Elliptic Curve Cryptography
... 1. Type of operations used to for transforming plaintext to cipher text: Most encryption algorithms are based on 2 general principles, a. Substitution, in which each element in plain text is mapped to some other element to form the cipher text b. Transposition, in which elements in plaintext are rea ...
... 1. Type of operations used to for transforming plaintext to cipher text: Most encryption algorithms are based on 2 general principles, a. Substitution, in which each element in plain text is mapped to some other element to form the cipher text b. Transposition, in which elements in plaintext are rea ...
Greatest Common Factor
... • Elena's backpack weighs the most. • Owen’s backpack weighs 0.45 lb less than Joe's backpack. • Samantha's lunch weighs 1.5 lb. With that lunch out of the backpack, the backpack weighs 16.55 lb. • Tuck's backpack weighs more than Owen's. • How much does each person's backpack weigh? ...
... • Elena's backpack weighs the most. • Owen’s backpack weighs 0.45 lb less than Joe's backpack. • Samantha's lunch weighs 1.5 lb. With that lunch out of the backpack, the backpack weighs 16.55 lb. • Tuck's backpack weighs more than Owen's. • How much does each person's backpack weigh? ...
and x
... STEP 1 Find the rational zero of f. because f is a polynomial function degree 5, it has 5 zero. The possible rational zeros are –+ 1 , –+2, –+ 3 and –+ 6. Using synthetic division, you can determine that 1 is a zero reputed twice and –3 is also a zero STEP 2 Write f (x) in factored form dividing f( ...
... STEP 1 Find the rational zero of f. because f is a polynomial function degree 5, it has 5 zero. The possible rational zeros are –+ 1 , –+2, –+ 3 and –+ 6. Using synthetic division, you can determine that 1 is a zero reputed twice and –3 is also a zero STEP 2 Write f (x) in factored form dividing f( ...
Logic in Computer Science
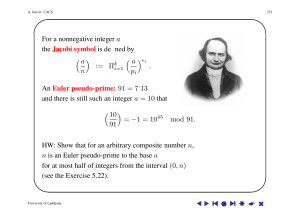
... In a sense, propositional logic (PL) is the coarsest logic: PL is domain-independent. Statements are only distinguished with respect to their truth values, e.g., there is no difference between the sentences “2 + 3 = 5” and “Konstanz is situated on Lake Constance” as both statements are true. So, sta ...
... In a sense, propositional logic (PL) is the coarsest logic: PL is domain-independent. Statements are only distinguished with respect to their truth values, e.g., there is no difference between the sentences “2 + 3 = 5” and “Konstanz is situated on Lake Constance” as both statements are true. So, sta ...
Global Consistency for Continuous Constraints
... to the case of CCSPs. We first have to extend the lemma on which his proofs are based. This can be done as follows: Lemma 1 Let F be a finite collection of x-convex regions in 6 = . If F is such that every pair of regions has a non null x-intersection, then the x-intersection of all these regions is ...
... to the case of CCSPs. We first have to extend the lemma on which his proofs are based. This can be done as follows: Lemma 1 Let F be a finite collection of x-convex regions in 6 = . If F is such that every pair of regions has a non null x-intersection, then the x-intersection of all these regions is ...
Very dense subsets of a topological space.
... Indeed, the k-rational points are the closed points, by (I, 6.4.2), and X is Jacobson. (10.4.9–11). A number of questions in algebraic geometry can be reduced to the case of a finitely generated algebra over Z or a field, so the fact that such rings are Jacobson is particularly important. EGA gives ...
... Indeed, the k-rational points are the closed points, by (I, 6.4.2), and X is Jacobson. (10.4.9–11). A number of questions in algebraic geometry can be reduced to the case of a finitely generated algebra over Z or a field, so the fact that such rings are Jacobson is particularly important. EGA gives ...