Unit 2
... requiring process that uses energy extracted from organic macromolecules to produce ATP. It is found in nearly all eukaryotic cells. The number of mitochondria per cell varies and directly correlates with the cell’s metabolic activity. They are dynamic structures that move, change their shape and di ...
... requiring process that uses energy extracted from organic macromolecules to produce ATP. It is found in nearly all eukaryotic cells. The number of mitochondria per cell varies and directly correlates with the cell’s metabolic activity. They are dynamic structures that move, change their shape and di ...
Animalia 1
... Animalia are Eukaryotes because they are multi-celled and they have a nucleus. Animalia cells do not have cell walls, but they do have a cell membrane. Inside the cells of Animalia, there are ribosomes and mitochondria, which provide the “power” for cellular reproduction. These cells reproduce throu ...
... Animalia are Eukaryotes because they are multi-celled and they have a nucleus. Animalia cells do not have cell walls, but they do have a cell membrane. Inside the cells of Animalia, there are ribosomes and mitochondria, which provide the “power” for cellular reproduction. These cells reproduce throu ...
Activity 1: Think-Pair
... Our first cell type is called a prokaryotic cell or prokaryote (pro-kar-e-oat). These cells are unique because they are only found in the smallest organisms on the planet, bacteria. Scientists believe that these bacterial cells (prokaryotes) were the very first life forms on Earth. That means that t ...
... Our first cell type is called a prokaryotic cell or prokaryote (pro-kar-e-oat). These cells are unique because they are only found in the smallest organisms on the planet, bacteria. Scientists believe that these bacterial cells (prokaryotes) were the very first life forms on Earth. That means that t ...
Daysheet 29 - We Read. We Write. We Work.
... Our first cell type is called a prokaryotic cell or prokaryote (pro-kar-e-oat). These cells are unique because they are only found in the smallest organisms on the planet, bacteria. Scientists believe that these bacterial cells (prokaryotes) were the very first life forms on Earth. That means that t ...
... Our first cell type is called a prokaryotic cell or prokaryote (pro-kar-e-oat). These cells are unique because they are only found in the smallest organisms on the planet, bacteria. Scientists believe that these bacterial cells (prokaryotes) were the very first life forms on Earth. That means that t ...
Topic 1 Cells Powerpoint
... • All cells have the same DNA, but they use or express different parts of it to become different types of cells. • Once they become specialized, some cells (nerve, muscle) lose the ability to reproduce themselves. • Different types of cells can accomplish more as a group than they could as individu ...
... • All cells have the same DNA, but they use or express different parts of it to become different types of cells. • Once they become specialized, some cells (nerve, muscle) lose the ability to reproduce themselves. • Different types of cells can accomplish more as a group than they could as individu ...
Sample Textbook
... the prokaryotic cells later in the course. Eukaryotes are more complex cell structures than the already complex prokaryotes. Eukaryotic cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus. They also have complicated, membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles. The cell’s s ...
... the prokaryotic cells later in the course. Eukaryotes are more complex cell structures than the already complex prokaryotes. Eukaryotic cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus. They also have complicated, membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles. The cell’s s ...
2017 MCB/LISCB/CRUK project short-list Structural investigation of
... nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of tumor suppressor proteins. Cell cycle progression is driven by the activity of cyclin-dependent kinases, CDKs. CDK activity is controlled by natural CDK inhibitors, CKIs of the INK/KIP families. CDKN1B of the KIP family, also known as p27KIP1, regulates cell cycle CDKs ...
... nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of tumor suppressor proteins. Cell cycle progression is driven by the activity of cyclin-dependent kinases, CDKs. CDK activity is controlled by natural CDK inhibitors, CKIs of the INK/KIP families. CDKN1B of the KIP family, also known as p27KIP1, regulates cell cycle CDKs ...
Components of a Cell Membrane
... other cells and proteins (collagen) together giving strength and support to a matrix. -work with Immune cells to attract bacteria to these sites, bind them, and then destroy them.. - vary between species to species, individual to individual, even from cell to cell within an individual. of glycoconju ...
... other cells and proteins (collagen) together giving strength and support to a matrix. -work with Immune cells to attract bacteria to these sites, bind them, and then destroy them.. - vary between species to species, individual to individual, even from cell to cell within an individual. of glycoconju ...
Slide 1 - Cloudfront.net
... Turgor Pressure Explained • Turgor pressure is The pressure exerted by water inside the cell by the vacuole against the cell wall. A decrease in turgor pressure causes wilting. ...
... Turgor Pressure Explained • Turgor pressure is The pressure exerted by water inside the cell by the vacuole against the cell wall. A decrease in turgor pressure causes wilting. ...
Vacuole
... The vacuole may store reserve materials such as proteins, sugars and organic acids or they can accumulate various compounds like tannins and anthocyanins. The vacuole can also be involved with cellular waste management, enzymatically digesting or storing unwanted substances. ...
... The vacuole may store reserve materials such as proteins, sugars and organic acids or they can accumulate various compounds like tannins and anthocyanins. The vacuole can also be involved with cellular waste management, enzymatically digesting or storing unwanted substances. ...
34 Chemotaxis
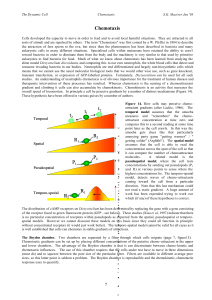
... Cells developed the capacity to move in order to feed and to avoid local harmful situations. They are attracted to all sorts of stimuli and are repulsed by others. The term "Chemotaxis" was first coined by a W. Pfeffer in 1884 to describe the attraction of fern sperm to the ova, but since then the p ...
... Cells developed the capacity to move in order to feed and to avoid local harmful situations. They are attracted to all sorts of stimuli and are repulsed by others. The term "Chemotaxis" was first coined by a W. Pfeffer in 1884 to describe the attraction of fern sperm to the ova, but since then the p ...
Conclusion Transmission electron microscopy Aim Materials
... 2-methoxyestradiol (2ME2) is an endogenous estradiol metabolite that has antiproliferative activity, antiangiogenic activity and antitumor activity. 2ME2 has shown positive results as a potential treatment of many types of cancer, in particular breast cancer. Inhibition of proliferation results main ...
... 2-methoxyestradiol (2ME2) is an endogenous estradiol metabolite that has antiproliferative activity, antiangiogenic activity and antitumor activity. 2ME2 has shown positive results as a potential treatment of many types of cancer, in particular breast cancer. Inhibition of proliferation results main ...
10-3 Regulating the Cell Cycle
... d. undergo cell division randomly. Slide 17 of 18 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
... d. undergo cell division randomly. Slide 17 of 18 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
The Cell - Ernst Klett
... Cell organelles and their functions All cells have a cell membrane which is a thin skin surrounding the cytoplasm. It acts like a boundary and stops the cell’s content from escaping. It also controls which substances like water, food, oxygen are allowed to enter the cell and which substances (usuall ...
... Cell organelles and their functions All cells have a cell membrane which is a thin skin surrounding the cytoplasm. It acts like a boundary and stops the cell’s content from escaping. It also controls which substances like water, food, oxygen are allowed to enter the cell and which substances (usuall ...
Cell Cycle Book PPT
... growth. Cancer cells do not respond to the signals that regulate the growth of most cells (G1 checkpoint is bypassed). As a result, they divide uncontrollably and form masses of cells called tumors that can damage the surrounding tissues. Cell Division - Notes Gallery ...
... growth. Cancer cells do not respond to the signals that regulate the growth of most cells (G1 checkpoint is bypassed). As a result, they divide uncontrollably and form masses of cells called tumors that can damage the surrounding tissues. Cell Division - Notes Gallery ...
Main Parts of the Cell
... materials that will be exported from the cell (the “shipping department” of the cell). (UPS/Fed Ex) • Vesicles pinch off from the golgi apparatus move to the cell membrane carrying the substances stored in the golgi bodies. These substances are ...
... materials that will be exported from the cell (the “shipping department” of the cell). (UPS/Fed Ex) • Vesicles pinch off from the golgi apparatus move to the cell membrane carrying the substances stored in the golgi bodies. These substances are ...
AP Bio Mitosis Overview
... QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
Introduction to Microbiology
... heads forming the inner and outer surfaces of the membrane. Membrane transport *Passive Transport Across the Cell Membrane Passive transport describes the movement of substances down a concentration gradient and does not require energy use the following . • Bulk flow is the collective movement of su ...
... heads forming the inner and outer surfaces of the membrane. Membrane transport *Passive Transport Across the Cell Membrane Passive transport describes the movement of substances down a concentration gradient and does not require energy use the following . • Bulk flow is the collective movement of su ...
Chapter 7 Section 2: Cell organelles Quiz: For 3 extra credit points
... 2. Which of the following cell parts have similar or related jobs? a. mitochondria and cell wall c. mitochondria and chloroplasts b. ribosomes and cell membrane d. nucleus and vacuole 3. Which of the following cell parts have similar or related jobs? a. cell wall and centriole c. cell membrane and n ...
... 2. Which of the following cell parts have similar or related jobs? a. mitochondria and cell wall c. mitochondria and chloroplasts b. ribosomes and cell membrane d. nucleus and vacuole 3. Which of the following cell parts have similar or related jobs? a. cell wall and centriole c. cell membrane and n ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).