+ X(t)
... • Consider a CT-LTI system. Assume the impulse response of the system is h(t)=e^(-at) for all a>0 and t>0 and input x(t)=u(t). Find the output. y (t ) h(t ) x(t ) h(t ) u (t ) ...
... • Consider a CT-LTI system. Assume the impulse response of the system is h(t)=e^(-at) for all a>0 and t>0 and input x(t)=u(t). Find the output. y (t ) h(t ) x(t ) h(t ) u (t ) ...
2007 Minnesota K-12 Academic Standards in Mathematics by
... graphing and the quadratic formula. Find non-real complex roots when they exist. Recognize that a particular solution may not be applicable in the original context. Know how to use calculators, graphing utilities or other technology to solve quadratic equations and inequalities. 9.2.4.2 Represent r ...
... graphing and the quadratic formula. Find non-real complex roots when they exist. Recognize that a particular solution may not be applicable in the original context. Know how to use calculators, graphing utilities or other technology to solve quadratic equations and inequalities. 9.2.4.2 Represent r ...
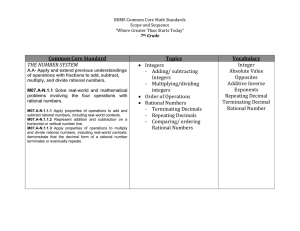
6th Grade Math Curriculum Map Created By Jason Hall Unit 1
... Vocabulary: capacity, Celsius, Fahrenheit, metric, customary, elapsed time, ante meridiem, post meridiem, unit rate ...
... Vocabulary: capacity, Celsius, Fahrenheit, metric, customary, elapsed time, ante meridiem, post meridiem, unit rate ...
Lesson 6-2
... – If a trinomial can be written in the form a2 + 2ab + b2 or a2 – 2ab + b2, then it can be factored as (a + b)2 or (a – b)2, respectively – For a trinomial to be factorable as a perfect square, the first term must be a perfect square, the middle must be twice the product of the square roots of the f ...
... – If a trinomial can be written in the form a2 + 2ab + b2 or a2 – 2ab + b2, then it can be factored as (a + b)2 or (a – b)2, respectively – For a trinomial to be factorable as a perfect square, the first term must be a perfect square, the middle must be twice the product of the square roots of the f ...
Ch9.5 - aianjack.com
... equation. A quadratic equation is an equation that can be written in the standard form ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. When writing a quadratic function as its related quadratic equation, you replace y with 0. So y = 0. y = ax2 + bx + c 0 = ax2 + bx + c ax2 + bx + c = ...
... equation. A quadratic equation is an equation that can be written in the standard form ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. When writing a quadratic function as its related quadratic equation, you replace y with 0. So y = 0. y = ax2 + bx + c 0 = ax2 + bx + c ax2 + bx + c = ...
Slide 1
... Step 2 Write the related function. y = x2 + 4x – 20 Step 3 Graph the related function. • The axis of symmetry is x = – . • The vertex is (–0.5, –20.25). • Two other points are (1, –18) and (2, –15) • Graph the points and reflect them across the axis of symmetry. ...
... Step 2 Write the related function. y = x2 + 4x – 20 Step 3 Graph the related function. • The axis of symmetry is x = – . • The vertex is (–0.5, –20.25). • Two other points are (1, –18) and (2, –15) • Graph the points and reflect them across the axis of symmetry. ...