IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... Gives the angle of inclination of each planet. ( n=1:Mercury, n=2:Venus, n=3:Earth…..etc) ...
... Gives the angle of inclination of each planet. ( n=1:Mercury, n=2:Venus, n=3:Earth…..etc) ...
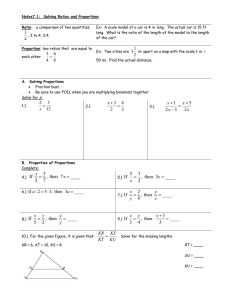
Name: EOC - Unit 1 Practice Slope Intercept Form Example What is
... The standard form of a linear equation is Ax + By = C, where A, B, and C are real numbers, and A and B are not both zero. You can easily determine the x- and y-intercepts of the graph from this form of the equation. Each intercept occurs when one coordinate is 0. When substituting 0 for either of x ...
... The standard form of a linear equation is Ax + By = C, where A, B, and C are real numbers, and A and B are not both zero. You can easily determine the x- and y-intercepts of the graph from this form of the equation. Each intercept occurs when one coordinate is 0. When substituting 0 for either of x ...
Solving Linear Inequalities in One Variable
... 6.2 Problem Solving Example: A cell phone company offers its customers a rate of $89 per month for 350 minutes, or a rate of $40 per month plus $0.50 for each minute used. How many minutes per month can a customer who chooses the second plan use before the charges exceed those of the first plan? Le ...
... 6.2 Problem Solving Example: A cell phone company offers its customers a rate of $89 per month for 350 minutes, or a rate of $40 per month plus $0.50 for each minute used. How many minutes per month can a customer who chooses the second plan use before the charges exceed those of the first plan? Le ...
Chapter #7
... To multiply radicals consider the following: √16 * √9 = 4 *3 =12 and √16 *9 = √144 = 12 ...
... To multiply radicals consider the following: √16 * √9 = 4 *3 =12 and √16 *9 = √144 = 12 ...
Dividing Polynomials
... Use synthetic division to divide 5x3 + 6x + 8 by x + 2. Solution The divisor must be in the form x – c. Thus, we write x + 2 as x – (-2). This means that c = -2. Writing a 0 coefficient for the missing x2term in the dividend, we can express the division as follows: x – (-2) 5x3 + 0x2 + 6x + 8 . ...
... Use synthetic division to divide 5x3 + 6x + 8 by x + 2. Solution The divisor must be in the form x – c. Thus, we write x + 2 as x – (-2). This means that c = -2. Writing a 0 coefficient for the missing x2term in the dividend, we can express the division as follows: x – (-2) 5x3 + 0x2 + 6x + 8 . ...
Chapter 8 - James Bac Dang
... • D is the determinant that results from the coefficients of all variables. • Dx is the determinant that results when each x coefficient is replaced with the given constants. • D y is the determinant that results when each y coefficient is replaced with the given constants. • Dz is the determinant t ...
... • D is the determinant that results from the coefficients of all variables. • Dx is the determinant that results when each x coefficient is replaced with the given constants. • D y is the determinant that results when each y coefficient is replaced with the given constants. • Dz is the determinant t ...