Mitosis PPT
... • DNA becomes visible as chromosomes • Nuclear membrane dissolves • Centrioles migrate to opposite poles • Spindle fibers form Easy to remember- Prophase- proceeding into mitosis ...
... • DNA becomes visible as chromosomes • Nuclear membrane dissolves • Centrioles migrate to opposite poles • Spindle fibers form Easy to remember- Prophase- proceeding into mitosis ...
Mitosis PPT
... • DNA becomes visible as chromosomes • Nuclear membrane dissolves • Centrioles migrate to opposite poles • Spindle fibers form Easy to remember- Prophase- proceeding into mitosis ...
... • DNA becomes visible as chromosomes • Nuclear membrane dissolves • Centrioles migrate to opposite poles • Spindle fibers form Easy to remember- Prophase- proceeding into mitosis ...
Aim: How can we apply our knowledge of cells?
... 1. Label the picture with each phase of mitosis. 2. Write a description of each phase of mitosis. 3. Identify the part of the cell cycle being discussed. a. b. c. d. ...
... 1. Label the picture with each phase of mitosis. 2. Write a description of each phase of mitosis. 3. Identify the part of the cell cycle being discussed. a. b. c. d. ...
NAME - cloudfront.net
... B. similar but not identical 5. Homologous chromosomes are _____________________. A. identical copies B. similar but not identical 6. Cells spend most of their lifetime in _____________________ phase of interphase. A. Mitosis B. S C. G1 D. G2 ...
... B. similar but not identical 5. Homologous chromosomes are _____________________. A. identical copies B. similar but not identical 6. Cells spend most of their lifetime in _____________________ phase of interphase. A. Mitosis B. S C. G1 D. G2 ...
MITOSIS
... b. Kinetochore fibers faster to the chromosomes and move them around METAPHASE 1. Kinetochore fibers move the 46 chromosomes to the middle of the cell where they line up ANAPHASE 1. Kindetochore fibers begin to shorten, thus pulling the chromosomes apart 2. now have 46 chromatids on each end of the ...
... b. Kinetochore fibers faster to the chromosomes and move them around METAPHASE 1. Kinetochore fibers move the 46 chromosomes to the middle of the cell where they line up ANAPHASE 1. Kindetochore fibers begin to shorten, thus pulling the chromosomes apart 2. now have 46 chromatids on each end of the ...
Cell Cycle: Mitosis Labeling
... Word bank for the above: prophase chromatids chromatin interphase nuclear membrane daughter cells ...
... Word bank for the above: prophase chromatids chromatin interphase nuclear membrane daughter cells ...
79099_Mitosis
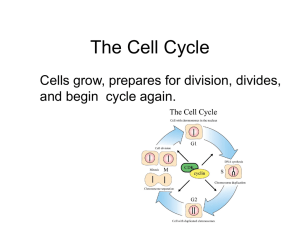
... of the cell cycle Busiest phase of the cell cycle G1: Cell grows in size and protein production is high S: Cell copies it’s chromosomes G2: After DNA is replicated organelles such as mitochondria are manufactured and cell parts needed for cell division are assembled. ...
... of the cell cycle Busiest phase of the cell cycle G1: Cell grows in size and protein production is high S: Cell copies it’s chromosomes G2: After DNA is replicated organelles such as mitochondria are manufactured and cell parts needed for cell division are assembled. ...
Mitosis
... Preparation For Mitosis ● S stage: DNA is copied ● G2 stage: organelles and molecules necessary for mitosis are produced ...
... Preparation For Mitosis ● S stage: DNA is copied ● G2 stage: organelles and molecules necessary for mitosis are produced ...
Cell Cycle Check
... 5. Centromeres attach to centrioles. 6. The nuclear membrane reforms in anaphase. 7. Chromatids form as a result of replication. 8. Centromeres break apart in telophase. 9. DNA strands in eukaryotic cells exist in multiples of two. 10. The “poles” are creaked by the spindle fibers. 11. Two pairs of ...
... 5. Centromeres attach to centrioles. 6. The nuclear membrane reforms in anaphase. 7. Chromatids form as a result of replication. 8. Centromeres break apart in telophase. 9. DNA strands in eukaryotic cells exist in multiples of two. 10. The “poles” are creaked by the spindle fibers. 11. Two pairs of ...
Mitosis
... Stage where dividing cells spend the most time The cells chromatin tightens, or condenses into chromosomes The chromosomes are shaped like an X Each chromosome is a single structure that contains the genetic material ...
... Stage where dividing cells spend the most time The cells chromatin tightens, or condenses into chromosomes The chromosomes are shaped like an X Each chromosome is a single structure that contains the genetic material ...
Section 9.2 * Mitosis and Cytokinesis
... Where Do I Find DNA? • Chromosomes are in the nucleus of every cell. • Chromosomes are made up of DNA. • Genes are pieces of DNA that contain the instructions for building a protein. ...
... Where Do I Find DNA? • Chromosomes are in the nucleus of every cell. • Chromosomes are made up of DNA. • Genes are pieces of DNA that contain the instructions for building a protein. ...
Mitosis Essay - msvictorialin
... Mitosis Essay Prepare to write an in class essay about the following topic: Describe the process of cell division in somatic cells. Include a description of what happens in each phase of mitosis. ...
... Mitosis Essay Prepare to write an in class essay about the following topic: Describe the process of cell division in somatic cells. Include a description of what happens in each phase of mitosis. ...
MITOSIS
... continued to grow until it is fully formed. At telophase the duplicate of each of the original centrioles is completed and each of the two centrioles at each pole begins to generate a new daughter centriole at right angles to it. When cytokinesis is nearly complete, and the spindle disappears as the ...
... continued to grow until it is fully formed. At telophase the duplicate of each of the original centrioles is completed and each of the two centrioles at each pole begins to generate a new daughter centriole at right angles to it. When cytokinesis is nearly complete, and the spindle disappears as the ...
Mitosis
... • Chromosomes lined up in Middle • Spindle fibers attach at centromere (Kinetochores) • Spindle apparatus stretches from pole to pole ...
... • Chromosomes lined up in Middle • Spindle fibers attach at centromere (Kinetochores) • Spindle apparatus stretches from pole to pole ...
Slide 1
... How do Molecules form Living, Moving, Reproducing Cells? 1683, Leeuwenhoek: “An unbelievably great company of living animalcules, a-swimming more nimbly than any I had ever seen up to this time. The biggest sort bent their body into curves in going forwards." ...
... How do Molecules form Living, Moving, Reproducing Cells? 1683, Leeuwenhoek: “An unbelievably great company of living animalcules, a-swimming more nimbly than any I had ever seen up to this time. The biggest sort bent their body into curves in going forwards." ...
Homologous chromosomes Homologous chromosomes Sister
... • DN A has been replicated • Centrioles replicate (animal cells) • Cell prepares for division ...
... • DN A has been replicated • Centrioles replicate (animal cells) • Cell prepares for division ...
Document
... nucleus. Centrioles move to the poles and the nuclear envelope breaks down. Kinetochore microtubules attach kinetochores of chromosomes to spindle poles. Polar microtubules extend toward the center of the cell and overlap. ...
... nucleus. Centrioles move to the poles and the nuclear envelope breaks down. Kinetochore microtubules attach kinetochores of chromosomes to spindle poles. Polar microtubules extend toward the center of the cell and overlap. ...
Bacterial cell Septum Bacterial chromosome: Double
... nucleus. Centrioles move to the poles and the nuclear envelope breaks down. Kinetochore microtubules attach kinetochores of chromosomes to spindle poles. Polar microtubules extend toward the center of the cell and overlap. ...
... nucleus. Centrioles move to the poles and the nuclear envelope breaks down. Kinetochore microtubules attach kinetochores of chromosomes to spindle poles. Polar microtubules extend toward the center of the cell and overlap. ...
A New Role for a Long-Studied DNA
... mitotic spindle—a spider-like array of microtubule proteins—via specialized structures called kinetochores, protein complexes that bind the chromosome’s centromere to connect sister chromatids to the spindle. For PLoS Biology | www.plosbiology.org ...
... mitotic spindle—a spider-like array of microtubule proteins—via specialized structures called kinetochores, protein complexes that bind the chromosome’s centromere to connect sister chromatids to the spindle. For PLoS Biology | www.plosbiology.org ...
Kinetochore

The kinetochore /kɪˈnɛtəkɔər/ is the protein structure on chromatids where the spindle fibers attach during cell division to pull sister chromatids apart.The kinetochore forms in eukaryotes, assembles on the centromere and links the chromosome to microtubule polymers from the mitotic spindle during mitosis and meiosis.""Monocentric"" organisms, including vertebrates, fungi, and most plants, have a single centromeric region on each chromosome which assembles one kinetochore. ""Holocentric"" organisms, such as nematodes and some plants, assemble a kinetochore along the entire length of a chromosome.The kinetochore contains two regions: an inner kinetochore, which is tightly associated with the centromere DNA, assembled in a specialized form of chromatin persistent throughout the cell cycle; an outer kinetochore, which interacts with microtubules; the outer kinetochore is a very dynamic structure, with many identical components, which are assembled and functional only during cell division.Kinetochores start, control and supervise the striking movements of chromosomes during cell division. During mitosis, which occurs after chromosomes are duplicated during S phase, two sister chromatids are held together each with its own kinetochore which face in opposing directions and attach to opposite poles of the mitotic spindle. Following the transition from metaphase to anaphase, the sister chromatids separate from each other, and the individual kinetochores on each chromatid drive their movement to the spindle poles that will define the two new daughter cells. Thus, the kinetochore is essential for the chromosome segregation that is classically associated with mitosis and meiosis.Even the simplest kinetochores consist of more than 19 different proteins. Many of these proteins are conserved between eukaryotic species, including a specialized histone H3 variant (called CENP-A or CenH3) which helps the kinetochore associate with DNA. Other proteins in the kinetochore attach it to the microtubules (MTs) of the mitotic spindle. There are also motor proteins, including both dynein and kinesin, which generate forces that move chromosomes during mitosis. Other proteins, such as MAD2 monitor the microtubule attachment as well as the tension between sister kinetochores and activate the spindle checkpoint to arrest the cell cycle when either of these is absent.In summary, kinetochore functions include anchoring of chromosomes to MTs in the spindle, verification of anchoring, activation of the spindle checkpoint and participation in force generation to propel chromosome movement during cell division.On the other hand, MTs are metastable polymers made of α- and β-tubulin, alternating between growing and shrinking phases, a phenomenon known as ""dynamic instability"". MTs are highly dynamic structures, whose behavior is integrated with kinetochore function to control chromosome movement and segregation.