week 4-5 inflammation
... Though it is protective in nature it may cause considerable harm to the body as well ...
... Though it is protective in nature it may cause considerable harm to the body as well ...
Cell Communication
... modify and manipulate biological systems and physiology. An understanding of the endocrine system, for example, allowed the development of birth control methods, as well as medicines that control depression, blood pressure and metabolism. Question: Should research continue that allows humans to mo ...
... modify and manipulate biological systems and physiology. An understanding of the endocrine system, for example, allowed the development of birth control methods, as well as medicines that control depression, blood pressure and metabolism. Question: Should research continue that allows humans to mo ...
Chapter 4: The Characteristics of Prokaryotic and
... Endosymbiotic Theory Organelles of eukaryotic cells may have arose from ...
... Endosymbiotic Theory Organelles of eukaryotic cells may have arose from ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... so that blood does not leak out between the cells as the heart pumps. The pressure of pumping would blow apart adjacent cells were they not held tightly together by a second specialized connection. Furthermore, coordinated pumping activity of these cells relies on a third specialization between thes ...
... so that blood does not leak out between the cells as the heart pumps. The pressure of pumping would blow apart adjacent cells were they not held tightly together by a second specialized connection. Furthermore, coordinated pumping activity of these cells relies on a third specialization between thes ...
Document
... high concentration to an area of lower concentration, speeded by large openings in the cell membrane ...
... high concentration to an area of lower concentration, speeded by large openings in the cell membrane ...
Microscope renaissance
... At the same time, other scientists are working on new cellular imaging techniques that can work on living tissue but don't depend on any of the fluorescent proteins. This is an important advantage because it means the scientist can see a completely natural system and potentially look at people. Harv ...
... At the same time, other scientists are working on new cellular imaging techniques that can work on living tissue but don't depend on any of the fluorescent proteins. This is an important advantage because it means the scientist can see a completely natural system and potentially look at people. Harv ...
Challenges to an obligate intracellular parasite
... • Ability to return to vegetative state for many in same or different cell (different disease - VZV) • Presence shown by PCR or probes ...
... • Ability to return to vegetative state for many in same or different cell (different disease - VZV) • Presence shown by PCR or probes ...
osmolarity regulates gene expression in intervertebral disc cells
... hypo-osmotic shock induces changes in cell volume that are regulated by the breakdown and reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton [5,6]. Thus, the observed modification of gene expression for cytoskeletalmediated signaling molecules following hypo-osmotic shock is consistent with the idea that cyto ...
... hypo-osmotic shock induces changes in cell volume that are regulated by the breakdown and reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton [5,6]. Thus, the observed modification of gene expression for cytoskeletalmediated signaling molecules following hypo-osmotic shock is consistent with the idea that cyto ...
HB Cell Structure
... Energy is used to form ATP molecules which is used for protein synthesis and transport ATP-molecule is able to store and transport energy for short periods of time ...
... Energy is used to form ATP molecules which is used for protein synthesis and transport ATP-molecule is able to store and transport energy for short periods of time ...
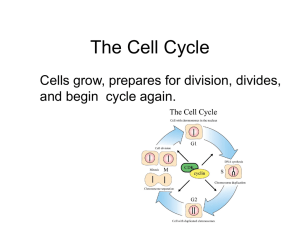
The Cell Cycle
... ◦ Messages from the nucleus take too long to travel to all cell parts ◦ Larger cells have less surface area (SA) than multiple cells of equal volume. Therefore, the larger cells cannot obtain enough nutrients from the surrounding environment ...
... ◦ Messages from the nucleus take too long to travel to all cell parts ◦ Larger cells have less surface area (SA) than multiple cells of equal volume. Therefore, the larger cells cannot obtain enough nutrients from the surrounding environment ...
Stages of the cell cycle
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
Using Microscopes
... Revolving nose piece Objective lens 4x (low); 10x (medium); 40x (high) Stage Stage clips Carrying arm Mirror or light source (lamp) Base PURPOSE To give them the experience of using a microscope and to further the students understanding of cells. ...
... Revolving nose piece Objective lens 4x (low); 10x (medium); 40x (high) Stage Stage clips Carrying arm Mirror or light source (lamp) Base PURPOSE To give them the experience of using a microscope and to further the students understanding of cells. ...
File
... Made up of channels that transport material made in the cell from one place to another ...
... Made up of channels that transport material made in the cell from one place to another ...
L.14.3 Cell Structure and Function Module
... the structures found in prokaryotic cells and in eukaryotic cells. How to compare and/or contrast the structures found in plant cells and in animal cells. Explain the role of the cell membrane during active and ...
... the structures found in prokaryotic cells and in eukaryotic cells. How to compare and/or contrast the structures found in plant cells and in animal cells. Explain the role of the cell membrane during active and ...
The World of Cells
... • The nucleus is the cells brain and it holds the hereditary material called chromosomes and directs most of the cell’s activity – Chromosomes contain DNA. This determines which traits and organism will receive • Example: the color of your eyes ...
... • The nucleus is the cells brain and it holds the hereditary material called chromosomes and directs most of the cell’s activity – Chromosomes contain DNA. This determines which traits and organism will receive • Example: the color of your eyes ...
cell
... around, plants need cell structures that help them to conserve water and make their own food. Animals don’t need these structures. Animal cells have to be more flexible to allow the animals to move around. ...
... around, plants need cell structures that help them to conserve water and make their own food. Animals don’t need these structures. Animal cells have to be more flexible to allow the animals to move around. ...
Chapter 13 – Review
... Prokaryotes have very simple internal structures, lacking a membrane-bound nucleus and other membrane-bound compartments, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts. The plasma membrane of prokaryotes is encased in a cell wall. The cell wall of bacteria is made of peptidoglycan, and the cell wall of arch ...
... Prokaryotes have very simple internal structures, lacking a membrane-bound nucleus and other membrane-bound compartments, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts. The plasma membrane of prokaryotes is encased in a cell wall. The cell wall of bacteria is made of peptidoglycan, and the cell wall of arch ...
Unit 1- Cells Test Review
... a. mitosis - asexual reproduction where non reproductive cells divide and create 2 daughter cells with identical material as the parent cell b. meiosis - sexual reproduction where gametes (sperm and eggs) divide and create 4 daughter cells with half the material as the parent cell c. osmosis - the m ...
... a. mitosis - asexual reproduction where non reproductive cells divide and create 2 daughter cells with identical material as the parent cell b. meiosis - sexual reproduction where gametes (sperm and eggs) divide and create 4 daughter cells with half the material as the parent cell c. osmosis - the m ...
Cell study guide
... The Rough ER is where most protein synthesis occurs in the cell. The secretory proteins grow from the attached ribosome and goes into the lumen of the Rough ER, where it is folded (naturally) and has carbohydrates attach to them. Insulin is an example of this. Other synthesized proteins (some that a ...
... The Rough ER is where most protein synthesis occurs in the cell. The secretory proteins grow from the attached ribosome and goes into the lumen of the Rough ER, where it is folded (naturally) and has carbohydrates attach to them. Insulin is an example of this. Other synthesized proteins (some that a ...
MITOSIS
... • Mitosis: the nuclear division of a cell • Cytokinesis- produces two identical daughter cells. • Recognizable phases of mitosis: ...
... • Mitosis: the nuclear division of a cell • Cytokinesis- produces two identical daughter cells. • Recognizable phases of mitosis: ...
ch 3 directed_reading_b
... 2.Robert Hooke was the first person to describe______________________. 3. Hooke built a(n) ______________________ and used it to look at cells. 4. Hooke spent most of his time looking at the cells of ______________________. 5. Hooke’s microscope could not see the cells of ______________________. Fin ...
... 2.Robert Hooke was the first person to describe______________________. 3. Hooke built a(n) ______________________ and used it to look at cells. 4. Hooke spent most of his time looking at the cells of ______________________. 5. Hooke’s microscope could not see the cells of ______________________. Fin ...
Unit 1- Cells Test Review
... a. mitosis - asexual reproduction where non reproductive cells divide and create 2 daughter cells with identical material as the parent cell b. meiosis - sexual reproduction where gametes (sperm and eggs) divide and create 4 daughter cells with half the material as the parent cell c. osmosis - the m ...
... a. mitosis - asexual reproduction where non reproductive cells divide and create 2 daughter cells with identical material as the parent cell b. meiosis - sexual reproduction where gametes (sperm and eggs) divide and create 4 daughter cells with half the material as the parent cell c. osmosis - the m ...
Ch 6 A Tour of the Cell
... Cell Surfaces and Junctions Cell walls prokaryotes, fungi, some protists protects cell, maintains shape, prevents lots of water from coming into cell support against gravity composition changes depending on species ...
... Cell Surfaces and Junctions Cell walls prokaryotes, fungi, some protists protects cell, maintains shape, prevents lots of water from coming into cell support against gravity composition changes depending on species ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).