Designing with Heart
... challenging. Due to its small size (about 28 mm diameter by 51 mm length), the design laws for adult-sized pumps do not apply, and they cannot be scaled. Therefore, the design of pediatric blood pumps must rely on modern design approaches to optimize the flow path. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) ...
... challenging. Due to its small size (about 28 mm diameter by 51 mm length), the design laws for adult-sized pumps do not apply, and they cannot be scaled. Therefore, the design of pediatric blood pumps must rely on modern design approaches to optimize the flow path. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) ...
Blood Typing PowerPoint
... 8. How are antibodies related to the type of blood a person can receive? a. They attack all blood types except those receivable by a person. b. They attack the RBCs of the recipient so they can receive blood from a donor. c. They have nothing to do with receiving blood. ...
... 8. How are antibodies related to the type of blood a person can receive? a. They attack all blood types except those receivable by a person. b. They attack the RBCs of the recipient so they can receive blood from a donor. c. They have nothing to do with receiving blood. ...
Ventricular_Tachycardia
... ventricles, the QRS complexes are wide and bizarre. Ventricular impulses can be sometimes conducted backwards to the atria. in which case, P-waves may be inverted. Otherwise, regular normal P waves (60-100 beats per minute) may be present but not associated with QRS complexes (AV dissociation). The ...
... ventricles, the QRS complexes are wide and bizarre. Ventricular impulses can be sometimes conducted backwards to the atria. in which case, P-waves may be inverted. Otherwise, regular normal P waves (60-100 beats per minute) may be present but not associated with QRS complexes (AV dissociation). The ...
Scenario: The patient having a blood transfusion
... volunteer any further information until the student asks you how you are doing. You are a 53 year old hospital cleaner who has had 2-3 episodes of chest pain (angina) in the past year with exercise. You underwent a total hip replacement 3 days ago but didn’t mention the angina to the doctors pre-ope ...
... volunteer any further information until the student asks you how you are doing. You are a 53 year old hospital cleaner who has had 2-3 episodes of chest pain (angina) in the past year with exercise. You underwent a total hip replacement 3 days ago but didn’t mention the angina to the doctors pre-ope ...
public exam_transport in humans
... The photograph below shows the transverse section of a pig’s heart, which has a structure similar to that of the human heart. ...
... The photograph below shows the transverse section of a pig’s heart, which has a structure similar to that of the human heart. ...
Passive Reporting Underestimates Rate of Platelet
... designated as TACO. However, proactive evaluation and surveillance of reactions revealed that TACO occurred in two patients who were not reported to the transfusion service. Their reactions were characterized by new-onset hypertension, crackles on lung auscultation, dyspnea, hypoxia, and supplementa ...
... designated as TACO. However, proactive evaluation and surveillance of reactions revealed that TACO occurred in two patients who were not reported to the transfusion service. Their reactions were characterized by new-onset hypertension, crackles on lung auscultation, dyspnea, hypoxia, and supplementa ...
MLAB 2431 - Immunohematology
... k. Differentiate alloantibody and autoantibody. l. Define cold antibody and give examples. Explain the process of identifying the specificity of a cold autoantibody and techniques to avoid cold autoantibody reactivity. m. Define and identify low-incidence antigens. Chapter 8 (1a-i, ii, iv, v. 1b-ii, ...
... k. Differentiate alloantibody and autoantibody. l. Define cold antibody and give examples. Explain the process of identifying the specificity of a cold autoantibody and techniques to avoid cold autoantibody reactivity. m. Define and identify low-incidence antigens. Chapter 8 (1a-i, ii, iv, v. 1b-ii, ...
Blood Vessels
... – Force per unit area exerted on the wall of a blood vessel by the blood • Expressed in mm Hg • Measured as systemic arterial BP in large arteries near the heart ...
... – Force per unit area exerted on the wall of a blood vessel by the blood • Expressed in mm Hg • Measured as systemic arterial BP in large arteries near the heart ...
Humipak Verification Test Summary March 2011 HUMIPAK
... as well as being highly corrosive. Lumened instruments are particularly troublesome due to the potential of biofilm formation. Thus, it is recommended that patient used instruments be cleaned immediately following a procedure. However, this is not always possible. In these cases the standards recomm ...
... as well as being highly corrosive. Lumened instruments are particularly troublesome due to the potential of biofilm formation. Thus, it is recommended that patient used instruments be cleaned immediately following a procedure. However, this is not always possible. In these cases the standards recomm ...
Year 2 Highlight Slides
... • After collecting specimens, a participant: Is fully enrolled … 2. Did not fulfill enrollment requirements … or 3. Withdrew consent before end of enrollment ...
... • After collecting specimens, a participant: Is fully enrolled … 2. Did not fulfill enrollment requirements … or 3. Withdrew consent before end of enrollment ...
AN40714 Pb Blood
... from its extensive use have been known for many hundreds of years. Through the introduction of stringent safety precautions in industry, and regulations limiting its use, the number of cases of severe inorganic lead poisoning has fallen dramatically. Instances of toxicity, both industrial and non-oc ...
... from its extensive use have been known for many hundreds of years. Through the introduction of stringent safety precautions in industry, and regulations limiting its use, the number of cases of severe inorganic lead poisoning has fallen dramatically. Instances of toxicity, both industrial and non-oc ...
Genetics
... Rh incompatibility during pregnancy (cont.) •This phenomenon has led to an effective preventive measure to avoid Rh sensitisation. •Shortly after each birth of an Rh+ baby, the mother is given an injection of anti-Rh antibodies (or Rhogam). •These passively acquired antibodies destroy any foetal ce ...
... Rh incompatibility during pregnancy (cont.) •This phenomenon has led to an effective preventive measure to avoid Rh sensitisation. •Shortly after each birth of an Rh+ baby, the mother is given an injection of anti-Rh antibodies (or Rhogam). •These passively acquired antibodies destroy any foetal ce ...
International society of blood transfusion working party on red cell
... and molecular analysis. The first, named DOLC, was based on the serology (DO9) and the identification of the c.566C>T (p.Thr189Met) change in exon 2 of DO. The proposita’s RBCs typed Do(a+b ), Hy+, Jo(a+), DOYA+, DOLG+ and her plasma was non-reactive with Gy(a ) RBCs and only weakly reactive with Hy ...
... and molecular analysis. The first, named DOLC, was based on the serology (DO9) and the identification of the c.566C>T (p.Thr189Met) change in exon 2 of DO. The proposita’s RBCs typed Do(a+b ), Hy+, Jo(a+), DOYA+, DOLG+ and her plasma was non-reactive with Gy(a ) RBCs and only weakly reactive with Hy ...
Blood Type Review Questions
... What are the four possible blood types? ____________________ Write out all of the possible genotypes for each blood type: Type A: ______________________ Type B: ______________________ Type AB: _____________________ Type O: ______________________ Which allele(s) are dominant? __________ Which allele( ...
... What are the four possible blood types? ____________________ Write out all of the possible genotypes for each blood type: Type A: ______________________ Type B: ______________________ Type AB: _____________________ Type O: ______________________ Which allele(s) are dominant? __________ Which allele( ...
Oxygen concentration in plasma and tissue
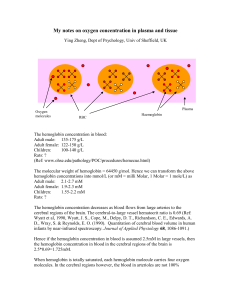
... The hemoglobin concentration decreases as blood flows from large arteries to the cerebral regions of the brain. The cerebral-to-large vessel hematocrit ratio is 0.69 (Ref: Wyatt et al, 1990, Wyatt, J. S., Cope, M., Delpy, D. T., Richardson, C. E., Edwards, A. D., Wray, S. & Reynolds, E. O. (1990). Q ...
... The hemoglobin concentration decreases as blood flows from large arteries to the cerebral regions of the brain. The cerebral-to-large vessel hematocrit ratio is 0.69 (Ref: Wyatt et al, 1990, Wyatt, J. S., Cope, M., Delpy, D. T., Richardson, C. E., Edwards, A. D., Wray, S. & Reynolds, E. O. (1990). Q ...
Newborn Exchange Transfusion
... Services to achieve a hematocrit of approximately 0.45 L/L. They will label the bag indicating total volume of the combined RBC and FFP contained in the unit. For double-volume exchanges two units may be issued. ...
... Services to achieve a hematocrit of approximately 0.45 L/L. They will label the bag indicating total volume of the combined RBC and FFP contained in the unit. For double-volume exchanges two units may be issued. ...
OSHA Bloodborne Standard
... 632; LASSA N.W., Ex. 20-680; Mission Bay Hospital, Ex. 20-666; Scripps Memorial Hospital, Ex. 20-522; The United Hospital, Ex. 20-682; Tucson Medical Center, Ex. 20141). However, the CDC's "Recommendations for Prevention of HIV Transmission in Health-Care Settings" states: 1. All health-care worker ...
... 632; LASSA N.W., Ex. 20-680; Mission Bay Hospital, Ex. 20-666; Scripps Memorial Hospital, Ex. 20-522; The United Hospital, Ex. 20-682; Tucson Medical Center, Ex. 20141). However, the CDC's "Recommendations for Prevention of HIV Transmission in Health-Care Settings" states: 1. All health-care worker ...
Document
... Type O makes it possible for it to be called the universal donor? Be specific. Type AB used to be considered the “Universal Recipient”. What does this mean? What exactly about Type AB makes it possible to be called the universal recipient? Be specific. B. What is a blood transfusion? Why are transfu ...
... Type O makes it possible for it to be called the universal donor? Be specific. Type AB used to be considered the “Universal Recipient”. What does this mean? What exactly about Type AB makes it possible to be called the universal recipient? Be specific. B. What is a blood transfusion? Why are transfu ...
Biohazard Exposure
... blood products, or blood components. OPIM includes all body fluids in situations where it is difficult or impossible to differentiate between body fluids. This primarily applies to employees routinely exposed to blood or OPIM such as; first responders, healthcare/medical treatment providers, etc. An ...
... blood products, or blood components. OPIM includes all body fluids in situations where it is difficult or impossible to differentiate between body fluids. This primarily applies to employees routinely exposed to blood or OPIM such as; first responders, healthcare/medical treatment providers, etc. An ...
Blood as a Soil on Surgical Instruments: Chemical Profile, Cleaning
... Myriad detection methods are described in the literature (10). In all these determination methods it is, however, essential to quantitatively bring the residual soil to solution. Since in the case of a residual soil in washer/disinfectors, water-soluble, surfactant-soluble and easily hydrolysed prot ...
... Myriad detection methods are described in the literature (10). In all these determination methods it is, however, essential to quantitatively bring the residual soil to solution. Since in the case of a residual soil in washer/disinfectors, water-soluble, surfactant-soluble and easily hydrolysed prot ...
Blood Typing Wksht - Mrs. Zedan`s Science
... Two parents think their baby was switched at the hospital. Its 1968, so DNA fingerprinting technology does not exist yet. The mother has blood type “O,” the father has blood type “AB,” and the baby has blood type “AB.” a. Mother’s genotype: _______ b. Father’s genotype: _______ c. Baby’s genotype: _ ...
... Two parents think their baby was switched at the hospital. Its 1968, so DNA fingerprinting technology does not exist yet. The mother has blood type “O,” the father has blood type “AB,” and the baby has blood type “AB.” a. Mother’s genotype: _______ b. Father’s genotype: _______ c. Baby’s genotype: _ ...
or rabbit anti-CD36 and mouse
... The effect of detergents on CD36-associated proteins.(A) Platelet membrane proteins were labeled with biotin and lysed in 1% CHAPS (lane 1), Triton X-100 (lane 2), Brij 96 (lane 3), or Brij 99 (lane 4), and CD36 was immunoprecipitated with the monoclonal an... ...
... The effect of detergents on CD36-associated proteins.(A) Platelet membrane proteins were labeled with biotin and lysed in 1% CHAPS (lane 1), Triton X-100 (lane 2), Brij 96 (lane 3), or Brij 99 (lane 4), and CD36 was immunoprecipitated with the monoclonal an... ...
5.5 Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure and Sharps Injury Policy
... Leak-proof on the sides and bottom. Bio-hazardous Storage Specimens of blood or other potentially infectious materials should be placed in a color-coded container, labeled “Biohazard Material”, which prevents leakage during collection, storage, transport, or shipping. A secondary container must be ...
... Leak-proof on the sides and bottom. Bio-hazardous Storage Specimens of blood or other potentially infectious materials should be placed in a color-coded container, labeled “Biohazard Material”, which prevents leakage during collection, storage, transport, or shipping. A secondary container must be ...
Blood donation
A blood donation occurs when a person voluntarily has blood drawn and used for transfusions and/or made into biopharmaceutical medications by a process called fractionation (separation of whole-blood components). Donation may be of whole blood (WB), or of specific components directly (the latter called apheresis). Blood banks often participate in the collection process as well as the procedures that follow it.Today, in the developed world, most blood donors are unpaid volunteers who donate blood for a community supply. In poorer countries, established supplies are limited and donors usually give blood when family or friends need a transfusion (directed donation). Many donors donate as an act of charity, but in countries that allow paid donation some donors are paid, and in some cases there are incentives other than money such as paid time off from work. Donors can also have blood drawn for their own future use (autologous donation). Donating is relatively safe, but some donors have bruising where the needle is inserted or may feel faint.Potential donors are evaluated for anything that might make their blood unsafe to use. The screening includes testing for diseases that can be transmitted by a blood transfusion, including HIV and viral hepatitis. The donor must also answer questions about medical history and take a short physical examination to make sure the donation is not hazardous to his or her health. How often a donor can give varies from days to months based on what he or she donates and the laws of the country where the donation takes place. For example, in the United States, donors must wait eight weeks (56 days) between whole blood donations but only seven days between platelet pheresis donations.The amount of blood drawn and the methods vary. The collection can be done manually or with automated equipment that only takes specific portions of the blood. Most of the components of blood used for transfusions have a short shelf life, and maintaining a constant supply is a persistent problem. This has led to some increased interest in autotransfusion, whereby a patient's blood is salvaged during surgery for continuous reinfusion — or alternatively, is ""self-donated"" prior to when it will be needed. (Generally, the notion of ""donation"" does not refer to giving to one's self, though in this context it has become somewhat acceptably idiomatic.)