Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell
... Cell Wall Cell wall Nonliving layer Gives structure and shape to plant and bacterial cells ...
... Cell Wall Cell wall Nonliving layer Gives structure and shape to plant and bacterial cells ...
Determining the proportional distribution of propagons between
... onto solid YPD media containing 5mM GdnHCl. At this concentration of GdnHCl, propagon replication is inhibited and the numbers of propagons the cells contain (n0) is fixed. 2) Incubate the cells at 30o C for approximately two hours until the cells have undertaken one round of cell division. ...
... onto solid YPD media containing 5mM GdnHCl. At this concentration of GdnHCl, propagon replication is inhibited and the numbers of propagons the cells contain (n0) is fixed. 2) Incubate the cells at 30o C for approximately two hours until the cells have undertaken one round of cell division. ...
Chapter 07
... Microfilaments, Intermediate Filaments, and Microtubules: Collectively, these form the cytoskeleton, which reinforces the cell’s shape and moves the cell. The components are made of protein. Microtubules are the thickest of the three and microfilaments are the thinnest of them. The intermediate fila ...
... Microfilaments, Intermediate Filaments, and Microtubules: Collectively, these form the cytoskeleton, which reinforces the cell’s shape and moves the cell. The components are made of protein. Microtubules are the thickest of the three and microfilaments are the thinnest of them. The intermediate fila ...
Cell - WordPress.com
... -The Golgi body further packages/stores proteins and carbohydrates into membrane-bound vesicles for "export". - Flattened, layered, sac-like organelle. ...
... -The Golgi body further packages/stores proteins and carbohydrates into membrane-bound vesicles for "export". - Flattened, layered, sac-like organelle. ...
Cell Organelles - MBBS Students Club
... usually in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. What type of microscope may have been used to take this picture? ...
... usually in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. What type of microscope may have been used to take this picture? ...
The Cell Cycle - Lake Stevens High School / Overview
... M checkpoint triggered by chromosome not attaching to spindle ...
... M checkpoint triggered by chromosome not attaching to spindle ...
The Cell: Organelles and Functions
... Network of MembraneLined Channels Function: 1. Transport of cellular products Processing of cellular products - Lipids to cell membrane - Proteins for export ...
... Network of MembraneLined Channels Function: 1. Transport of cellular products Processing of cellular products - Lipids to cell membrane - Proteins for export ...
Cell Organelles
... usually in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. What type of microscope may have been used to take this picture? ...
... usually in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. What type of microscope may have been used to take this picture? ...
Cell Organelles - Fall River Public Schools
... usually in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. What type of microscope may have been used to take this picture? ...
... usually in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. What type of microscope may have been used to take this picture? ...
Six Kingdoms of Life
... b. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria) to basic cell functions. Organelle ...
... b. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria) to basic cell functions. Organelle ...
Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells
... -‐Be able to label at least 10 organelles in a Eukaryotic cell -‐Know how eukaryotic cells obtain energy -‐Be able to compare and contrast Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (size, age, complexity, struc ...
... -‐Be able to label at least 10 organelles in a Eukaryotic cell -‐Know how eukaryotic cells obtain energy -‐Be able to compare and contrast Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (size, age, complexity, struc ...
Document
... Cell – smallest unit that can live and reproduce on its own or as part of a multicelled organism. It has an outer membrane, DNA, and other components called organelles. Tissue – cells form tissues. It is an organized group of similar cells that perform the same task. For example, muscle is a tissue ...
... Cell – smallest unit that can live and reproduce on its own or as part of a multicelled organism. It has an outer membrane, DNA, and other components called organelles. Tissue – cells form tissues. It is an organized group of similar cells that perform the same task. For example, muscle is a tissue ...
CELLS - Clever Teach
... The rigid cell wall in plant cells is made of cellulose and gives the cell membrane and contents extra support It gives plants their rigidity - their stable 3D structure. ...
... The rigid cell wall in plant cells is made of cellulose and gives the cell membrane and contents extra support It gives plants their rigidity - their stable 3D structure. ...
Intro to Cells Webquest
... 1. All ____________ things are made up of _________. Each of us has about 50 million cells - an enormous number which is difficult to imagine (NOW WE KNOW IT IS EVEN MORE THAN THAT!). Each cell is a sort of bag made from a sort of skin called a __________________. The inside of a cell is ___________ ...
... 1. All ____________ things are made up of _________. Each of us has about 50 million cells - an enormous number which is difficult to imagine (NOW WE KNOW IT IS EVEN MORE THAN THAT!). Each cell is a sort of bag made from a sort of skin called a __________________. The inside of a cell is ___________ ...
Check Your Knowledge Set 1(Download)
... hydrogen peroxide as a by-product, which is converted to water by other enzymes Large membrane-bounded vesicle in plants for digestion, storage, waste disposal, water balance, cell growth, and protection Extensive network of membrane-bound tubules and sacs, one of the functions is detoxification of ...
... hydrogen peroxide as a by-product, which is converted to water by other enzymes Large membrane-bounded vesicle in plants for digestion, storage, waste disposal, water balance, cell growth, and protection Extensive network of membrane-bound tubules and sacs, one of the functions is detoxification of ...
organ system - Scholieren.com
... Plants and animals are made up of small parts: cells. These are tiny building blocks. You can’t see them with the naked eye so you need a microscope. When you look at the cells through a microscope the cells seem to be flat, but in reality they are a kind of boxes because something is in it. There a ...
... Plants and animals are made up of small parts: cells. These are tiny building blocks. You can’t see them with the naked eye so you need a microscope. When you look at the cells through a microscope the cells seem to be flat, but in reality they are a kind of boxes because something is in it. There a ...
Chapter 2 Review 1. What is the difference between the cell
... 13. What did Schwann discover? All animals are made of cells. 14. What did Schleiden discover? All plants are made of cells. 15. What did Hooke discover? First to see cells under a microscope (in slides of cork) 16. What did van Leewenhoek discover? Saw “wee beasties” under the microscope 17. Stora ...
... 13. What did Schwann discover? All animals are made of cells. 14. What did Schleiden discover? All plants are made of cells. 15. What did Hooke discover? First to see cells under a microscope (in slides of cork) 16. What did van Leewenhoek discover? Saw “wee beasties” under the microscope 17. Stora ...
Chapter 7 Notes - BellevilleBiology.com
... animals cells only Microtubules and filaments: help maintain cell shape- help amoeba move ...
... animals cells only Microtubules and filaments: help maintain cell shape- help amoeba move ...
ERYTHROPOIESIS Erythropoiesis: is the formation of red blood
... ERYTHROPOIESIS Erythropoiesis: is the formation of red blood cells, i.e., the developmental processes of the red blood cell. occurs in the red bone marrow from the descendants of the proerythroblast stem cell by the processes of proliferation and differentiation each hemocytoblast stem cell ...
... ERYTHROPOIESIS Erythropoiesis: is the formation of red blood cells, i.e., the developmental processes of the red blood cell. occurs in the red bone marrow from the descendants of the proerythroblast stem cell by the processes of proliferation and differentiation each hemocytoblast stem cell ...
Slide 1
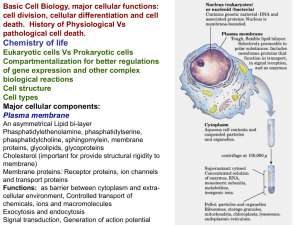
... Compartmentalization for better regulations of gene expression and other complex biological reactions Cell structure Cell types Major cellular components: Plasma membrane An asymmetrical Lipid bi-layer Phasphatidylethenolamine, phasphatidylserine, phasphatidylcholine, sphingomylein, membrane protein ...
... Compartmentalization for better regulations of gene expression and other complex biological reactions Cell structure Cell types Major cellular components: Plasma membrane An asymmetrical Lipid bi-layer Phasphatidylethenolamine, phasphatidylserine, phasphatidylcholine, sphingomylein, membrane protein ...
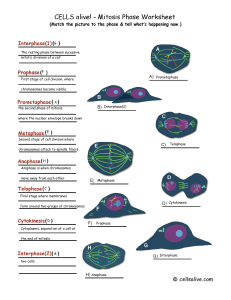
Cell Cycle PowerPoint
... Cut out the diagrams. Glue diagrams to flashcards. On the back write the following: 1. Phase of cell cycle 2. What is occurring in the diagram. ...
... Cut out the diagrams. Glue diagrams to flashcards. On the back write the following: 1. Phase of cell cycle 2. What is occurring in the diagram. ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).