Wednesday 10/23 -Get notebooks SMART START * on page 24
... ◦ Rounded in shape ◦ Do not contain chloroplasts, cell wall, large vacuole ◦ Found only in animals ...
... ◦ Rounded in shape ◦ Do not contain chloroplasts, cell wall, large vacuole ◦ Found only in animals ...
Cell Organelle Analogy: City Matching Cards Directions: Allow
... City Hall: Nucleus City Plans: Chromosomes City Border: Cell Wall City Entrance: Cell Membrane Community: Cytoplasm Power Plant: Mitochondria City Food Processing Plant: Chloroplast ...
... City Hall: Nucleus City Plans: Chromosomes City Border: Cell Wall City Entrance: Cell Membrane Community: Cytoplasm Power Plant: Mitochondria City Food Processing Plant: Chloroplast ...
Document
... Identify molecules in the membrane and how they contribute the characteristics of the membrane Describe hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions ...
... Identify molecules in the membrane and how they contribute the characteristics of the membrane Describe hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protists Produces a usable form of energy for the cell ...
... Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protists Produces a usable form of energy for the cell ...
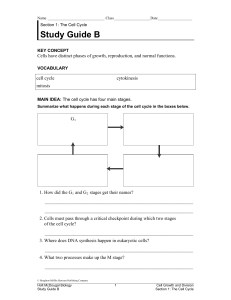
Study Guide B
... 5. Among different types of cells, which stage of the cell cycle varies most in length? _______________________________________________________________ 6. Why does a skin cell divide more often than a liver cell? _______________________________________________________________ 7. What is G 0 ? ______ ...
... 5. Among different types of cells, which stage of the cell cycle varies most in length? _______________________________________________________________ 6. Why does a skin cell divide more often than a liver cell? _______________________________________________________________ 7. What is G 0 ? ______ ...
Cell Book Notes Pgs. 1
... window screen that keeps bugs out, but lets air in.) Cytoplasm – The region inside the cell membrane where organelles are. It is a gel-like fluid. Some organelles can move within the cytoplasm. Cytoskeleton – strands or filaments made out of proteins that go through the cytoplasm. Helps to maintain ...
... window screen that keeps bugs out, but lets air in.) Cytoplasm – The region inside the cell membrane where organelles are. It is a gel-like fluid. Some organelles can move within the cytoplasm. Cytoskeleton – strands or filaments made out of proteins that go through the cytoplasm. Helps to maintain ...
BIOLOGY 2311 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I LECTURE 1
... Cytosol is actually more like a highly organized gelatinous mass with difference in composition and gelatinous consistency between various regions and states of the cells. ...
... Cytosol is actually more like a highly organized gelatinous mass with difference in composition and gelatinous consistency between various regions and states of the cells. ...
science words chapter 3
... ATP Adenosine TriPhosphate; molecule that provides energy for a cell’s activities ...
... ATP Adenosine TriPhosphate; molecule that provides energy for a cell’s activities ...
HW#17: Diffusion Loops
... damaged in this way? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ___________ ...
... damaged in this way? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ ___________ ...
PDF
... ubiquitin-related modifiers (SUMOs) regulates the activity and degradation of numerous proteins during various eukaryotic developmental processes. Now, Thomas Dresselhaus and colleagues describe the important role that a diSUMO-like protein called ZmDSUL plays in female gametophyte (embryo sac) deve ...
... ubiquitin-related modifiers (SUMOs) regulates the activity and degradation of numerous proteins during various eukaryotic developmental processes. Now, Thomas Dresselhaus and colleagues describe the important role that a diSUMO-like protein called ZmDSUL plays in female gametophyte (embryo sac) deve ...
cell cycle - user web page
... cytoplasm which is composed of the fluid and organelles of the cell. The contents of a cell are called the protoplasm. Cells are small compartments that hold all of the biological equipment necessary to keep an organism alive and successful on Earth. The nucleus is a membrane bound organelle that co ...
... cytoplasm which is composed of the fluid and organelles of the cell. The contents of a cell are called the protoplasm. Cells are small compartments that hold all of the biological equipment necessary to keep an organism alive and successful on Earth. The nucleus is a membrane bound organelle that co ...
Cell Organelles - Mayfield City Schools
... • The Golgi will release these proteins in vesicles: sort of like a sac, which will protect the protein(s). An example are lysosomes, which are produced by Rough ER /Golgi activity. These sacs (lysosomes), are often considered a type of cell organelle, and they contain enzymes, which digest and brea ...
... • The Golgi will release these proteins in vesicles: sort of like a sac, which will protect the protein(s). An example are lysosomes, which are produced by Rough ER /Golgi activity. These sacs (lysosomes), are often considered a type of cell organelle, and they contain enzymes, which digest and brea ...
Cellular Growth - Biology-RHS
... If the cell becomes to large, it becomes almost impossible for cellular communications, many of which involve movement of substances and signals to various organelles For example: signals that trigger protein synthesis might not reach the ribosome fast enough for protein synthesis to occur ...
... If the cell becomes to large, it becomes almost impossible for cellular communications, many of which involve movement of substances and signals to various organelles For example: signals that trigger protein synthesis might not reach the ribosome fast enough for protein synthesis to occur ...
Levels of Organization
... • Cells take in food and get rid of wastes • They use materials in food to grow and repair wounds • Cells sense and respond to changes in their surroundings • They communicate and work with other cells ...
... • Cells take in food and get rid of wastes • They use materials in food to grow and repair wounds • Cells sense and respond to changes in their surroundings • They communicate and work with other cells ...
cell
... A) Cells are the basic units of life. Every cell has got a cell membrane, organelles and cytoplasm. ...
... A) Cells are the basic units of life. Every cell has got a cell membrane, organelles and cytoplasm. ...
The eucaryotic cell
... Present-day living cells are classified as procaryotic (bacteria and their close relatives) or eucaryotic. Although they have a relatively simple structure, procaryotic cells are biochemically versatile and diverse - for example, all of the major metabolic pathways can be found in bacteria, includin ...
... Present-day living cells are classified as procaryotic (bacteria and their close relatives) or eucaryotic. Although they have a relatively simple structure, procaryotic cells are biochemically versatile and diverse - for example, all of the major metabolic pathways can be found in bacteria, includin ...
• dendrite - Dental Decks
... Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells: 1. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses. 2. Neuroglial cells (glial cells) - are non-conducting “support cells” of nervous tissue. Structure of a neuron: • Cell body (perikaryon) - contains the nucleus and most of the cytoplasm. Located mostly in the ce ...
... Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells: 1. Neurons - transmit nerve impulses. 2. Neuroglial cells (glial cells) - are non-conducting “support cells” of nervous tissue. Structure of a neuron: • Cell body (perikaryon) - contains the nucleus and most of the cytoplasm. Located mostly in the ce ...
Lecture 4: A Seperate Self: The Cell
... • Humans have 46 DNA molecules per cell • Some organisms have more, some fewer – One strand of each gene is copied into an RNA molecule, which exits the nucleus (through nuclear pores in the nuclear envelope) and travels to where proteins are made, the cytoplasm. • Average size of a gene in bacteria ...
... • Humans have 46 DNA molecules per cell • Some organisms have more, some fewer – One strand of each gene is copied into an RNA molecule, which exits the nucleus (through nuclear pores in the nuclear envelope) and travels to where proteins are made, the cytoplasm. • Average size of a gene in bacteria ...
Plant and Animal Cell Parts
... Plant cells are characterized by a thick _____________ and small bodies within the cytoplasm called _________________, which give the green colour to the plants. These tiny structures are the primary food factory for all living things on Earth. ______________________ within the chloroplast is also r ...
... Plant cells are characterized by a thick _____________ and small bodies within the cytoplasm called _________________, which give the green colour to the plants. These tiny structures are the primary food factory for all living things on Earth. ______________________ within the chloroplast is also r ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).