contractile vacuoles
... The cell will gain water and grow larger. In plant cells, the central vacuoles will fill and the plant becomes stiff and rigid, the cell wall keeps the plant from bursting In animal cells, the cell may be in danger of bursting, organelles called CONTRACTILE VACUOLES will pump water out of the cell t ...
... The cell will gain water and grow larger. In plant cells, the central vacuoles will fill and the plant becomes stiff and rigid, the cell wall keeps the plant from bursting In animal cells, the cell may be in danger of bursting, organelles called CONTRACTILE VACUOLES will pump water out of the cell t ...
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... Animal Cells - Don’t have a cell wall - Contain centrioles - Contain many small vacuoles ...
... Animal Cells - Don’t have a cell wall - Contain centrioles - Contain many small vacuoles ...
Cell Biology Study Guide - Westerville City Schools
... Be able to relate the organelles and their functions to a city. Explain how each organelles interacts within the city. Explain four differences between a plant cell and an animal cell. Which scientist was most influential in the discovery of cells? (Hooke, Leuwenhoek) Support with 3 ideas. Which two ...
... Be able to relate the organelles and their functions to a city. Explain how each organelles interacts within the city. Explain four differences between a plant cell and an animal cell. Which scientist was most influential in the discovery of cells? (Hooke, Leuwenhoek) Support with 3 ideas. Which two ...
Functions of Cellular Organelles and Structures
... Each organelle functions like a department in a factory. The job of each organelle is to help in the production of protein. ...
... Each organelle functions like a department in a factory. The job of each organelle is to help in the production of protein. ...
Document
... *Know the pictures/diagrams for the cell and all its parts, including the parts that make up the cell membrane. 35. What is a cell? 36. What are the three parts of the cell theory? 37. What is an organelle? 38. What are the two types of cells? 39. How are prokaryotes different from eukaryotes? 40. W ...
... *Know the pictures/diagrams for the cell and all its parts, including the parts that make up the cell membrane. 35. What is a cell? 36. What are the three parts of the cell theory? 37. What is an organelle? 38. What are the two types of cells? 39. How are prokaryotes different from eukaryotes? 40. W ...
1. The drawing shows part of a root hair cell. (a) Use words from the
... Use words from the list to label the parts of the root hair cell. cell membrane ...
... Use words from the list to label the parts of the root hair cell. cell membrane ...
Science Lesson Plan
... 1. The students will read as and class or in pairs pages 26 and 27 in the text book. 2. Teacher will discuss. 3. We will, as a class, review the definition of cell unicellular and multi cellular and define the parts of the cell: cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuoles. (Notes) 4. Students wi ...
... 1. The students will read as and class or in pairs pages 26 and 27 in the text book. 2. Teacher will discuss. 3. We will, as a class, review the definition of cell unicellular and multi cellular and define the parts of the cell: cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuoles. (Notes) 4. Students wi ...
2015 cell notes
... – Living things are made of cells. (ex. – Living things maintain their internal environment. (ex. – Living things pass on their traits. (ex. – Living things perform chemical activities. This is known as metabolism. (ex. – Living things grow and develop. (ex. – Living things respond to a stimulus. (e ...
... – Living things are made of cells. (ex. – Living things maintain their internal environment. (ex. – Living things pass on their traits. (ex. – Living things perform chemical activities. This is known as metabolism. (ex. – Living things grow and develop. (ex. – Living things respond to a stimulus. (e ...
provide support and protection for the cell.
... Lipid Bi- layer • Water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide flow freely through the lipid bi-layer • Besides lipids the cell membrane also contains ...
... Lipid Bi- layer • Water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide flow freely through the lipid bi-layer • Besides lipids the cell membrane also contains ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... name _ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... name _ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ...
BRADIKYNIN AFFECTS THE INVASIVENESS OF MURINE
... development, is observed at all stages of tumor progression. The nonapeptide Bradykinin (BK) is modulated by proteases present in the tumor microenvironment and may be involved in tumor progression. BK participates as a primary mediator of tumor angiogenesis, and the involvement of this molecule in ...
... development, is observed at all stages of tumor progression. The nonapeptide Bradykinin (BK) is modulated by proteases present in the tumor microenvironment and may be involved in tumor progression. BK participates as a primary mediator of tumor angiogenesis, and the involvement of this molecule in ...
Life Science
... animal cells. These include the cell wall, a very large vacuole, and chloroplasts. You will notice these structures immediately when you look at plant cells under the microscope. Cell walls help a plant cell maintain its shape. The walls also help the plant keep its structure consistent. If the wind ...
... animal cells. These include the cell wall, a very large vacuole, and chloroplasts. You will notice these structures immediately when you look at plant cells under the microscope. Cell walls help a plant cell maintain its shape. The walls also help the plant keep its structure consistent. If the wind ...
Moving Cellular Material
... 6. What is only used in active transport? 7. How do substances move in active transport? 8. Which proteins are used in active and passive transport? 9. What does a cell do to a substance in endocytosis? 10. What does a cell use to eliminate a substance that is too large to leave by diffusion? 11. Wh ...
... 6. What is only used in active transport? 7. How do substances move in active transport? 8. Which proteins are used in active and passive transport? 9. What does a cell do to a substance in endocytosis? 10. What does a cell use to eliminate a substance that is too large to leave by diffusion? 11. Wh ...
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle A cell, whether it is one part of a larger
... the chromosome material, which contains all the information the cell needs (DNA). In order to divide it undergoes a process called MITOSIS, which is division of the nucleus. This is followed by division of the cytoplasm, which is called CYTOKINESIS. The entire process is best studied in stages, but ...
... the chromosome material, which contains all the information the cell needs (DNA). In order to divide it undergoes a process called MITOSIS, which is division of the nucleus. This is followed by division of the cytoplasm, which is called CYTOKINESIS. The entire process is best studied in stages, but ...
File
... organelles where cellular energy is produced, providing the energy needed to power chemical reactions. This process, known as cellular respiration, produces energy is in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Cells that use a lot of energy may have thousands of mitochondria. 6. Vacuoles are small ...
... organelles where cellular energy is produced, providing the energy needed to power chemical reactions. This process, known as cellular respiration, produces energy is in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Cells that use a lot of energy may have thousands of mitochondria. 6. Vacuoles are small ...
Cell Structure Notes - Center Grove Schools
... – For cells with cell walls – cell membrane is inside the cell wall – A cell membrane allows food and oxygen into the cell and waste out of the cell (semipermeable) ...
... – For cells with cell walls – cell membrane is inside the cell wall – A cell membrane allows food and oxygen into the cell and waste out of the cell (semipermeable) ...
Cell Structure and Function Exam
... O C. cell wall, plasma membrane, nucleus O D. cell wall, organelles, cytoplasm 15. Why are dyes used to stain cell specimens on a slide for viewing in a light microscope? O A. The dye keeps the cells fresh longer. O B. The dye helps the viewer see the structures inside the cell. O C. The dye helps h ...
... O C. cell wall, plasma membrane, nucleus O D. cell wall, organelles, cytoplasm 15. Why are dyes used to stain cell specimens on a slide for viewing in a light microscope? O A. The dye keeps the cells fresh longer. O B. The dye helps the viewer see the structures inside the cell. O C. The dye helps h ...
Extracellular matrix

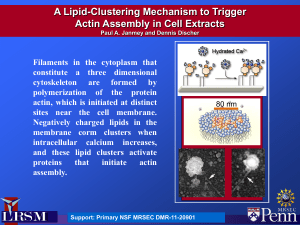
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).