LAB – HOW DO ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS DIFFER
... 2. Using a dropper put two drops of yeast cells into the iodine stain. 3. Cover the slide with a coverslip. 4. Use a microscope: Look at the yeast cells under low power, then under high power. 5. Locate the cytoplasm, cell membrane, nucleus, and cell wall. Fill in the table by putting a check mark i ...
... 2. Using a dropper put two drops of yeast cells into the iodine stain. 3. Cover the slide with a coverslip. 4. Use a microscope: Look at the yeast cells under low power, then under high power. 5. Locate the cytoplasm, cell membrane, nucleus, and cell wall. Fill in the table by putting a check mark i ...
Vocabulary Inventory
... outside of the cell. A cell wall helps to protect the cell from damage. It also helps to hold the shape of a cell. Animal cells do not have cell walls. Plant cells also have structures that help them make their own food using sunlight. These structures are called chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are what ...
... outside of the cell. A cell wall helps to protect the cell from damage. It also helps to hold the shape of a cell. Animal cells do not have cell walls. Plant cells also have structures that help them make their own food using sunlight. These structures are called chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are what ...
Ultrastructural 3D investigations of cells and cell organelles
... reconstruction method allows the visualization of a cell volume of about 3000µm3 enabling investigations of the 3D integrity of several organelles, including for instance chloroplasts with volumes of about 30-40µm3, or even complete small cells like yeast cells. Therefore this method is advantageous ...
... reconstruction method allows the visualization of a cell volume of about 3000µm3 enabling investigations of the 3D integrity of several organelles, including for instance chloroplasts with volumes of about 30-40µm3, or even complete small cells like yeast cells. Therefore this method is advantageous ...
Cell Analogy Project : DUE___________________ Introduction
... Cells need to carry on the same basic functions as we do to sustain life; the difference is cells do this with much smaller parts. These smaller structures that allow the cell to function are called organelles – “tiny organs.” Also plant and animal cells have some similar parts and some parts that a ...
... Cells need to carry on the same basic functions as we do to sustain life; the difference is cells do this with much smaller parts. These smaller structures that allow the cell to function are called organelles – “tiny organs.” Also plant and animal cells have some similar parts and some parts that a ...
1. Define: Prokaryotic Cells without a nucleus. Very primitive
... Eukaryotic Cells with a nucleus. 2. List the 3 parts to the cell theory. a. All living things are composed of cells b. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things c. All new cells come from pre-existing cells ...
... Eukaryotic Cells with a nucleus. 2. List the 3 parts to the cell theory. a. All living things are composed of cells b. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things c. All new cells come from pre-existing cells ...
Calcium Signaling - Georgia Institute of Technology
... Satellite Cells • Define the myonuclear domain • Describe the satellite cell niche • Describe the signaling networks controlling SC proliferation and fusion – HGF, FGF, myostatin – MRFs, pax ...
... Satellite Cells • Define the myonuclear domain • Describe the satellite cell niche • Describe the signaling networks controlling SC proliferation and fusion – HGF, FGF, myostatin – MRFs, pax ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Network of protein structures that extend throughout the cytoplasm Provides the cell with an internal framework ...
... Network of protein structures that extend throughout the cytoplasm Provides the cell with an internal framework ...
HERE - Gallopade International
... 3) “I am the packaging center. I box up proteins and put ions in storage. As the endoplasmic reticulum, I have two different parts— rough and smooth. My rough parts are responsible for packaging proteins. The ribosomes on my sides make me rough. My smooth parts are the smooth tubes that store spare ...
... 3) “I am the packaging center. I box up proteins and put ions in storage. As the endoplasmic reticulum, I have two different parts— rough and smooth. My rough parts are responsible for packaging proteins. The ribosomes on my sides make me rough. My smooth parts are the smooth tubes that store spare ...
All About Cells - Bluford Grade School
... Who Discovered the Cell? Unfortunately, it was not Mrs. Putt or Mrs. Scarbrough. Robert Hooke is credited for first observing the cell by using a microscope. This was back in 1665. ...
... Who Discovered the Cell? Unfortunately, it was not Mrs. Putt or Mrs. Scarbrough. Robert Hooke is credited for first observing the cell by using a microscope. This was back in 1665. ...
Document
... Cartilage: A versatile connective tissue that supports body structures. It is avascular and possesses no lymph vessels or nerves. Bone: Bone is a type of connective tissue that has a supportive and protective function; and also serves as a reservoir for calcium and phosphate. ...
... Cartilage: A versatile connective tissue that supports body structures. It is avascular and possesses no lymph vessels or nerves. Bone: Bone is a type of connective tissue that has a supportive and protective function; and also serves as a reservoir for calcium and phosphate. ...
Course outline cell biology 2016 2017 (2) modified (1)
... topics such as endocytosis, intramembrane transport, protein targeting, organelle biosynthesis, protein sorting, exocytosis, cell shape, motility, and cell-to-cell interaction. In addition, lectures will deal with signal transduction processes, cell cycle, mitosis, cancer and cellular functions that ...
... topics such as endocytosis, intramembrane transport, protein targeting, organelle biosynthesis, protein sorting, exocytosis, cell shape, motility, and cell-to-cell interaction. In addition, lectures will deal with signal transduction processes, cell cycle, mitosis, cancer and cellular functions that ...
Unit 4 Cell Transport Notes Packet - Dallastown Area School District
... Unit 4 = Cell Transport Honors Biology ...
... Unit 4 = Cell Transport Honors Biology ...
CELL MEMBRANES
... specific molecules to pass freely. molecules move in and out more quickly than they could through regular diffusion and is known as facilitated diffusion. ...
... specific molecules to pass freely. molecules move in and out more quickly than they could through regular diffusion and is known as facilitated diffusion. ...
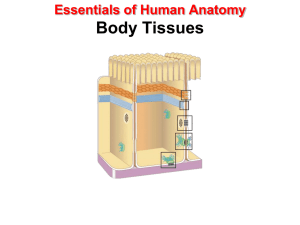
Essentials of Human Anatomy
... – Duct secretes materials onto the surface of the skin or onto an epithelial surface lining an internal passageway. ...
... – Duct secretes materials onto the surface of the skin or onto an epithelial surface lining an internal passageway. ...
Bio07_TR_U03_CH07.QXD
... and protein found throughout the cytoplasm. Proteins are assembled on ribosomes. Eukaryotic cells contain an internal membrane system known as the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER. The ER is where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled, along with proteins and other materials that are expor ...
... and protein found throughout the cytoplasm. Proteins are assembled on ribosomes. Eukaryotic cells contain an internal membrane system known as the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER. The ER is where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled, along with proteins and other materials that are expor ...
CellStructureSE-1_2016Gizmo
... Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are some of the structures inside a cell that help it to live and perform its role in an organism? ________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are some of the structures inside a cell that help it to live and perform its role in an organism? ________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
Membranes - Continuing Education Gateway
... for making a slide, "a lacy network of fibers was revealed." These fibers look similar to girders that hold up a bridge, so it was hypothesized that they would do the same for the cell, hold its shape. These fibers can be broken down into three main groups: Microfilaments, microtubules, and intermed ...
... for making a slide, "a lacy network of fibers was revealed." These fibers look similar to girders that hold up a bridge, so it was hypothesized that they would do the same for the cell, hold its shape. These fibers can be broken down into three main groups: Microfilaments, microtubules, and intermed ...
Cell - Fair Lawn Schools
... and acts a barrier. The cell membrane controls what enters and exits the cell. ...
... and acts a barrier. The cell membrane controls what enters and exits the cell. ...
Quiz5ch5new.doc
... (e.g., ions) between cells through small passageways that directly link the cytoplasm of one cell to the cytoplasm of another cell d. None of these are correct. ...
... (e.g., ions) between cells through small passageways that directly link the cytoplasm of one cell to the cytoplasm of another cell d. None of these are correct. ...
NAME DATE ______ PERIOD _____
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle all that are TRUE. There may be MORE THAN ONE correct answer. 1. Which of the following is TRUE of a cell membranes? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more lik ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle all that are TRUE. There may be MORE THAN ONE correct answer. 1. Which of the following is TRUE of a cell membranes? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more lik ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).