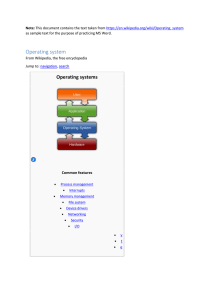
Process Management
... – Each process has one or more last-in-first-out (LIFO) system stacks associated with it. A stack is used to store parameters and calling addresses for procedure and system calls. The stack pointer points to the top of the stack. ...
... – Each process has one or more last-in-first-out (LIFO) system stacks associated with it. A stack is used to store parameters and calling addresses for procedure and system calls. The stack pointer points to the top of the stack. ...
Processes and Threads
... Exact type and amount of information vary according to OS and call Three general methods used to pass parameters to the OS Simplest: pass the parameters in registers In some cases, may be more parameters than registers Parameters stored in a block, or table, in memory, and address of block p ...
... Exact type and amount of information vary according to OS and call Three general methods used to pass parameters to the OS Simplest: pass the parameters in registers In some cases, may be more parameters than registers Parameters stored in a block, or table, in memory, and address of block p ...
Monday, 26 November, 2007.
... A process is a program in execution. It is a unit of work within the system. Program is a passive entity, process is an active entity. Process needs resources to accomplish its task CPU, memory, I/O, files Initialization data Process termination requires reclaim of any reusable resources Single- ...
... A process is a program in execution. It is a unit of work within the system. Program is a passive entity, process is an active entity. Process needs resources to accomplish its task CPU, memory, I/O, files Initialization data Process termination requires reclaim of any reusable resources Single- ...
資工系網媒所NEWS實驗室
... separate module of the operating system, allowing it to be replaced with a different algorithm if necessary. Either SSTF or LOOK is a reasonable choice for the default algorithm. 資工系網媒所 NEWS實驗室 ...
... separate module of the operating system, allowing it to be replaced with a different algorithm if necessary. Either SSTF or LOOK is a reasonable choice for the default algorithm. 資工系網媒所 NEWS實驗室 ...
Slide 1 - RSWiki
... separate module of the operating system, allowing it to be replaced with a different algorithm if necessary. Either SSTF or LOOK is a reasonable choice for the default algorithm. 資工系網媒所 NEWS實驗室 ...
... separate module of the operating system, allowing it to be replaced with a different algorithm if necessary. Either SSTF or LOOK is a reasonable choice for the default algorithm. 資工系網媒所 NEWS實驗室 ...
Chapter 2: Operating
... File-system manipulation - The file system is of particular interest. Programs need to read and write files and directories, create and delete them, search them, list file Information, permission management. ...
... File-system manipulation - The file system is of particular interest. Programs need to read and write files and directories, create and delete them, search them, list file Information, permission management. ...
Module 7: Process Synchronization
... Event queue inserts all the appropriate events based on the process arrival times before you try to right any of the event handlers. Use cout statements and the display( ) function (part of the NextEventSimulator and the list classes) to make sure your function is doing the right thing. ...
... Event queue inserts all the appropriate events based on the process arrival times before you try to right any of the event handlers. Use cout statements and the display( ) function (part of the NextEventSimulator and the list classes) to make sure your function is doing the right thing. ...
Introduction:- CS-502 Operating Systems
... security: how is the integrity of the OS and its resources ensured? protection: how is one user/program protected from another? performance: how do we make it all go fast? reliability: what happens if something goes wrong – hardware or software extensibility: can we add new features? communication: ...
... security: how is the integrity of the OS and its resources ensured? protection: how is one user/program protected from another? performance: how do we make it all go fast? reliability: what happens if something goes wrong – hardware or software extensibility: can we add new features? communication: ...
Operating System Services
... Internal structure of different Operating Systems can vary widely Start the design by defining goals and specifications Affected by choice of hardware, type of system User goals and System goals User goals – operating system should be convenient to use, easy to learn, reliable, safe, and f ...
... Internal structure of different Operating Systems can vary widely Start the design by defining goals and specifications Affected by choice of hardware, type of system User goals and System goals User goals – operating system should be convenient to use, easy to learn, reliable, safe, and f ...
A real-time operating system
... universities, and in the early ARPANET community. From the late 1960s through the late 1970s, several hardware capabilities evolved that allowed similar or ported software to run on more than one system. Early systems had utilized microprogramming to implement features on their systems in order to p ...
... universities, and in the early ARPANET community. From the late 1960s through the late 1970s, several hardware capabilities evolved that allowed similar or ported software to run on more than one system. Early systems had utilized microprogramming to implement features on their systems in order to p ...
Solution to Lab Project 2.1
... Answers to Essay Quiz 1. The operating system functions DOS supports are: user interface, memory management, file management, and device management. The job management, task management, and security functions are completely unsupported in DOS. User interface, file management, memory management, and ...
... Answers to Essay Quiz 1. The operating system functions DOS supports are: user interface, memory management, file management, and device management. The job management, task management, and security functions are completely unsupported in DOS. User interface, file management, memory management, and ...
3 Threads SMP Microkernel
... • Reliability and Fault Tolerance – Graceful degradation in case of processor failure CS-550: Threads, SMP, and Microkernels ...
... • Reliability and Fault Tolerance – Graceful degradation in case of processor failure CS-550: Threads, SMP, and Microkernels ...
sample unformatted document
... ARPANET community. From the late 1960s through the late 1970s, several hardware capabilities evolved that allowed similar or ported software to run on more than one system. Early systems had utilized microprogramming to implement features on their systems in order to permit different underlying comp ...
... ARPANET community. From the late 1960s through the late 1970s, several hardware capabilities evolved that allowed similar or ported software to run on more than one system. Early systems had utilized microprogramming to implement features on their systems in order to permit different underlying comp ...
amoeba - IJTRE
... processor pool model. The main components makingup the architecture are the processor pool,X-terminals, workstations (SUN-3s and VAXstations are supported), servers and gateways. The gateways arebasically used for connecting Amoeba sites over WANs. The assumptions behind this architecture are that m ...
... processor pool model. The main components makingup the architecture are the processor pool,X-terminals, workstations (SUN-3s and VAXstations are supported), servers and gateways. The gateways arebasically used for connecting Amoeba sites over WANs. The assumptions behind this architecture are that m ...
lecture1422914790
... 4. Distributed System/Loosely Coupled Systems: In contrast to tightly coupled systems, the processors do not share memory or a clock. Instead, each processor has its own local memory. The processors communicate with each other by various communication lines such as high speed buses or telephone line ...
... 4. Distributed System/Loosely Coupled Systems: In contrast to tightly coupled systems, the processors do not share memory or a clock. Instead, each processor has its own local memory. The processors communicate with each other by various communication lines such as high speed buses or telephone line ...
Operating Systems II
... Hardware Support for Operating Systems Recall that OS should securely multiplex resources. ⇒ we need to ensure that an application cannot: • compromise the operating system. • compromise other applications. • deny others service (e.g. abuse resources) To achieve this efficiently and flexibly, we ne ...
... Hardware Support for Operating Systems Recall that OS should securely multiplex resources. ⇒ we need to ensure that an application cannot: • compromise the operating system. • compromise other applications. • deny others service (e.g. abuse resources) To achieve this efficiently and flexibly, we ne ...
Computer Architecture CS 355 I/O System Text: Computer
... Timer: Interrupts the processor every n time units. I/O: Signals completion of an operation or an error condition. Software Trap: Command in system call interface changes mode from user to kernel mode Interrupt Processing includes: 1. Device controller issues an interrupt signal to the process ...
... Timer: Interrupts the processor every n time units. I/O: Signals completion of an operation or an error condition. Software Trap: Command in system call interface changes mode from user to kernel mode Interrupt Processing includes: 1. Device controller issues an interrupt signal to the process ...
Chapter 2 - Processes
... – If no process is waiting on the condition, signaling the condition variable has NO effect at all! – A process that waits on a condition variable can be awakened and resume execution in entry procedure – So what about the process that woke the waiting process up? - May force it to wait (on a stack) ...
... – If no process is waiting on the condition, signaling the condition variable has NO effect at all! – A process that waits on a condition variable can be awakened and resume execution in entry procedure – So what about the process that woke the waiting process up? - May force it to wait (on a stack) ...
Operating Systems 2014/2015 Part VII – Storage Devices
... Can be more reliable because they have no moving parts ...
... Can be more reliable because they have no moving parts ...
Multicores
... mentioned earlier in the chapter. Even when the two - way or one - way traffic requirements are properly managed, you face issues of the integrity of the information transmitted between two or more processes. The message passing scheme might encounter issues such as interrupted transmissions (partia ...
... mentioned earlier in the chapter. Even when the two - way or one - way traffic requirements are properly managed, you face issues of the integrity of the information transmitted between two or more processes. The message passing scheme might encounter issues such as interrupted transmissions (partia ...
資工系網媒所NEWS實驗室Chapter 13
... separate module of the operating system, allowing it to be replaced with a different algorithm if necessary. Either SSTF or LOOK is a reasonable choice for the default algorithm. 資工系網媒所 NEWS實驗室 ...
... separate module of the operating system, allowing it to be replaced with a different algorithm if necessary. Either SSTF or LOOK is a reasonable choice for the default algorithm. 資工系網媒所 NEWS實驗室 ...
Lecture 28
... immediate allocation leaves the system in a safe state. System is in safe state if there exists a safe sequence of all processes. Sequence is safe if for each Pi, the resources that Pi
...
... immediate allocation leaves the system in a safe state. System is in safe state if there exists a safe sequence of all processes. Sequence
Real-time operating system survey
... For multiple threads to communicate among each other, in a timely fashion, predictable inter-thread communication and synchronization mechanisms are required. Also, supported should be the ability to lock/unlock resources to achieve data integrity. ...
... For multiple threads to communicate among each other, in a timely fashion, predictable inter-thread communication and synchronization mechanisms are required. Also, supported should be the ability to lock/unlock resources to achieve data integrity. ...
Lecture Notes- Operating Systems
... o I/O operations - A running program may require I/O, which may involve a file or an I/O device o File-system manipulation - The file system is of particular interest. Programs need to read and write files and directories, create and delete them, search them, list file Information, permission manage ...
... o I/O operations - A running program may require I/O, which may involve a file or an I/O device o File-system manipulation - The file system is of particular interest. Programs need to read and write files and directories, create and delete them, search them, list file Information, permission manage ...
Implementing Processes, Threads, and Resources
... • The Process Manager is that part of the OS that is responsible for managing all the processes on the system. • When the computer is powered on, there is only one program in execution: the initial process. • The initial process creates the OS, which can then create other processes as needed. • A pr ...
... • The Process Manager is that part of the OS that is responsible for managing all the processes on the system. • When the computer is powered on, there is only one program in execution: the initial process. • The initial process creates the OS, which can then create other processes as needed. • A pr ...