amino acids to the peptide chain. ...
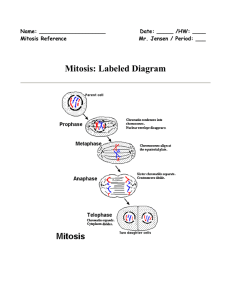
Mitosis: Labeled Diagram
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
... Illustration of the process by which somatic cells multiply and divide. Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mi ...
Semester 1 Exam Study Guide with answers
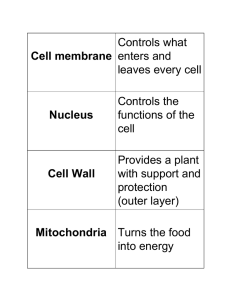
... 11. What is mitosis? The cell divides into 2 new cells Why is it important? It’s how cells reproduce 12. Which organelle is the control center of a cell? Nucleus 13. Which organelles store food and other materials needed by the cell? Vacuoles 14. What is the function of a cell membrane? To control w ...
... 11. What is mitosis? The cell divides into 2 new cells Why is it important? It’s how cells reproduce 12. Which organelle is the control center of a cell? Nucleus 13. Which organelles store food and other materials needed by the cell? Vacuoles 14. What is the function of a cell membrane? To control w ...
The Discovery of Cells
... 1. All living things are made of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things. 3. All cells come from other cells. ...
... 1. All living things are made of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things. 3. All cells come from other cells. ...
Intro to Cells and Biochemistry Molecule General Molecular Shape
... 2. Choose a sports game you like to play or watch. Explain how life is like that game. 5 sentences minimum. Use actual examples from both sport and life to illustrate. 3. What is the cell considered the basic unit of life and why is it considered alive? 4. Copy onto your paper the picture of the cel ...
... 2. Choose a sports game you like to play or watch. Explain how life is like that game. 5 sentences minimum. Use actual examples from both sport and life to illustrate. 3. What is the cell considered the basic unit of life and why is it considered alive? 4. Copy onto your paper the picture of the cel ...
SPECIALIZED CELLS
... – Muscle cells make specialized tissue that can contract. – Muscle tissue contains the specialized proteins actin and myosin that slide past one another. ...
... – Muscle cells make specialized tissue that can contract. – Muscle tissue contains the specialized proteins actin and myosin that slide past one another. ...
A1 Cell Structure Notes
... Plasmolysed cells are cells that have a low water concentration (hypertonic solution) Flaccid cells are cells that that have a normal water concentration (isotonic solution) Turgid cells are cells that have a high water concentration (hypotonic solution) ...
... Plasmolysed cells are cells that have a low water concentration (hypertonic solution) Flaccid cells are cells that that have a normal water concentration (isotonic solution) Turgid cells are cells that have a high water concentration (hypotonic solution) ...
Cell Membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell Wall Ribosome Reticulum
... passageways that carry materials from one part of the cell to ...
... passageways that carry materials from one part of the cell to ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).