Scientists not found in the book: Zacharias Janssen 1590: Janssen`s
... 2. Have dates clearly show and in chronological order 3. Include 5 pictures of the scientists or their contribution 4. BE NEAT & LEGIBLE!! With the final product posted in your spiral ...
... 2. Have dates clearly show and in chronological order 3. Include 5 pictures of the scientists or their contribution 4. BE NEAT & LEGIBLE!! With the final product posted in your spiral ...
Unit Details: Bio 1
... Summarize the structure and function of organelles in eukaryotic cells (including the nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes) and ways that these organelles interact with each other to perform the function of the cell. Bio.1.1.2 Compare prokaryotic a ...
... Summarize the structure and function of organelles in eukaryotic cells (including the nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes) and ways that these organelles interact with each other to perform the function of the cell. Bio.1.1.2 Compare prokaryotic a ...
to Study Guide for Test 1-Stephen Grant
... 9. Integral proteins - imbedded within cell, very difficult if not impossible to remove Transmembrane proteins - extends the entire tength of the membrane Peripheral proteins - loosely attached to the cell membrane on the inside or the outside Transport proteins - allow the movement of materials int ...
... 9. Integral proteins - imbedded within cell, very difficult if not impossible to remove Transmembrane proteins - extends the entire tength of the membrane Peripheral proteins - loosely attached to the cell membrane on the inside or the outside Transport proteins - allow the movement of materials int ...
Cells Alive Tutorial 08-09
... Objective: You will observe computer models of cells, learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and their components. Navigating the site: Cells alive has a navigation bar at the left. After accessing the page, click on CELL BIOLOGY on the left side navigation bar. From here, you will ac ...
... Objective: You will observe computer models of cells, learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and their components. Navigating the site: Cells alive has a navigation bar at the left. After accessing the page, click on CELL BIOLOGY on the left side navigation bar. From here, you will ac ...
2.3 Guided Notes
... starch (polysaccharide/polymer) Lipids Made mostly of C & H’s and are generally not soluble in water Examples are fats, oils, waxes, and steroids Functions: 1.) _____________________________________________________ 2.) _____________________________________________________ 3.) _______________________ ...
... starch (polysaccharide/polymer) Lipids Made mostly of C & H’s and are generally not soluble in water Examples are fats, oils, waxes, and steroids Functions: 1.) _____________________________________________________ 2.) _____________________________________________________ 3.) _______________________ ...
MICROSCOPE - Use the cards to help identify the parts of the
... of transport goes down the concentration gradient. Types includes diffusion (the movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration), osmosis (the movement of water from areas of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration), and facilitated diffusion (diffusion of ...
... of transport goes down the concentration gradient. Types includes diffusion (the movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration), osmosis (the movement of water from areas of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration), and facilitated diffusion (diffusion of ...
The Cell: The basic unit of life The Cell Theory states that: Cellular
... They help digest food particles __________________________________________________ the cell. They are instrumental in recycling _____________________________________________________. ...
... They help digest food particles __________________________________________________ the cell. They are instrumental in recycling _____________________________________________________. ...
Grade 10 Science: Biology Unit Test
... 5. __________________ stores a fluid called bile, which is secreted by the liver and it breaks down fat during digestion. a) spleen b) pancreas c) duodenum d) gall bladder 6. Which of the following is plant tissue? a) epithelial b) connective c) vascular ...
... 5. __________________ stores a fluid called bile, which is secreted by the liver and it breaks down fat during digestion. a) spleen b) pancreas c) duodenum d) gall bladder 6. Which of the following is plant tissue? a) epithelial b) connective c) vascular ...
Key Points on Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
... a. Must be made up of cells. i. Cells are the smallest unit of life. b. Must have different levels of organization. i. Atoms are organized into molecules that make up the cell. ii. Different types of cells are organized together to do different jobs. c. Must get and use energy. i. Living things take ...
... a. Must be made up of cells. i. Cells are the smallest unit of life. b. Must have different levels of organization. i. Atoms are organized into molecules that make up the cell. ii. Different types of cells are organized together to do different jobs. c. Must get and use energy. i. Living things take ...
mitosis
... require more DNA (to make the necessary proteins) than can be supported by a single nucleus. ...
... require more DNA (to make the necessary proteins) than can be supported by a single nucleus. ...
Cells
... All living organisms are made up of one or more cells and their products The cell is the simplest unit that carries out all life processes All cells come from other living cells (first cell ~ 4 billion years ago) ...
... All living organisms are made up of one or more cells and their products The cell is the simplest unit that carries out all life processes All cells come from other living cells (first cell ~ 4 billion years ago) ...
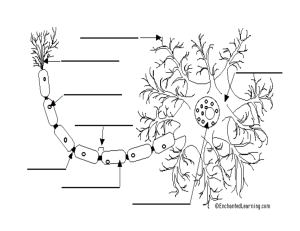
axon diagram
... myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers ...
... myelin sheath - the fatty substance that surrounds and protects some nerve fibers ...
Plant and Animal Cell Lab 1. List the 3 parts of the Cell Theory 2
... adjustment knob at this point) *You are looking for light colored blobs with dark spots in them. Perfect circles with black outlines are air bubbles. 3. Sketch the cell at low and high power. Label the nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane. Draw your cells to scale. ...
... adjustment knob at this point) *You are looking for light colored blobs with dark spots in them. Perfect circles with black outlines are air bubbles. 3. Sketch the cell at low and high power. Label the nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane. Draw your cells to scale. ...
CYTOLOGY STUDY GUIDE
... The scientist who said all plants are made of cells The scientist who viewed cork under a ...
... The scientist who said all plants are made of cells The scientist who viewed cork under a ...
File - Githens Jaguars
... to do the same job • Organ system – several similar organs doing the same job, like the circulatory system • Organism –multiple organ systems that work together, functioning to keep the organism alive *** Organelles - Tiny cell structures that are specialized parts of a cell that have specific funct ...
... to do the same job • Organ system – several similar organs doing the same job, like the circulatory system • Organism –multiple organ systems that work together, functioning to keep the organism alive *** Organelles - Tiny cell structures that are specialized parts of a cell that have specific funct ...
Cellular Transport
... Control of the Cell Cycle • The cell cycle is controlled by key enzymes that are produced at specific points in the cell cycle. • Cancer is caused by genetic & environmental factors that change the genes that control the cell cycle. ...
... Control of the Cell Cycle • The cell cycle is controlled by key enzymes that are produced at specific points in the cell cycle. • Cancer is caused by genetic & environmental factors that change the genes that control the cell cycle. ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).