L3.b Spiral Review
... 1. Which of these is NOT present in an animal cell? a. chloroplast b. cytoplasm c. membrane d. nucleus 2. Which of these cell parts is CORRECTLY paired with its function? a. cell membrane - traps light energy b. nucleus - stores water, food, and wastes c. chloroplast - controls all the activities in ...
... 1. Which of these is NOT present in an animal cell? a. chloroplast b. cytoplasm c. membrane d. nucleus 2. Which of these cell parts is CORRECTLY paired with its function? a. cell membrane - traps light energy b. nucleus - stores water, food, and wastes c. chloroplast - controls all the activities in ...
active transport
... the process by which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells, either as a defense mechanism or as a means to obtain food ...
... the process by which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells, either as a defense mechanism or as a means to obtain food ...
The basic unit of life is the CELL. This is the smallest entity that is
... information necessary to sustain and propagate life. The nucleic acids (DNA & RNA) and associated enzymes and proteins are found in the nucleus. 4. The ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM. Closely associated with the nucleus is a system of membrane bound tubules, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The membrane surro ...
... information necessary to sustain and propagate life. The nucleic acids (DNA & RNA) and associated enzymes and proteins are found in the nucleus. 4. The ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM. Closely associated with the nucleus is a system of membrane bound tubules, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The membrane surro ...
02/28 PPT - Molecular and Cell Biology
... One extracellular cue that influences cortex formation Reeler mutant mice (missing Reelin protein) • Identified because of severe movement disorders • Mutation in an extracellular matrix protein (?) • Cortex is built outside in • 26 human disorders associated with cortex malformation • One form of ...
... One extracellular cue that influences cortex formation Reeler mutant mice (missing Reelin protein) • Identified because of severe movement disorders • Mutation in an extracellular matrix protein (?) • Cortex is built outside in • 26 human disorders associated with cortex malformation • One form of ...
Chapter Objectives
... d. Compose nuclear lamina G. Cell Surfaces and Junctions 1. Plant cells are encased by cell walls 2. The extracellular matrix (ECM) of animal cells functions in support, adhesion, movement, and development 3. Intercellular junctions help integrate cells into higher levels of structure and function H ...
... d. Compose nuclear lamina G. Cell Surfaces and Junctions 1. Plant cells are encased by cell walls 2. The extracellular matrix (ECM) of animal cells functions in support, adhesion, movement, and development 3. Intercellular junctions help integrate cells into higher levels of structure and function H ...
applications of animal cell culture
... Tissue culture is the growth of tissues or cells separate from the organism. This is typically facilitated via use of a liquid, semi-solid, or solid growth medium, such as broth or agar. Tissue culture commonly refers to the culture of animal cells and tissues. ...
... Tissue culture is the growth of tissues or cells separate from the organism. This is typically facilitated via use of a liquid, semi-solid, or solid growth medium, such as broth or agar. Tissue culture commonly refers to the culture of animal cells and tissues. ...
Chapter 4
... • Gland – consists of one or more cells that make and secrete (export) a particular product called a secretion. • Secretion – an aqueous solution that ...
... • Gland – consists of one or more cells that make and secrete (export) a particular product called a secretion. • Secretion – an aqueous solution that ...
File chapter 7
... 2. What is the function of mitochondria? 3. Which cell organelle is the shipping and packaging center for the cell? 4. What are the functions of lysosomes? 5. Why do mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA? 6. Name three structures found in plant cells that are not found in animal cells ...
... 2. What is the function of mitochondria? 3. Which cell organelle is the shipping and packaging center for the cell? 4. What are the functions of lysosomes? 5. Why do mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA? 6. Name three structures found in plant cells that are not found in animal cells ...
5.1 The Cell Cycle
... • What are the four main stages of the cell cycle? – Gap 1, synthesis, Gap 2, mitosis • What can you infer about the relative amount of time a cell spends in each stage? – An actively dividing cell spends the least amount of time in the mitosis stage. The length of Gap 1 varies the most and is usual ...
... • What are the four main stages of the cell cycle? – Gap 1, synthesis, Gap 2, mitosis • What can you infer about the relative amount of time a cell spends in each stage? – An actively dividing cell spends the least amount of time in the mitosis stage. The length of Gap 1 varies the most and is usual ...
BIO_130_132_Test_Questions_files/practice test 3 questions
... 30. The fastest rate of mitosis is seen in A. the stratum corneum. B. the stratum lucidum. C. the stratum granulosum. D. the stratum spinosum. E. the stratum basale 31. Which of the following is an epidermal cell functions as a macrophage? A. a keratinocyte B. a melanocyte C. a plasma cell D. a Lang ...
... 30. The fastest rate of mitosis is seen in A. the stratum corneum. B. the stratum lucidum. C. the stratum granulosum. D. the stratum spinosum. E. the stratum basale 31. Which of the following is an epidermal cell functions as a macrophage? A. a keratinocyte B. a melanocyte C. a plasma cell D. a Lang ...
Hedgehog Learning. Copying permitted for purchasing campus only
... _______ regulation of conditions within a cell which allows for stable equilibrium ...
... _______ regulation of conditions within a cell which allows for stable equilibrium ...
Prokaryots Prokaryot is the name given to those single
... Prokaryot is the name given to those single-cell organisms having a certain primitive cell structure. (The alternative cell structure, eukaryotic, is much more advanced.) The prokaryots comprise the bacteria and blue-green algae. (The latter are also known as cyanobacteria.) Principally prokaryots l ...
... Prokaryot is the name given to those single-cell organisms having a certain primitive cell structure. (The alternative cell structure, eukaryotic, is much more advanced.) The prokaryots comprise the bacteria and blue-green algae. (The latter are also known as cyanobacteria.) Principally prokaryots l ...
Document
... identification of ES cell-restricted micro-RNAs produced by Drosha, similar to the siRNAs involved in RNA silencing that are produced by the Rnase III nuclease, Dicer. Expression analysis before and after EB differentiation has identified novel miRNAs that may play an important role in both maintain ...
... identification of ES cell-restricted micro-RNAs produced by Drosha, similar to the siRNAs involved in RNA silencing that are produced by the Rnase III nuclease, Dicer. Expression analysis before and after EB differentiation has identified novel miRNAs that may play an important role in both maintain ...
THE CHEMICAL BUILDING BLOCKS OF LIFE
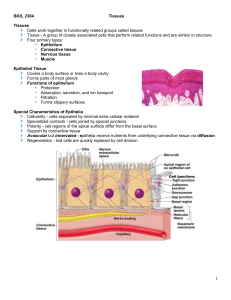
... Special Characteristics of Epithelia Cellularity - cells separated by minimal extra cellular material Specialized contacts - cells joined by special junctions Polarity - cell regions of the apical surface differ from the basal surface Support by connective tissue Avascular but innervated - epithelia ...
... Special Characteristics of Epithelia Cellularity - cells separated by minimal extra cellular material Specialized contacts - cells joined by special junctions Polarity - cell regions of the apical surface differ from the basal surface Support by connective tissue Avascular but innervated - epithelia ...
Solutions and Biochemistry
... Elements that make up fats are C, H, and O Two types of fats ◦ Saturated and Unsaturated ...
... Elements that make up fats are C, H, and O Two types of fats ◦ Saturated and Unsaturated ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).