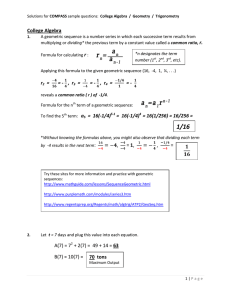
Gr04_Ch_03 - Etiwanda E
... Identify any missing or extra information. Use the four-step plan in this problem; solve if possible. Viviana is taking a late train from home to visit her cousins. The train leaves Savannah at 11 A.M. and arrives in Charleston at 1:30 P.M. on July 13. How long is Viviana’s trip? A. 2 hours and 30 m ...
... Identify any missing or extra information. Use the four-step plan in this problem; solve if possible. Viviana is taking a late train from home to visit her cousins. The train leaves Savannah at 11 A.M. and arrives in Charleston at 1:30 P.M. on July 13. How long is Viviana’s trip? A. 2 hours and 30 m ...
Pre-Algebra
... Variables and Expressions Variable – a symbol used to represent a quantity that can change. Coefficient – the number that is multiplied by the variable in an algebraic expression. Numerical expression – an expression that contains only numbers and operations. Algebraic expression – an expression th ...
... Variables and Expressions Variable – a symbol used to represent a quantity that can change. Coefficient – the number that is multiplied by the variable in an algebraic expression. Numerical expression – an expression that contains only numbers and operations. Algebraic expression – an expression th ...
Generalized Eigenvectors
... This new pair of equations is not completely decoupled, but the equation for qn does not involve pn. We can solve the equation for qn first and substitute the solution into the equation for pn and then solve that. For the equation for qn the solution to the homogeneous equation qn+1 = 2qn is qn = C ...
... This new pair of equations is not completely decoupled, but the equation for qn does not involve pn. We can solve the equation for qn first and substitute the solution into the equation for pn and then solve that. For the equation for qn the solution to the homogeneous equation qn+1 = 2qn is qn = C ...
Document
... The remainder, r(x), equals 0 or its is of degree less than the degree of d(x). If r(x) = 0, we say that d(x) divides evenly in to f (x) and that d(x) and q(x) are factors of f (x). ...
... The remainder, r(x), equals 0 or its is of degree less than the degree of d(x). If r(x) = 0, we say that d(x) divides evenly in to f (x) and that d(x) and q(x) are factors of f (x). ...