Cells - BrainPOP
... a. They help cells think b. Cells could not function without them c. They require a lot of blood to operate properly d. They are located at the top of the cell 8. How are eukaryotic cells different from prokaryotic cells? a. Eukaryotic cells have nuclei; prokaryotic cells don't b. Eukaryotic cells h ...
... a. They help cells think b. Cells could not function without them c. They require a lot of blood to operate properly d. They are located at the top of the cell 8. How are eukaryotic cells different from prokaryotic cells? a. Eukaryotic cells have nuclei; prokaryotic cells don't b. Eukaryotic cells h ...
Ch_4-5_Review
... (a) The cell is the smallest unit of life. (b) Cells must come from preexisting cells. (c) Cells are able to make their own food. (d) Organisms are made up of one or more cells. ...
... (a) The cell is the smallest unit of life. (b) Cells must come from preexisting cells. (c) Cells are able to make their own food. (d) Organisms are made up of one or more cells. ...
Host Defence
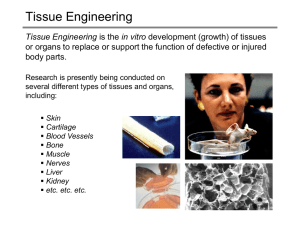
... Cell Sources Since the ultimate goal of tissue engineering is to develop replacement tissue (or organs) for individuals, the use of autologous cells would avoid ...
... Cell Sources Since the ultimate goal of tissue engineering is to develop replacement tissue (or organs) for individuals, the use of autologous cells would avoid ...
Cell Cycle - Canyon ISD
... There are several factors that regulate the cell cycle and assure a cell divides correctly. Before a cell divides, the DNA is checked to make sure it has replicated correctly. If DNA does not copy itself correctly, a gene mutation occurs. Neighboring cells also communicate with dividing cells to re ...
... There are several factors that regulate the cell cycle and assure a cell divides correctly. Before a cell divides, the DNA is checked to make sure it has replicated correctly. If DNA does not copy itself correctly, a gene mutation occurs. Neighboring cells also communicate with dividing cells to re ...
Cell Division and Cancer Study Guide
... Daughter cells – two identical cells formed at the end of the cell cycle; have the same amount of chromosomes as the parent cell ...
... Daughter cells – two identical cells formed at the end of the cell cycle; have the same amount of chromosomes as the parent cell ...
Chapter 2 – Chemistry of Life and the Cell
... 2. High pH is basic and has more OHProkaryotic organisms are one celled and have no nucleus, bacteria is an example of this kind of cell. Eukaryotic organisms are made up of one or more nucleated cells that contain organelles that perform specific functions. An example of a eukaryote is the human. T ...
... 2. High pH is basic and has more OHProkaryotic organisms are one celled and have no nucleus, bacteria is an example of this kind of cell. Eukaryotic organisms are made up of one or more nucleated cells that contain organelles that perform specific functions. An example of a eukaryote is the human. T ...
mrmahmood
... The Coarse Adjustment Knob is used to focus the image in the microscope. To calculate Total Magnification, multiply the eyepiece times the objective. An example of a unicellular organism is a person. All living things do not move. The microscope bag should go somewhere safe. Always start in Scanning ...
... The Coarse Adjustment Knob is used to focus the image in the microscope. To calculate Total Magnification, multiply the eyepiece times the objective. An example of a unicellular organism is a person. All living things do not move. The microscope bag should go somewhere safe. Always start in Scanning ...
Learning Outcomes
... Vesicles and Vacuoles Have Varied Functions 6. Describe the structure and function of lysosomes and peroxisomes. 7. Describe the varied functions of vacuoles and/or vesicles in protists, plants, and animals. A Cell Carries Out Energy Transformations 8. Compare and contrast the structure and function ...
... Vesicles and Vacuoles Have Varied Functions 6. Describe the structure and function of lysosomes and peroxisomes. 7. Describe the varied functions of vacuoles and/or vesicles in protists, plants, and animals. A Cell Carries Out Energy Transformations 8. Compare and contrast the structure and function ...
Cells
... • Plants’ cell walls are made of cellulose, a complex sugar. This is why celery crunches when you bite it. • Chloroplasts have their own membranes and DNA. They contain chlorophyll, which makes them green. This is also what traps the energy of sunlight. ...
... • Plants’ cell walls are made of cellulose, a complex sugar. This is why celery crunches when you bite it. • Chloroplasts have their own membranes and DNA. They contain chlorophyll, which makes them green. This is also what traps the energy of sunlight. ...
Slide () - Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research
... From: Biotechnology in the Treatment of Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Foundations and Future of Hair Cell Regeneration J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2011;54(6):1709-1731. doi:10.1044/1092-4388(2011/10-0149) ...
... From: Biotechnology in the Treatment of Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Foundations and Future of Hair Cell Regeneration J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2011;54(6):1709-1731. doi:10.1044/1092-4388(2011/10-0149) ...
Year 7 Cells Exchanges objectives
... 6) Explain that animal and plant cells have several similar features (nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm) and several differences (cell wall, chloroplasts, vacuole). Be able to describe how these features allow the cell to function. 7) Explain that some of the life processes take place within individ ...
... 6) Explain that animal and plant cells have several similar features (nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm) and several differences (cell wall, chloroplasts, vacuole). Be able to describe how these features allow the cell to function. 7) Explain that some of the life processes take place within individ ...
biology terms cells mixed
... cells used for the temporary storage of materials. 2. A ___________________________ in animal cells is a pair of small cylindrical structures composed of microtubules that only form during cell division and aid in the dividing of the cell. 3. The ___________________________ is an organelle in eukary ...
... cells used for the temporary storage of materials. 2. A ___________________________ in animal cells is a pair of small cylindrical structures composed of microtubules that only form during cell division and aid in the dividing of the cell. 3. The ___________________________ is an organelle in eukary ...
Development of the Cell Theory
... drops of blood, scrapings from their own teeth, and other small things. Cells weren't discovered until the m scop improved. 1665, Ro ert Hooker cut a thin slice of cor an 00 ed ...
... drops of blood, scrapings from their own teeth, and other small things. Cells weren't discovered until the m scop improved. 1665, Ro ert Hooker cut a thin slice of cor an 00 ed ...
Cells how to post it activity
... 1. Think of a place you could draw that would represent the cell and all of its organelles. EX: A drawing of a basketball court with teams playing basketball, match up the cell words with the drawing. Don’t use our classroom since that is the analogy I will use in class (coach – nucleus, gym walls – ...
... 1. Think of a place you could draw that would represent the cell and all of its organelles. EX: A drawing of a basketball court with teams playing basketball, match up the cell words with the drawing. Don’t use our classroom since that is the analogy I will use in class (coach – nucleus, gym walls – ...
SNC2P (1.3) Cell Differences rev
... become a specialized cell as it matures. • Some will become blood cells, some nerve cells, and some muscle cells. ...
... become a specialized cell as it matures. • Some will become blood cells, some nerve cells, and some muscle cells. ...
Histology Practical 1
... 2. The small tunnels that connect one bone cell to another are called? 3. What epithelium is found in the urinary tract? 4. The small cells found around and supporting neurons are called? 5. Intercalated discs are found in what tissue? 6. Bone and cartilage cells live in small cavities called? 7. Ty ...
... 2. The small tunnels that connect one bone cell to another are called? 3. What epithelium is found in the urinary tract? 4. The small cells found around and supporting neurons are called? 5. Intercalated discs are found in what tissue? 6. Bone and cartilage cells live in small cavities called? 7. Ty ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).