You Gotta Know
... Nucleus The nucleus is the "command central" of the cell because it contains almost all of the cell's DNA, which encodes the information needed to make all the proteins that the cell uses. The DNA appears as chromatin through most of the cell cycle but condenses to form chromosomes when the cell is ...
... Nucleus The nucleus is the "command central" of the cell because it contains almost all of the cell's DNA, which encodes the information needed to make all the proteins that the cell uses. The DNA appears as chromatin through most of the cell cycle but condenses to form chromosomes when the cell is ...
Cellular Structures and Organelles
... • Certain small molecules such as CO2, H2O, & O2 can easily pass through the phospholipids ...
... • Certain small molecules such as CO2, H2O, & O2 can easily pass through the phospholipids ...
The Multiscale Physics-Biology-Chemistry and cancer (molecules
... UMR144 CNRS, UMR168 CNRS, and UMR3666 CNRS – U1143 INSERM. The common theme is the use of cross-disciplinary approaches involving physics, chemistry and biology to produce fundamental insights in cell biology and innovative tools for biomedical research. Our scientific interests are focused on questi ...
... UMR144 CNRS, UMR168 CNRS, and UMR3666 CNRS – U1143 INSERM. The common theme is the use of cross-disciplinary approaches involving physics, chemistry and biology to produce fundamental insights in cell biology and innovative tools for biomedical research. Our scientific interests are focused on questi ...
The Cell - Angelfire
... • The first name is always the Genus name • The second name is always the species name • The first letter of the first name is always in upper case & the first letter of the species name is always in the lower ...
... • The first name is always the Genus name • The second name is always the species name • The first letter of the first name is always in upper case & the first letter of the species name is always in the lower ...
Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes - Duncanville Middle School
... Ribosomes are produced inside the nucleus at the nucleolus. ...
... Ribosomes are produced inside the nucleus at the nucleolus. ...
Cell Organelles BioH
... Everything in the space between the membrane and nucleus in a cell is the cytoplasm. ...
... Everything in the space between the membrane and nucleus in a cell is the cytoplasm. ...
Lecture Notes
... organism, in part or as a whole, or of movement of materials within the body. The cells are packed with the protein filaments actin and myosin, which work together to produce contraction of the muscle cell. There are three types of muscle tissue: smooth, skeletal, and cardiac. Skeletal and cardiac m ...
... organism, in part or as a whole, or of movement of materials within the body. The cells are packed with the protein filaments actin and myosin, which work together to produce contraction of the muscle cell. There are three types of muscle tissue: smooth, skeletal, and cardiac. Skeletal and cardiac m ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... important components and carbohydrates attached to membrane proteins are important as “name tags” that help the body recognize its own cells. 3. Membrane proteins have the following functions: - transport proteins move substances into and out of cells; - enzymes facilitate chemical reactions; - reco ...
... important components and carbohydrates attached to membrane proteins are important as “name tags” that help the body recognize its own cells. 3. Membrane proteins have the following functions: - transport proteins move substances into and out of cells; - enzymes facilitate chemical reactions; - reco ...
END OF CHAPTER QUESTIONS
... The parts of interphase are: the G1 phase, characterized by cell growth, protein production, and metabolic activities; the S phase, during which DNA is replicated prior to cell division and growth activities continue; and the G2 phase, characterized by completion of centriole replication, organelle ...
... The parts of interphase are: the G1 phase, characterized by cell growth, protein production, and metabolic activities; the S phase, during which DNA is replicated prior to cell division and growth activities continue; and the G2 phase, characterized by completion of centriole replication, organelle ...
AP BIOLOGY-EXAM REVIEW The Cell
... The organelles that contain their own DNA are all enclosed in double membranes. Relate this observation to the endosymbiotic theory. ...
... The organelles that contain their own DNA are all enclosed in double membranes. Relate this observation to the endosymbiotic theory. ...
Exploring the Cell - Tamalpais Union High School District
... components. As we have learned in our study of the origin of life, singled celled organisms were the first living things on Earth. Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life. Some organisms are composed of a single cell while others are composed of trillions of cells. In order to ga ...
... components. As we have learned in our study of the origin of life, singled celled organisms were the first living things on Earth. Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life. Some organisms are composed of a single cell while others are composed of trillions of cells. In order to ga ...
Cell Project demo
... education as the cell is a system that provides for growth, repair and reproduction. ...
... education as the cell is a system that provides for growth, repair and reproduction. ...
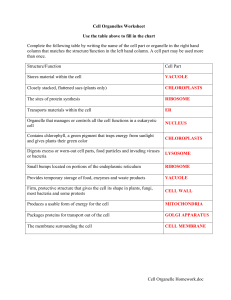
Cell Organelle Homework.doc Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria ...
... Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria ...
A Tour of the Cell - Ursuline High School
... Golgi Apparatus package and modify proteins and lipids into vesicles (small, spherical shaped sacs that bud form the Golgi apparatus). The vesicles often merge and merge with the plasma membrane to release contents to the outside of the cell. ...
... Golgi Apparatus package and modify proteins and lipids into vesicles (small, spherical shaped sacs that bud form the Golgi apparatus). The vesicles often merge and merge with the plasma membrane to release contents to the outside of the cell. ...
The Organization of Living Things
... Cells can be specialized (have a certain function) Function is related to the cell structure Structure = how parts of the cell are put together ...
... Cells can be specialized (have a certain function) Function is related to the cell structure Structure = how parts of the cell are put together ...
Structure and Function of the Cell
... 7. Ribosomes are made up of RNA. They are synthesized in the nucleolus. Ribosomes are the site of protein systhesis. Some ribosomes float freely in the cell and other attach themselves to the endoplasmic reticulum. 8. Vacuoles are fluid-filled sacs that store nutrients, water, and waste. 9. What is ...
... 7. Ribosomes are made up of RNA. They are synthesized in the nucleolus. Ribosomes are the site of protein systhesis. Some ribosomes float freely in the cell and other attach themselves to the endoplasmic reticulum. 8. Vacuoles are fluid-filled sacs that store nutrients, water, and waste. 9. What is ...
CELLS
... take nutrients/energy from environment for their own use can repair themselves can reproduce Cell is an organized container of chemicals that behaves in a way that we say is living. 3 parts of the cell: ...
... take nutrients/energy from environment for their own use can repair themselves can reproduce Cell is an organized container of chemicals that behaves in a way that we say is living. 3 parts of the cell: ...
Cell membrane
... include protists, fungi, plants, and animals. The diagram below shows link between bacteria, archaea, and the four other kingdoms. ...
... include protists, fungi, plants, and animals. The diagram below shows link between bacteria, archaea, and the four other kingdoms. ...
How does a cell survive
... • The cells “power plant” • Food molecules are broken down in the cell to release energy. • Then, ATP moves energy to Mitochondria • Bean shaped • 2 membranes • Work only with oxygen Outer and Inner Membranes ...
... • The cells “power plant” • Food molecules are broken down in the cell to release energy. • Then, ATP moves energy to Mitochondria • Bean shaped • 2 membranes • Work only with oxygen Outer and Inner Membranes ...
General Biology Study Guide
... Be able to calculate the actual size of a cell from an estimated apparent size using metric conversions. ...
... Be able to calculate the actual size of a cell from an estimated apparent size using metric conversions. ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).