GENERATORS AND TRANSFORMERS
... given voltage into electrical energy at a different voltage level. It consists of two coils arranged in such a way that the magnetic field surrounding one coil cuts through the other coil. When an alternating voltage is applied to (across) one coil, the varying magnetic field set up around that coil ...
... given voltage into electrical energy at a different voltage level. It consists of two coils arranged in such a way that the magnetic field surrounding one coil cuts through the other coil. When an alternating voltage is applied to (across) one coil, the varying magnetic field set up around that coil ...
generators and transformers
... given voltage into electrical energy at a different voltage level. It consists of two coils arranged in such a way that the magnetic field surrounding one coil cuts through the other coil. When an alternating voltage is applied to (across) one coil, the varying magnetic field set up around that coil ...
... given voltage into electrical energy at a different voltage level. It consists of two coils arranged in such a way that the magnetic field surrounding one coil cuts through the other coil. When an alternating voltage is applied to (across) one coil, the varying magnetic field set up around that coil ...
Magnetism - West Ashley Advanced Studies Magnet
... wrapped around an iron core is rotated near a magnet. • Generators at power plants produce electric energy for our homes. • A generator contains coils of wire that are stationary, and rotating magnets are rotated by turbines. Turbines are huge wheels that rotate when pushed by water, wind, or steam. ...
... wrapped around an iron core is rotated near a magnet. • Generators at power plants produce electric energy for our homes. • A generator contains coils of wire that are stationary, and rotating magnets are rotated by turbines. Turbines are huge wheels that rotate when pushed by water, wind, or steam. ...
III. Producing Electric Current
... A. Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic Induction producing a current by moving a wire through a ...
... A. Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic Induction producing a current by moving a wire through a ...
III. Producing Electric Current
... A. Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic Induction producing a current by moving a wire through a ...
... A. Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic Induction producing a current by moving a wire through a ...
Light It Up Content Standards and Objectives
... Explain the relationship between protons, electrons, and static electricity. Identify the key components of an electric circuit. Describe how current electricity is generated within a circuit. Compare simple, parallel, and series circuits. Explain the role of conductors and insulators in an electric ...
... Explain the relationship between protons, electrons, and static electricity. Identify the key components of an electric circuit. Describe how current electricity is generated within a circuit. Compare simple, parallel, and series circuits. Explain the role of conductors and insulators in an electric ...
Generating Electricity
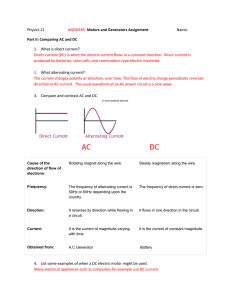
... complete cycle is called the period of alternating current – this is represented by the length of one wave. The height of the wave is the maximum voltage. Practical Generators: A simple generator consists of a coil of wire rotating between the poles of a magnet: - The coil cuts through the magnetic ...
... complete cycle is called the period of alternating current – this is represented by the length of one wave. The height of the wave is the maximum voltage. Practical Generators: A simple generator consists of a coil of wire rotating between the poles of a magnet: - The coil cuts through the magnetic ...
Unit 8: Electricity and Magnetism
... Time Frame: April 6th thru April 30th Science>Physical Science> Unit 8 ...
... Time Frame: April 6th thru April 30th Science>Physical Science> Unit 8 ...
WSEAS TRANSACTIONS on POWER SYSTEMS, August 2006
... Electromagnetic Disturbances in High Voltage Networks Connected to Large Electrical Installations. Evaluation of the Power System Contribution ...
... Electromagnetic Disturbances in High Voltage Networks Connected to Large Electrical Installations. Evaluation of the Power System Contribution ...
Science 9: Electricity
... 7. How can knowing the voltage and amperage of an electrical device keep you safe? 8. What is the difference between static and current electricity? List some examples of each. 9. List some examples of electrical conductors and insulators. 10. Which wire conducts electricity the best? The worst? 11. ...
... 7. How can knowing the voltage and amperage of an electrical device keep you safe? 8. What is the difference between static and current electricity? List some examples of each. 9. List some examples of electrical conductors and insulators. 10. Which wire conducts electricity the best? The worst? 11. ...
Lecture 7
... All magnets have north and south poles. When two magnets are brought together, like poles repel and unlike poles attract. ...
... All magnets have north and south poles. When two magnets are brought together, like poles repel and unlike poles attract. ...
Cable Specification for +/- 12 V Power Supply Used in Electric
... power-pole boards). Elpac Power Systems power supply WM072-1950-D5 with +/-12 V output was earlier used. However, this power supply is no longer in production. Elpac WM063-1950-D5 or SL Power SW301MA0012F01 has been identified as a suitable replacement. These power supplies, however, are triple outp ...
... power-pole boards). Elpac Power Systems power supply WM072-1950-D5 with +/-12 V output was earlier used. However, this power supply is no longer in production. Elpac WM063-1950-D5 or SL Power SW301MA0012F01 has been identified as a suitable replacement. These power supplies, however, are triple outp ...
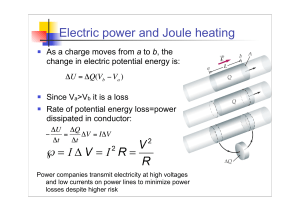
Electric power and Joule heating
... houses, whereas in the UK a typical urban or suburban low-voltage substation might be rated at 2 MW and supply a whole neighborhood. This is because the higher voltage used in Europe (380 V vs 230 V) may be carried over a greater distance with acceptable power loss. An advantage of the North America ...
... houses, whereas in the UK a typical urban or suburban low-voltage substation might be rated at 2 MW and supply a whole neighborhood. This is because the higher voltage used in Europe (380 V vs 230 V) may be carried over a greater distance with acceptable power loss. An advantage of the North America ...
Name_______________________Test Date
... A motor is not needed in an electromagnet; however, a battery (or power source) is needed. A soup can will stick to a magnet but WILL NOT conduct electricity. ...
... A motor is not needed in an electromagnet; however, a battery (or power source) is needed. A soup can will stick to a magnet but WILL NOT conduct electricity. ...
Conversion Circuit Design for High Efficiency
... In this project the bridgeless rectification circuit could reduce the power loss from the rectification and could improve the conversion efficiency by more than 94%. The interleaved switch boosting technology could substantially reduce the input ripple current to 0.8A, which is about one-fifth that ...
... In this project the bridgeless rectification circuit could reduce the power loss from the rectification and could improve the conversion efficiency by more than 94%. The interleaved switch boosting technology could substantially reduce the input ripple current to 0.8A, which is about one-fifth that ...
Abstract
... The need for Power Factor Correction (PFC) is driven by the worldwide concern for the quality of the power line supplies. Injection of high current harmonics into the power line and poor Power Factor (PF) in general, are known to cause many power distribution problems. In the light of the practical ...
... The need for Power Factor Correction (PFC) is driven by the worldwide concern for the quality of the power line supplies. Injection of high current harmonics into the power line and poor Power Factor (PF) in general, are known to cause many power distribution problems. In the light of the practical ...
PMG Excitation
... Drilling rigs may be described as mechanical or electric. These terms refer to the method in which power is supplied to the larger equipment on the rig. On mechanical rigs, power from the engines drives the rig equipment either directly, through a clutch or through a torque converter. ...
... Drilling rigs may be described as mechanical or electric. These terms refer to the method in which power is supplied to the larger equipment on the rig. On mechanical rigs, power from the engines drives the rig equipment either directly, through a clutch or through a torque converter. ...
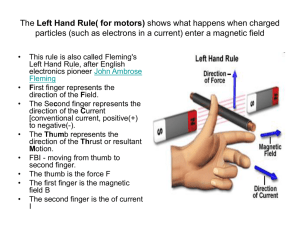
The Left Hand Rule - World of Teaching
... • An electric motor is a motor that uses electrical energy to produce mechanical energy, usually through the interaction of magnetic fields and currentcarrying conductors. • Electric motors are used in most, modern machines. Obvious uses would be in rotating machines such as fans, turbines, drills, ...
... • An electric motor is a motor that uses electrical energy to produce mechanical energy, usually through the interaction of magnetic fields and currentcarrying conductors. • Electric motors are used in most, modern machines. Obvious uses would be in rotating machines such as fans, turbines, drills, ...
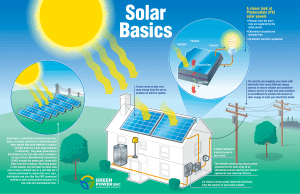
Solar Energy Basics
... rent or have a shaded roof or a roof that isn’t ideally positioned to capture the sun’s rays. Individuals may also like this EMC sponsored method of solar participation because it is low-cost and maintenance-free. ...
... rent or have a shaded roof or a roof that isn’t ideally positioned to capture the sun’s rays. Individuals may also like this EMC sponsored method of solar participation because it is low-cost and maintenance-free. ...
Electrification

Electrification is the process of powering by electricity and is usually associated with changing over from another power source. The broad meaning of the term, such as in the history of technology and economic history, usually applies to a region or national economy. Broadly speaking, electrification was the build out of the electrical generating and distribution systems which occurred in Britain, the United States, and other countries from the mid-1880s until around 1950 and is in progress in rural areas in some developing countries. This included the change over from line shaft and belt drive using steam engines and water power to electric motors.The electrification of particular sectors of the economy is called by terms such as factory electrification, household electrification, rural electrification or railway electrification. It may also apply to changing industrial processes such as smelting, melting, separating or refining from coal or coke heating or chemical processes to some type of electric process such as electric arc furnace, electric induction or resistance heating or electrolysis or electrolytic separating.Electrification was called ""the greatest engineering achievement of the 20th Century"" by the National Academy of Engineering.