The s-Block Elements - GCG-42
... The ionic character of hydrides increases from Li to Cs. The stability of hydrides decreases from Li to Cs. The hydrides behave as strong reducing agents and the latter increases from Li to Cs. ...
... The ionic character of hydrides increases from Li to Cs. The stability of hydrides decreases from Li to Cs. The hydrides behave as strong reducing agents and the latter increases from Li to Cs. ...
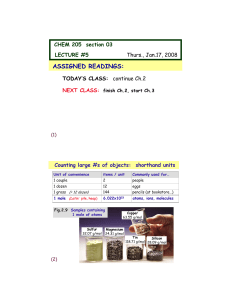
atomic number
... element has. For instance, hydrogen has 1 proton, so it’s atomic number is 1. The atomic number is unique to that element. No two elements have the same atomic number. ...
... element has. For instance, hydrogen has 1 proton, so it’s atomic number is 1. The atomic number is unique to that element. No two elements have the same atomic number. ...
Unit 3 Review - RHSChemistry
... states of matter (s, l, g) f. React readily with ________, metals especially alkali, to produce salts. (halogen = salt former) ...
... states of matter (s, l, g) f. React readily with ________, metals especially alkali, to produce salts. (halogen = salt former) ...
ELEMENTS and THEIR PROPERTIES
... The Periodic Table • In the late 1800’s Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, discovered a way of organizing the elements. This became known as the first periodic table. • He put the elements in order by their atomic mass, today we have them in order of their atomic number. • He left blank spaces in ...
... The Periodic Table • In the late 1800’s Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, discovered a way of organizing the elements. This became known as the first periodic table. • He put the elements in order by their atomic mass, today we have them in order of their atomic number. • He left blank spaces in ...
SCH3U Periodic Table Worksheet 1. Where are the most active
... 1. Where are the most active metals located? Group 1. Also, the bottom periods of the periodic table. 2. Where are the most active non-metals located? Top right of the periodic table. Fluorine being the highest. Group 17 very reactive. 3. As you go from left to right across a period, the atomic radi ...
... 1. Where are the most active metals located? Group 1. Also, the bottom periods of the periodic table. 2. Where are the most active non-metals located? Top right of the periodic table. Fluorine being the highest. Group 17 very reactive. 3. As you go from left to right across a period, the atomic radi ...
STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 8 TEST AND ELEMENT SYMBOLS
... for life on Earth. CARBOHYDRATES Germanium and _______________________ are used to make computer chips. SILICON Nitrogen and _______________________ can be combined to make ammonia. ...
... for life on Earth. CARBOHYDRATES Germanium and _______________________ are used to make computer chips. SILICON Nitrogen and _______________________ can be combined to make ammonia. ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
4-3 Families of Elements
... d. Technetium and promethium are synthetic elements i. Technetium and promethium are both man-made, radioactive elements ii. The last two periods of the transition metals are placed toward the bottom of the periodic table so that similar elements elsewhere in the table still line up. iii. All elemen ...
... d. Technetium and promethium are synthetic elements i. Technetium and promethium are both man-made, radioactive elements ii. The last two periods of the transition metals are placed toward the bottom of the periodic table so that similar elements elsewhere in the table still line up. iii. All elemen ...
Periodic Table
... This conductivity can be changed and controlled Very useful for the binary language of computers ...
... This conductivity can be changed and controlled Very useful for the binary language of computers ...
Textbook Questions - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... 30. Cations are always __________ than the atoms from which they form; anions are always _________. 31. Why are the electrons drawn closer to the nucleus when a sodium atom loses an electron? ...
... 30. Cations are always __________ than the atoms from which they form; anions are always _________. 31. Why are the electrons drawn closer to the nucleus when a sodium atom loses an electron? ...
Periodic Table Workshop
... • Def: “the min. am’t of energy required to remove the most loosely held e-” • top to bottom: decreases, since as atomic size increases, e- from higher energy levels are "shielded*" from the nucleus and are therefore not as tightly bound. (the "*shielding effect") • left to right: increases, as elem ...
... • Def: “the min. am’t of energy required to remove the most loosely held e-” • top to bottom: decreases, since as atomic size increases, e- from higher energy levels are "shielded*" from the nucleus and are therefore not as tightly bound. (the "*shielding effect") • left to right: increases, as elem ...
GO 3_3 The Periodic Table
... They react when exposed to air or water As you move down the group, reactivity increases. Lithium ...
... They react when exposed to air or water As you move down the group, reactivity increases. Lithium ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE 25 FEBRUARY 2014
... Atomic radius = a measure of the size of an atom. Ionisation energy = the energy needed to remove one electron from an atom in the gas phase. Could also be used to define second, third ionisation energies. Electronegativity = the tendency of atoms to attract electrons. ...
... Atomic radius = a measure of the size of an atom. Ionisation energy = the energy needed to remove one electron from an atom in the gas phase. Could also be used to define second, third ionisation energies. Electronegativity = the tendency of atoms to attract electrons. ...
Unit 3 Practice Test
... Periodic Families 1. You were just digging in your backyard and came across what you believe is a new element! It is in Group 4 and it has a high melting point. a. Do you think it’s a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid? Why? ...
... Periodic Families 1. You were just digging in your backyard and came across what you believe is a new element! It is in Group 4 and it has a high melting point. a. Do you think it’s a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid? Why? ...
HonorsCh6PracticeTest14
... _______ 11. In the modern periodic table, there is a periodic pattern in the physical and chemical properties of elements when they are arranged in order of a. increasing atomic mass. b. increasing electronegativity. c. increasing atomic radius. d. increasing atomic number. 12. Which sublevel corres ...
... _______ 11. In the modern periodic table, there is a periodic pattern in the physical and chemical properties of elements when they are arranged in order of a. increasing atomic mass. b. increasing electronegativity. c. increasing atomic radius. d. increasing atomic number. 12. Which sublevel corres ...
Name: Chemistry A Date: Period: Unit 1 Test Review Packet
... atomic number and atomic mass. 1b Students know how to use the periodic table to identify metals, semimetals, nonmetals, and halogens. 1c Students know how to use the periodic table to identify alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals, trends in ionization energy, electronegativity ...
... atomic number and atomic mass. 1b Students know how to use the periodic table to identify metals, semimetals, nonmetals, and halogens. 1c Students know how to use the periodic table to identify alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals, trends in ionization energy, electronegativity ...
Port Said International Schools
... Because when the temperature decreases than 4 c the water molecules are collected by hydrogen bonds forming large sized hexagonal crystals with many spaces between them 20. Thermal pollution is very dangerous on marine creatures. Due to separation of dissolved oxygen in water D. What is meant by: 1. ...
... Because when the temperature decreases than 4 c the water molecules are collected by hydrogen bonds forming large sized hexagonal crystals with many spaces between them 20. Thermal pollution is very dangerous on marine creatures. Due to separation of dissolved oxygen in water D. What is meant by: 1. ...
Periodic table intro
... A group is a vertical column on the periodic table. It is also called a chemical family, because the elements in it have similar characteristics. ...
... A group is a vertical column on the periodic table. It is also called a chemical family, because the elements in it have similar characteristics. ...
HISTORY OF THE PERIODIC TABLE
... I GREEKS (400 B.C.) – used the words “element” and “atom”. II Antoine Lavoisier (1700’s) – divided the element into 4 Classes III Dobereiner (1800’s) – noted the similar elements often had relative atomic masses A.E. Beguyer de Chancourtois – created a cylindrical table of elements to display the pe ...
... I GREEKS (400 B.C.) – used the words “element” and “atom”. II Antoine Lavoisier (1700’s) – divided the element into 4 Classes III Dobereiner (1800’s) – noted the similar elements often had relative atomic masses A.E. Beguyer de Chancourtois – created a cylindrical table of elements to display the pe ...
lecture
... • Noble Gases or inert gases are colorless gases that are extremely un-reactive. • One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. • The family of noble gases includes helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon. • All ...
... • Noble Gases or inert gases are colorless gases that are extremely un-reactive. • One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. • The family of noble gases includes helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon. • All ...
Chapter 5
... d-block elements Group 3-12: Transition metals Electron configurations end in d1 for group 3 and end in d10 for group 12 Good conductors of heat and electricity Less reactive than s block metals Some exist in nature as free elements ...
... d-block elements Group 3-12: Transition metals Electron configurations end in d1 for group 3 and end in d10 for group 12 Good conductors of heat and electricity Less reactive than s block metals Some exist in nature as free elements ...
Organization & Characteristics of the Periodic Table
... Easily lose valence electron (Reducing agents) React violently with water Large hydration energy React with halogens to form salts ...
... Easily lose valence electron (Reducing agents) React violently with water Large hydration energy React with halogens to form salts ...
Chapter 6 - Fredericksburg City Schools
... S The representative elements are the Group A elements. S The representative elements always behave the same. And any one member of the group is “representative” of all the other members in its group. S The representative elements are all the elements in the s and p blocks. S The transition metals a ...
... S The representative elements are the Group A elements. S The representative elements always behave the same. And any one member of the group is “representative” of all the other members in its group. S The representative elements are all the elements in the s and p blocks. S The transition metals a ...