CHAPTER 7 A TOUR OF THE CELL
... 1. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in size and complexity • All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. (What is this made of?) • The “liquid” inside the membrane is the cytosol, which contains the organelles. • All cells contain chromosomes which have genes in the form of DNA. • All cel ...
... 1. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in size and complexity • All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. (What is this made of?) • The “liquid” inside the membrane is the cytosol, which contains the organelles. • All cells contain chromosomes which have genes in the form of DNA. • All cel ...
Pretest
... 12. The cell wall helps to protect and support the cell in plants and some other organisms. 13. An element is any substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances. A compound is made up of two or more elements. 14. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions in living things. Without enzymes, ma ...
... 12. The cell wall helps to protect and support the cell in plants and some other organisms. 13. An element is any substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances. A compound is made up of two or more elements. 14. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions in living things. Without enzymes, ma ...
1
... cells together in tissues and protects and supports the plasma membrane. The main components of the ECM are glycoproteins (proteins bonded with carbohydrates). The most abundant glycoprotein is collagen, which forms strong fibers outside the cell. The ECM may attach to the cell through other glycopr ...
... cells together in tissues and protects and supports the plasma membrane. The main components of the ECM are glycoproteins (proteins bonded with carbohydrates). The most abundant glycoprotein is collagen, which forms strong fibers outside the cell. The ECM may attach to the cell through other glycopr ...
Lab - TeacherWeb
... ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ...
... ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ...
Cell Structure and Function The cell is the smallest unit of life that
... to break down large molecules of carbs, proteins, lipids, and old organelles no longer useful. ...
... to break down large molecules of carbs, proteins, lipids, and old organelles no longer useful. ...
Biology Notes: Mitosis
... 1) _______________________________________ 2) _______________________________________ 3) _______________________________________ 4) _______________________________________ 5) _______________________________________ 2) During which interphase stage do organelles replicate? ______________________ ...
... 1) _______________________________________ 2) _______________________________________ 3) _______________________________________ 4) _______________________________________ 5) _______________________________________ 2) During which interphase stage do organelles replicate? ______________________ ...
types of cells and their size
... 1. You should know the functional parts of a microscope, how to determine the magnification, how to focus a microscope, and estimate the size of cells under low, medium, and high power. You should also be familiar with the major cellular characteristics that allow people to distinguish between plant ...
... 1. You should know the functional parts of a microscope, how to determine the magnification, how to focus a microscope, and estimate the size of cells under low, medium, and high power. You should also be familiar with the major cellular characteristics that allow people to distinguish between plant ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Biology Notes: Mitosis Directions: Fill in
... 1) _______________________________________ 2) _______________________________________ 3) _______________________________________ 4) _______________________________________ 5) _______________________________________ 2) During which interphase stage do organelles replicate? ___________________________ ...
... 1) _______________________________________ 2) _______________________________________ 3) _______________________________________ 4) _______________________________________ 5) _______________________________________ 2) During which interphase stage do organelles replicate? ___________________________ ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... Organisms that cannot make their own food and must obtain energy from the foods they eat are called ________ What are the three parts of an ATP molecule? When is energy is released from ATP? Photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into _______________ n the overall equation ...
... Organisms that cannot make their own food and must obtain energy from the foods they eat are called ________ What are the three parts of an ATP molecule? When is energy is released from ATP? Photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into _______________ n the overall equation ...
Worksheet
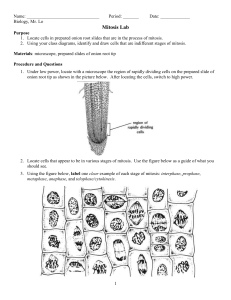
... 2. Locate cells that appear to be in various stages of mitosis. Use the figure below as a guide of what you should see. 3. Using the figure below, label one clear example of each stage of mitosis: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase/cytokinesis. ...
... 2. Locate cells that appear to be in various stages of mitosis. Use the figure below as a guide of what you should see. 3. Using the figure below, label one clear example of each stage of mitosis: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase/cytokinesis. ...
Fertilization, cell proliferation and differentiation
... • Mesoderm -> support tissues, e.g. skeleton, muscle, connective tissues, blood, urogential system • Ectoderm - > epidermis, nervous system ...
... • Mesoderm -> support tissues, e.g. skeleton, muscle, connective tissues, blood, urogential system • Ectoderm - > epidermis, nervous system ...
Lab Quiz 4 Study Guide Know the Domain, Kingdom and cellular
... membrane, cytoplasm (fluid part called cytosol), nucleus, contractile vacuole, and food vacuoles; the cytoplasm is the outer and gelatinous ectoplasm and the inner, more fluid endoplasm. iii. Pseudopods: false-feet; temporary cytoplasmic extrusions that are used for eating (via phagocytosis) and mov ...
... membrane, cytoplasm (fluid part called cytosol), nucleus, contractile vacuole, and food vacuoles; the cytoplasm is the outer and gelatinous ectoplasm and the inner, more fluid endoplasm. iii. Pseudopods: false-feet; temporary cytoplasmic extrusions that are used for eating (via phagocytosis) and mov ...
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
... have been duplicated, the cell enters another shorter growth period in which mitochondria and ...
... have been duplicated, the cell enters another shorter growth period in which mitochondria and ...
Cells - Science A 2 Z
... proteins; smooth ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newly-made proteins and lipids to the Golgi body, lysosomes, and membranes. ...
... proteins; smooth ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newly-made proteins and lipids to the Golgi body, lysosomes, and membranes. ...
Cell Cycle and Mitosis - Willimon-PHS
... have been duplicated, the cell enters another shorter growth period in which mitochondria and ...
... have been duplicated, the cell enters another shorter growth period in which mitochondria and ...
Cell Biology - Land of Mayo
... is selective about what goes in or comes out They are found around all animal and plant cells It is composed of a lipid bilayer * with numerous proteins ...
... is selective about what goes in or comes out They are found around all animal and plant cells It is composed of a lipid bilayer * with numerous proteins ...
cells webquest
... You did not You described most You described all describe most of of the necessary the necessary the necessary structures and structures and structures and functions correctly functions functions correctly and they are almost correctly and and completely, and complete. You completely and you did not ...
... You did not You described most You described all describe most of of the necessary the necessary the necessary structures and structures and structures and functions correctly functions functions correctly and they are almost correctly and and completely, and complete. You completely and you did not ...
31.3 Immune Responses
... • Nonspecific responses are those that are the same everytime. • In inflammation, blood vessels become leaky. capillary wall – white blood cells move extracellular space toward infection and damaged tissue – characterized by swelling, redness, and pain Another Example: Fever ...
... • Nonspecific responses are those that are the same everytime. • In inflammation, blood vessels become leaky. capillary wall – white blood cells move extracellular space toward infection and damaged tissue – characterized by swelling, redness, and pain Another Example: Fever ...
Plant Anatomy
... plant cells = least specialized photosynthetic cells, storage cells tissue of leaves, stem, fruit, storage roots ...
... plant cells = least specialized photosynthetic cells, storage cells tissue of leaves, stem, fruit, storage roots ...
LAB: CELL STUDIES This is a class set! Do ALL of this in your LAB
... LAB: CELL STUDIES This is a class set! Do ALL of this in your LAB book. The Cell Theory states that all living organisms are made of cells. It was only after microscopes were developed and we were able to view the universality of cells that this theory was accepted. Although cells are the building b ...
... LAB: CELL STUDIES This is a class set! Do ALL of this in your LAB book. The Cell Theory states that all living organisms are made of cells. It was only after microscopes were developed and we were able to view the universality of cells that this theory was accepted. Although cells are the building b ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).