Cell Part Functions
... A cell sac. In plants they are large and may make up most of the cell’s volume. In animals they are smaller. Strands of DNA in the nucleus ...
... A cell sac. In plants they are large and may make up most of the cell’s volume. In animals they are smaller. Strands of DNA in the nucleus ...
Name - SimplyBio
... structure and function in living things, all cells come from preexisting cells 3. What happens in endocytosis? Materials are taken into the cell by infoldings of the cell membrane, requires energy! 4. Which type of organism encloses their DNA in a nucleus? eukaryotic 5. What is diffusion? Movement o ...
... structure and function in living things, all cells come from preexisting cells 3. What happens in endocytosis? Materials are taken into the cell by infoldings of the cell membrane, requires energy! 4. Which type of organism encloses their DNA in a nucleus? eukaryotic 5. What is diffusion? Movement o ...
Stem Cells
... Embryonic stem cells – research shows can form into any cell type in human body Adult stem cells – “pools” to replenish damaged/dead cells * Are multipotent typically develop into cells from the type of tissue they originated * Ex. Bone marrow transplants = stem cell transplants for blood ...
... Embryonic stem cells – research shows can form into any cell type in human body Adult stem cells – “pools” to replenish damaged/dead cells * Are multipotent typically develop into cells from the type of tissue they originated * Ex. Bone marrow transplants = stem cell transplants for blood ...
Plant Cells
... The golgi apparatus makes chemicals smaller to work better and stores chemicals. ...
... The golgi apparatus makes chemicals smaller to work better and stores chemicals. ...
Duration: …………….. First Periodical exam (15 marks)
... ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------12- Lysozyme is digestive enzyme that occurs naturally in tears and saliva ( T ). --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13- Lipid A is the l ...
... ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------12- Lysozyme is digestive enzyme that occurs naturally in tears and saliva ( T ). --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------13- Lipid A is the l ...
Why dread a bump on the head? October 2014 Lesson 5: What
... 4. The whole cell breaks apart into circular components called apoptotic bodies. These apoptotic bodies are enclosed inside cellular membrane. 5. During the final stages of apoptosis, the dying cell displays a molecule on its surface that marks the cell for removal. This signal molecule is detected ...
... 4. The whole cell breaks apart into circular components called apoptotic bodies. These apoptotic bodies are enclosed inside cellular membrane. 5. During the final stages of apoptosis, the dying cell displays a molecule on its surface that marks the cell for removal. This signal molecule is detected ...
Cell Parts - Humble ISD
... Protects the cell Outer membrane of cell that controls movement in and out of the cell ...
... Protects the cell Outer membrane of cell that controls movement in and out of the cell ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: The Difference between
... control center separating the genetic material, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), from the rest of the cell. ...
... control center separating the genetic material, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), from the rest of the cell. ...
Cell Division and Reproduction
... When ___________ grow to a certain ___________ they must either __________ or __________. If a cell continued to __________ without ____________, the surface __________ of the ___________ would become too _________ to hold the cell’s ___________. Cell Division Cell _____________ is a complex s ...
... When ___________ grow to a certain ___________ they must either __________ or __________. If a cell continued to __________ without ____________, the surface __________ of the ___________ would become too _________ to hold the cell’s ___________. Cell Division Cell _____________ is a complex s ...
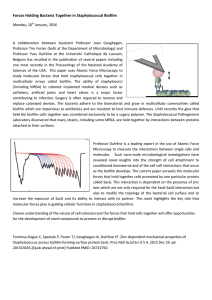
Forces Holding Bacteria Together in Staphylococcal Biofilm
... revealed novel insights into the strength of cell attachment to conditioned biomaterial and of the cell-cell interactions that occur as the biofilm develops. The current paper unravels the molecular forces that hold together cells promoted by one particular protein called SasG. This interaction is d ...
... revealed novel insights into the strength of cell attachment to conditioned biomaterial and of the cell-cell interactions that occur as the biofilm develops. The current paper unravels the molecular forces that hold together cells promoted by one particular protein called SasG. This interaction is d ...
Unit Study Guide
... m. large central vacuole (plants) d. cell membrane i. Golgi body n. chloroplast e. mitochondria j. vesicle o. cell wall p. cytoplasm Explain the relationship between the ribosome, ER, Golgi body, vesicles, and mitochondria. What are three major differences between plant and animal cells? What is the ...
... m. large central vacuole (plants) d. cell membrane i. Golgi body n. chloroplast e. mitochondria j. vesicle o. cell wall p. cytoplasm Explain the relationship between the ribosome, ER, Golgi body, vesicles, and mitochondria. What are three major differences between plant and animal cells? What is the ...
Ch 6 Slides - people.iup.edu
... • Intermediate filaments range in diameter from 8–12 nanometers, larger than microfilaments but smaller than microtubules • They support cell shape and fix organelles in place • Intermediate filaments are more permanent cytoskeleton fixtures than the other two classes they do not assemble and disass ...
... • Intermediate filaments range in diameter from 8–12 nanometers, larger than microfilaments but smaller than microtubules • They support cell shape and fix organelles in place • Intermediate filaments are more permanent cytoskeleton fixtures than the other two classes they do not assemble and disass ...
Name: Block: Cell Structure Lab Answer Sheet A. Cork Cells 1. What
... Important Directions for Drawings: 1. Make all drawings in the highest magnification possible. 2. For each specimen, you do not need to fill the circle (field of view) with cells. Just draw several cells for each. 3. These several cells must be clear drawings. Take your time and draw what you see. S ...
... Important Directions for Drawings: 1. Make all drawings in the highest magnification possible. 2. For each specimen, you do not need to fill the circle (field of view) with cells. Just draw several cells for each. 3. These several cells must be clear drawings. Take your time and draw what you see. S ...
Nucleoid region Prokaryotic cell Nucleus
... C. [As cells grow, it becomes more difficult for diffusion to take place because the surface area does not grow proportionately] D. [A and C are true] E. [B and C are true] ...
... C. [As cells grow, it becomes more difficult for diffusion to take place because the surface area does not grow proportionately] D. [A and C are true] E. [B and C are true] ...
SR 50(12) 18-19
... neurotransmitters, cytokines and enzymes that have to be delivered to other places inside the cell, or exported out of the cell, at the right moment. Miniature bubblelike vesicles, surrounded by membranes, shuttle the cargo between organelles or fuse with the outer membrane of the cell and release t ...
... neurotransmitters, cytokines and enzymes that have to be delivered to other places inside the cell, or exported out of the cell, at the right moment. Miniature bubblelike vesicles, surrounded by membranes, shuttle the cargo between organelles or fuse with the outer membrane of the cell and release t ...
Supplementary Materials and Methods Transfection and expression
... Splenocytes were added to a 96-well plate (1x105/well) and were stimulated with pooled HPV16 E6/E7 pooled peptide for 5-6 hours at 37C/5% CO2 in the presence of Protein Transport Inhibitor Cocktail (Brefeldin A and Monensin) (eBioscience) according to the manufacturers instructions. The Cell Stimula ...
... Splenocytes were added to a 96-well plate (1x105/well) and were stimulated with pooled HPV16 E6/E7 pooled peptide for 5-6 hours at 37C/5% CO2 in the presence of Protein Transport Inhibitor Cocktail (Brefeldin A and Monensin) (eBioscience) according to the manufacturers instructions. The Cell Stimula ...
The Extracellular Matrix
... **Review: A Aszodi, KR Legate, I Nakchbandi, and R. Fassler: What mouse mutants teach us about extracellular matrix function. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 22:591-621, 2006. **Review: JF Bateman, RP Boot-Handford, SR Lamandé: Genetic diseases of connective tissues: cellular and extracellular effets of ...
... **Review: A Aszodi, KR Legate, I Nakchbandi, and R. Fassler: What mouse mutants teach us about extracellular matrix function. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 22:591-621, 2006. **Review: JF Bateman, RP Boot-Handford, SR Lamandé: Genetic diseases of connective tissues: cellular and extracellular effets of ...
Cell-jeopardy-26
... This is the organelle that keeps the cell together and allows the “good stuff” in and keeps the “bad stuff” out. ...
... This is the organelle that keeps the cell together and allows the “good stuff” in and keeps the “bad stuff” out. ...
Details - Nile College
... reception, transduction, & response Be familiar with the dynamic nature and activities of the cell membranes, and their contribution to homeostasis and the diversified specific cell functions. The dynamic architecture of the plasmalemma, selective permeability, diffusion, osmosis, endocytosis, exocy ...
... reception, transduction, & response Be familiar with the dynamic nature and activities of the cell membranes, and their contribution to homeostasis and the diversified specific cell functions. The dynamic architecture of the plasmalemma, selective permeability, diffusion, osmosis, endocytosis, exocy ...
Notes
... • The cell is the basic unit of organization of organisms. (basic unit of life) – cells—tissues—organs—systems—organism ...
... • The cell is the basic unit of organization of organisms. (basic unit of life) – cells—tissues—organs—systems—organism ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).