Cell Webquest
... Go to the interactive cell model at http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model_js.htm. Click and explore each organelle to answer the following questions. 1. What does the nucleus contain? ...
... Go to the interactive cell model at http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model_js.htm. Click and explore each organelle to answer the following questions. 1. What does the nucleus contain? ...
Microtubules Show their Sensitive Nature
... their structural properties put to useful work as scaffolds and barriers. Just how microtubules do this, however, is still a matter of debate, and recent conflicting interpretations (compare, for example, Burk and Ye 2002 and Sugimoto et al. 2003) suggest that we are far away from understanding this ...
... their structural properties put to useful work as scaffolds and barriers. Just how microtubules do this, however, is still a matter of debate, and recent conflicting interpretations (compare, for example, Burk and Ye 2002 and Sugimoto et al. 2003) suggest that we are far away from understanding this ...
Lecture 7: Intro to the cell, cont
... • maintain cell shape by resisting compression • motility via flagella/cilia • anchor nucleus • move organelles and some other organelles • move chromosomes during cell division ...
... • maintain cell shape by resisting compression • motility via flagella/cilia • anchor nucleus • move organelles and some other organelles • move chromosomes during cell division ...
Stages of Mitosis
... Metaphase plate – Plane that is equidistant from both of the spindles’ poles ...
... Metaphase plate – Plane that is equidistant from both of the spindles’ poles ...
The Cytoskeleton… but first:
... • The position of the centrioles determines the location of the nucleus, cell shape, and the location of flagella and cilia in Eukaryotic cells that have these. • NOT found in: prokaryotes, most plants, fungi. – Eukaryotic cell types have a tubulin network attached to different protein structures MT ...
... • The position of the centrioles determines the location of the nucleus, cell shape, and the location of flagella and cilia in Eukaryotic cells that have these. • NOT found in: prokaryotes, most plants, fungi. – Eukaryotic cell types have a tubulin network attached to different protein structures MT ...
MB207_15 - MB207Jan2010
... cells) that associate laterally to form a 24nm wide hollow cylinder. • Different polymerization rates at two ends: → In each protofilament, the heterodimers are oriented with their β-tubulin monomer pointing towards the faster-growing end (plus end) and their α-tubulin monomer exposed at the slower- ...
... cells) that associate laterally to form a 24nm wide hollow cylinder. • Different polymerization rates at two ends: → In each protofilament, the heterodimers are oriented with their β-tubulin monomer pointing towards the faster-growing end (plus end) and their α-tubulin monomer exposed at the slower- ...
Ch 3 Check Your Progress Answers BC Biology 12 3.1 p 67 1
... Actin: long, extremely thin, flexible fibers that occur in bundles or meshlike networks, 2 chains of globular actin monomers twisted about each other in a helical manner intermediate: intermediate in size between actin and microtubules; rope-like assembly of fibrous polypeptides microtubules: small ...
... Actin: long, extremely thin, flexible fibers that occur in bundles or meshlike networks, 2 chains of globular actin monomers twisted about each other in a helical manner intermediate: intermediate in size between actin and microtubules; rope-like assembly of fibrous polypeptides microtubules: small ...
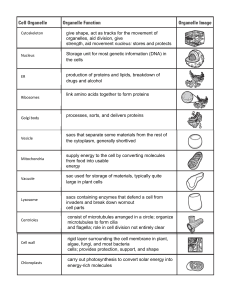
Ch 6 Organelles
... h. __________________ Connects the cytoplasm of one plant cell to another i. __________________Packages proteins for transport out of the cell j. __________________The site of cellular respiration k. __________________Composed mainly of cellulose l. __________________Synthesizes lipids m. __________ ...
... h. __________________ Connects the cytoplasm of one plant cell to another i. __________________Packages proteins for transport out of the cell j. __________________The site of cellular respiration k. __________________Composed mainly of cellulose l. __________________Synthesizes lipids m. __________ ...
Slide 1
... like mitochondria, and chromosomes via special attachment proteins. They also serve a cytoskeletal role. Structurally, they are polymers of tubulin which is a globular protein.. The tubulin molecules are the bead like structures. A protofilament is a linear row of tubulin dimers. Microtubules may wo ...
... like mitochondria, and chromosomes via special attachment proteins. They also serve a cytoskeletal role. Structurally, they are polymers of tubulin which is a globular protein.. The tubulin molecules are the bead like structures. A protofilament is a linear row of tubulin dimers. Microtubules may wo ...
Cytoskeleton Handout
... Actin participates in force generation (eg., cell motility) via interactions with myosin. Myosin is an actin-activated ATPase that converts chemical energy (i.e., ATP) into mechanical energy by moving along microfilaments (or by moving the actin filaments). Cellular motility is a dynamic process inv ...
... Actin participates in force generation (eg., cell motility) via interactions with myosin. Myosin is an actin-activated ATPase that converts chemical energy (i.e., ATP) into mechanical energy by moving along microfilaments (or by moving the actin filaments). Cellular motility is a dynamic process inv ...
Introduction Part1
... Neck linker of leading head “zips up” agains catalytic core trailing head is thrown forward (trailing head has bound ADP and reduced affinity to microtubule): Trailing head swings by ~ 160 Å, net movement of dimeric kinesin is ~ 80 Å = length of one microtubule dimer ATP in new trailing head is hydr ...
... Neck linker of leading head “zips up” agains catalytic core trailing head is thrown forward (trailing head has bound ADP and reduced affinity to microtubule): Trailing head swings by ~ 160 Å, net movement of dimeric kinesin is ~ 80 Å = length of one microtubule dimer ATP in new trailing head is hydr ...
Actin filaments
... "scaffolding" or "skeleton" contained within the cytoplasm that is made out of protein. The cytoskeleton is present in all cells; it was once thought this structure was unique to eukaryotes, but recent research has identified the prokaryotic cytoskeleton. ...
... "scaffolding" or "skeleton" contained within the cytoplasm that is made out of protein. The cytoskeleton is present in all cells; it was once thought this structure was unique to eukaryotes, but recent research has identified the prokaryotic cytoskeleton. ...
Biology 52: Problem Set for Lectures 9, 10, and 11
... internal stores in the ER, and diacylglycerol (DAG). The combined effect of a calcium transient and DAG production is to activate protein kinase C and recruit it to the membrane for phosphorylation of its downstream targets. 3. Of the two types of signaling molecules we discussed in class (large hyd ...
... internal stores in the ER, and diacylglycerol (DAG). The combined effect of a calcium transient and DAG production is to activate protein kinase C and recruit it to the membrane for phosphorylation of its downstream targets. 3. Of the two types of signaling molecules we discussed in class (large hyd ...
Tutorial 8 – Cytoskeleton
... FUNCTION: These macromolecular assemblies are involved mainly in the movement and positioning of cell organelles. - Minus end is attached to centrosome (or Microtubule organization Center) - Plus end is free ...
... FUNCTION: These macromolecular assemblies are involved mainly in the movement and positioning of cell organelles. - Minus end is attached to centrosome (or Microtubule organization Center) - Plus end is free ...
Lecture 16 Outline
... assembly slows, now loses GTP cap- rapid shortening of MT. Drugs and MAPS (Microtubule Associated Proteins) can influence rate of assembly/ disassembly. Microtubules nucleate at MTOCs – centrosome is main one of animal cells. Gamma tubulin present in rings- sites for MT assembly. Serves several func ...
... assembly slows, now loses GTP cap- rapid shortening of MT. Drugs and MAPS (Microtubule Associated Proteins) can influence rate of assembly/ disassembly. Microtubules nucleate at MTOCs – centrosome is main one of animal cells. Gamma tubulin present in rings- sites for MT assembly. Serves several func ...
A1981LH86500001
... been so puzzlingly empty. The newly found microtubules were in an appropriate place to influence wall deposition and, moreover, they mirrored in orientation the adjacent microfibrils of cellulose being deposited in the walls Once we tied the arrangement of these structures in the cytoplasm to a prob ...
... been so puzzlingly empty. The newly found microtubules were in an appropriate place to influence wall deposition and, moreover, they mirrored in orientation the adjacent microfibrils of cellulose being deposited in the walls Once we tied the arrangement of these structures in the cytoplasm to a prob ...
A molecular mechanism involved in cellular proliferation
... the scientific community as microtubules. Key molecules for cellular proliferation "During cell division, alterations in microtubule formation may bring about chromosome instability and aneuploidy. In other words, alterations in the number of chromosomes, which can lead to a tumour process," explain ...
... the scientific community as microtubules. Key molecules for cellular proliferation "During cell division, alterations in microtubule formation may bring about chromosome instability and aneuploidy. In other words, alterations in the number of chromosomes, which can lead to a tumour process," explain ...
Advanced Cell Biology
... A solution of pure abtubulin dimers is thought to nucleate microtubules by forming a linear protofilament about seven dimers in length. At that point, the probabilities that the next αß-dimer will bind laterally or to the end of the protofilament are bound equal. The critical event for microtubule f ...
... A solution of pure abtubulin dimers is thought to nucleate microtubules by forming a linear protofilament about seven dimers in length. At that point, the probabilities that the next αß-dimer will bind laterally or to the end of the protofilament are bound equal. The critical event for microtubule f ...
carry out photosynthesis to convert solar energy into energy
... give shape, act as tracks for the movement of organelles, aid division, give strength, aid movement nucleus: stores and protects the DNA Storage unit for most genetic information (DNA) in the cells production of proteins and lipids, breakdown of drugs and alcohol link amino acids together to form pr ...
... give shape, act as tracks for the movement of organelles, aid division, give strength, aid movement nucleus: stores and protects the DNA Storage unit for most genetic information (DNA) in the cells production of proteins and lipids, breakdown of drugs and alcohol link amino acids together to form pr ...
Microtubule

Microtubules (micro- + tube + -ule) are a component of the cytoskeleton, found throughout the cytoplasm. These tubular polymers of tubulin can grow as long as 50 micrometres and are highly dynamic. The outer diameter of a microtubule is about 24 nm while the inner diameter is about 12 nm. They are found in eukaryotic cells and are formed by the polymerization of a dimer of two globular proteins, alpha and beta tubulin.Microtubules are very important in a number of cellular processes. They are involved in maintaining the structure of the cell and, together with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, they form the cytoskeleton. They also make up the internal structure of cilia and flagella.They provide platforms for intracellular transport and are involved in a variety of cellular processes, including the movement of secretory vesicles, organelles, and intracellular macromolecular assemblies (see entries for dynein and kinesin). They are also involved in chromosome separation (mitosis and meiosis), and are the major constituents of mitotic spindles, which are used to pull apart eukaryotic chromosomes.Microtubules are nucleated and organized by microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs), such as the centrosome found in the center of many animal cells or the basal bodies found in cilia and flagella, or the spindle pole bodies found in fungi.There are many proteins that bind to microtubules, including the motor proteins kinesin and dynein, severing proteins like katanin, and other proteins important for regulating microtubule dynamics.