Forces in Earth`s Crust
... work over millions of years to change the shape and volume of rock. • When Earth’s plates move, rocks are pushed and pulled. The pushes and pulls are called stress. • Stress adds energy to rocks. Rocks keep storing the energy until they cannot stand any more stress. Then the rocks break or change sh ...
... work over millions of years to change the shape and volume of rock. • When Earth’s plates move, rocks are pushed and pulled. The pushes and pulls are called stress. • Stress adds energy to rocks. Rocks keep storing the energy until they cannot stand any more stress. Then the rocks break or change sh ...
Inside Earth: Chapter 1
... they occur? • How does movement along faults change Earth’s surface? ...
... they occur? • How does movement along faults change Earth’s surface? ...
Geologic Structure Notes Powerpoint
... the strike of the fault plane – A viewer looking across to the other side of a right-lateral strike-slip fault would observe it to be offset to their right – A viewer looking across to the other side of a left-lateral strike-slip fault would observe it to be offset to their left ...
... the strike of the fault plane – A viewer looking across to the other side of a right-lateral strike-slip fault would observe it to be offset to their right – A viewer looking across to the other side of a left-lateral strike-slip fault would observe it to be offset to their left ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... Types of Faults • Strike-slip faults have movement that is predominantly horizontal and parallel to the strike of the fault plane – A viewer looking across to the other side of a right-lateral strike-slip fault would observe it to be offset to their right – A viewer looking across to the other side ...
... Types of Faults • Strike-slip faults have movement that is predominantly horizontal and parallel to the strike of the fault plane – A viewer looking across to the other side of a right-lateral strike-slip fault would observe it to be offset to their right – A viewer looking across to the other side ...
Pre-Test: Chapter 7-Plate Tectonics
... 24. Magnetic reversals are preserved in a. compass needles. b. magnetic minerals. ...
... 24. Magnetic reversals are preserved in a. compass needles. b. magnetic minerals. ...
1. What was the name of the super continent that was
... 3. What is the Theory proposed by Wegener that explains the movement of the continents over millions of years? Continental Drift 4. Define divergent boundary. Places where plates pull or move away from each ...
... 3. What is the Theory proposed by Wegener that explains the movement of the continents over millions of years? Continental Drift 4. Define divergent boundary. Places where plates pull or move away from each ...
It`s your fault - Westminster Public Schools Wiki
... 2. Cut out the fault model and fold each side down to form a box with the drawn features on top. Tape or glue the corners together. This box is a three dimensional model of the top layers of the Earth's crust. 3. The dashed lines on your model represent a fault. Carefully cut along the dashed lines. ...
... 2. Cut out the fault model and fold each side down to form a box with the drawn features on top. Tape or glue the corners together. This box is a three dimensional model of the top layers of the Earth's crust. 3. The dashed lines on your model represent a fault. Carefully cut along the dashed lines. ...
At what grain diameter will the lower yield point be 310 Mpa?
... • Dislocations are the elementary carriers of plastic flow thus they define material mechanical properties • Dislocations allow deformation at much lower stress than in a perfect crystal because slip does not require all bonds across the slip line to break simultaneously, but only small fraction of ...
... • Dislocations are the elementary carriers of plastic flow thus they define material mechanical properties • Dislocations allow deformation at much lower stress than in a perfect crystal because slip does not require all bonds across the slip line to break simultaneously, but only small fraction of ...
tectonic landforms
... ❶ Rocks that are buried deep beneath the Earth’s surface become hot as a result of the escape of heat from the Earth’s interior. Under these conditions the behaviour of the rock changes from being brittle, to more like plastic. (Plastic in this case doesn’t refer to the material itself, but rathe ...
... ❶ Rocks that are buried deep beneath the Earth’s surface become hot as a result of the escape of heat from the Earth’s interior. Under these conditions the behaviour of the rock changes from being brittle, to more like plastic. (Plastic in this case doesn’t refer to the material itself, but rathe ...
Structural Geology Stress and Strain
... •Monoclinal folds form when deepseated faults occur at depth and are not propagated through overlying sedimentary rocks to the surface •More pliant sedimentary rocks are able to accommodate strain by folding instead of fracturing in a brittle manner ...
... •Monoclinal folds form when deepseated faults occur at depth and are not propagated through overlying sedimentary rocks to the surface •More pliant sedimentary rocks are able to accommodate strain by folding instead of fracturing in a brittle manner ...
Reading Study Guide B - Swartz Creek Schools
... Fill in the main idea and detail notes with information about how rocks move along faults. Main Ideas 1. Rocks move along faults. ...
... Fill in the main idea and detail notes with information about how rocks move along faults. Main Ideas 1. Rocks move along faults. ...
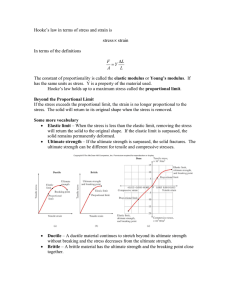
Hooke`s law in terms of stress and strain is strain stress∝ In terms of
... without breaking and the stress decreases from the ultimate strength. Brittle – A brittle material has the ultimate strength and the breaking point close together. ...
... without breaking and the stress decreases from the ultimate strength. Brittle – A brittle material has the ultimate strength and the breaking point close together. ...
Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks Metamorphism is defined
... e.g. Q sandstone can only yield quartzite protolith - rock name prior to metamorphism 2) T, P conditions In general, P and T increase together. metamorphic grade or intensity: low, medium, high instead of pressure, we generally refer to stress (which has connotation of direction) pressure (scalar) i ...
... e.g. Q sandstone can only yield quartzite protolith - rock name prior to metamorphism 2) T, P conditions In general, P and T increase together. metamorphic grade or intensity: low, medium, high instead of pressure, we generally refer to stress (which has connotation of direction) pressure (scalar) i ...
Ch4and5ReviewJeopardyGame
... A general type of fold, which are upcurved folds in the layers of rock. ...
... A general type of fold, which are upcurved folds in the layers of rock. ...
Structural Geology: Deformation and Mountain Building
... to the footwall • Reverse Fault: hanging wall moved upwards compared to the footwall • Thrust fault: low angle reverse fault ...
... to the footwall • Reverse Fault: hanging wall moved upwards compared to the footwall • Thrust fault: low angle reverse fault ...
Geologic Structures
... Faults (Any type of stress may cause brittle strain. The type of fault depends on the type of stress) ...
... Faults (Any type of stress may cause brittle strain. The type of fault depends on the type of stress) ...
MOUNTAIN BUILDING AND EVOLUTION OF CONTINENTS
... Extensional stress (often called tensional stress) pulls rock apart and is the opposite of tectonic compression Rocks at a divergent plate boundary stretch and pull apart because they are subject to extensional stress. ...
... Extensional stress (often called tensional stress) pulls rock apart and is the opposite of tectonic compression Rocks at a divergent plate boundary stretch and pull apart because they are subject to extensional stress. ...
Geomorphology Final Exam Study Guide
... Geologic Structures STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY – concerned with shapes, arrangement, interrelationships of bedrock units & endogenic (within) forces that cause them. ...
... Geologic Structures STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY – concerned with shapes, arrangement, interrelationships of bedrock units & endogenic (within) forces that cause them. ...
Simplified Thermal Stress Analysis
... Match TCE of component and substrate as much as possible Use an intermediate layer with a TCE in between that of the die and substrate; molybdenum often used (TCE between that of silicon and alumina) Choose materials that need the lowest processing temperatures – a large amount of stress is induced ...
... Match TCE of component and substrate as much as possible Use an intermediate layer with a TCE in between that of the die and substrate; molybdenum often used (TCE between that of silicon and alumina) Choose materials that need the lowest processing temperatures – a large amount of stress is induced ...