Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2013 Semester Lecture 30 – Geometric Optics
... • All you need to know about a lens is its focal length ...
... • All you need to know about a lens is its focal length ...
telestar instruction manual
... The telescope is shipped with the following parts: • Optical tube • Aluminum tripod with an accessory tray • Two 1.25" eyepieces: MA25mm (28X), MH9mm (78X) • 2x 1.25" Barlow lens • Diagonal mirror • Red dot viewfinder with bracket • Telescope mount The tube has a focal length of 700mm, and its objec ...
... The telescope is shipped with the following parts: • Optical tube • Aluminum tripod with an accessory tray • Two 1.25" eyepieces: MA25mm (28X), MH9mm (78X) • 2x 1.25" Barlow lens • Diagonal mirror • Red dot viewfinder with bracket • Telescope mount The tube has a focal length of 700mm, and its objec ...
Celestron Manual
... Although the power is variable, every telescope under average skies has a limit to the highest useful magnification. The general rule is that 60 power can be used for every inch of aperture. For example, the Travel Scope 70 is 2.8” inches in diameter. Multiplying 2.8 by 60 gives a maximum useful mag ...
... Although the power is variable, every telescope under average skies has a limit to the highest useful magnification. The general rule is that 60 power can be used for every inch of aperture. For example, the Travel Scope 70 is 2.8” inches in diameter. Multiplying 2.8 by 60 gives a maximum useful mag ...
TOPS Optical Bench Finding Focal Length of Lenses and
... Procedure to determine the focal length of the 50mm mirror: 1. Replace the 150mm lens with the 50mm mirror. Mount the mirror on the right side of the component holder with the writing facing to the right. 2. Put the mirror at the 22cm mark. 3. Remove the viewing screen from its component holder 4. T ...
... Procedure to determine the focal length of the 50mm mirror: 1. Replace the 150mm lens with the 50mm mirror. Mount the mirror on the right side of the component holder with the writing facing to the right. 2. Put the mirror at the 22cm mark. 3. Remove the viewing screen from its component holder 4. T ...
Sample Pages
... the eye. Therefore, the depth of field is calculated by the difference between two working distances: the working distance of the objective lens when the final image is located 250 mm from the exit pupil of the eyepiece and the working distance when the image is at infinity. When a CCD or CMOS senso ...
... the eye. Therefore, the depth of field is calculated by the difference between two working distances: the working distance of the objective lens when the final image is located 250 mm from the exit pupil of the eyepiece and the working distance when the image is at infinity. When a CCD or CMOS senso ...
Observational Astronomy
... ESO flagship. Twin 8-m telescopes in the Northern and Southern hemispheres. Twin 6.5-m telescopes; also known as the Walter Baade and Landon Clay telescopes. ...
... ESO flagship. Twin 8-m telescopes in the Northern and Southern hemispheres. Twin 6.5-m telescopes; also known as the Walter Baade and Landon Clay telescopes. ...
Chapter 3 Geometric Optics
... 3.3.1 Measuring the Index of Refraction The index of refraction of a material can be precisely measured by the deflection of a light beam. Arrange the low voltage lamp, the light baffle with slit, a prism and a white screen as shown in Figure 3.12 below. The refracted beam is deflected through a fai ...
... 3.3.1 Measuring the Index of Refraction The index of refraction of a material can be precisely measured by the deflection of a light beam. Arrange the low voltage lamp, the light baffle with slit, a prism and a white screen as shown in Figure 3.12 below. The refracted beam is deflected through a fai ...
Exercise 13 Geometrical and Technical Optics WS 2013/2014
... focal length. The data (optimized for a beam diameter of 40 mm) are: R1=68.818 mm, R2=-49.523 mm, R3=-107.738 mm. Material between the first two surfaces with distance 15 mm is BK7 and material between the second and third surface with distance 5 mm is SF10. Compare that element with the hybrid achr ...
... focal length. The data (optimized for a beam diameter of 40 mm) are: R1=68.818 mm, R2=-49.523 mm, R3=-107.738 mm. Material between the first two surfaces with distance 15 mm is BK7 and material between the second and third surface with distance 5 mm is SF10. Compare that element with the hybrid achr ...
F - DCS Physics
... An optical fibre has an outer less dense layer of glass. What is the role of this layer of glass? An optical fibre is manufactured using glass of refractive index of 1.5. Calculate the speed of light travelling through the optical fibre. ...
... An optical fibre has an outer less dense layer of glass. What is the role of this layer of glass? An optical fibre is manufactured using glass of refractive index of 1.5. Calculate the speed of light travelling through the optical fibre. ...
powerpoint
... Benefits of Reflecting Telescopes Less expensive. Only the front surface of the mirror must be ground. The glass doesn’t need to be perfectly Transparent The mirror can be supported over its back surface to reduce sagging. They do not suffer from chromatic aberration because the light is reflected ...
... Benefits of Reflecting Telescopes Less expensive. Only the front surface of the mirror must be ground. The glass doesn’t need to be perfectly Transparent The mirror can be supported over its back surface to reduce sagging. They do not suffer from chromatic aberration because the light is reflected ...
Tidbits from the Hood (John Hood)
... It is interesting to note that the human eye is a telescope in its own right, using refraction to transmit images to the brain. Refraction is the change in direction of a wave, in this case a light wave, as it passes from one medium to another. As a wave of light enters the eye it passes through the ...
... It is interesting to note that the human eye is a telescope in its own right, using refraction to transmit images to the brain. Refraction is the change in direction of a wave, in this case a light wave, as it passes from one medium to another. As a wave of light enters the eye it passes through the ...
APPENDIX When designing shape magnification into a lens, the two
... Step 1. After determining the amount of aniseikonia to correct, the lens for the eye with larger perceived image is designed first. This lens must be made as flat and as thin as possible. The optical laboratory can be consulted to determine how thin a particular lens can be made given the power and ...
... Step 1. After determining the amount of aniseikonia to correct, the lens for the eye with larger perceived image is designed first. This lens must be made as flat and as thin as possible. The optical laboratory can be consulted to determine how thin a particular lens can be made given the power and ...
Chapter 12 - GEOCITIES.ws
... Measure the focal length fm of a convex mirror • It is not possible to capture a virtual image on a screen. • Put a converging lens of focal length flens in front of the convex mirror. • Adjust the position of the object so that a real image is at the same position as the object. ...
... Measure the focal length fm of a convex mirror • It is not possible to capture a virtual image on a screen. • Put a converging lens of focal length flens in front of the convex mirror. • Adjust the position of the object so that a real image is at the same position as the object. ...
Overview of various methods for measuring a lens focal length
... The lens power is measured for different positions of the source. The author of this method claims that routinely measurements are made with less than 0.5% accuracy. ...
... The lens power is measured for different positions of the source. The author of this method claims that routinely measurements are made with less than 0.5% accuracy. ...
Optical Instruments - Dr. Dr. Bill`s Page
... microscope consists of two converging lenses. The first forms a real magnified image of the object while the second is a simple magnifier used to view the image from the first lens. ...
... microscope consists of two converging lenses. The first forms a real magnified image of the object while the second is a simple magnifier used to view the image from the first lens. ...
To determine the wavelength of a monochromatic source of light
... plate of glass by suitable grinding and polishing, the obtuse angle of the prism (which is only slightly less than 1800). The optical bench consists of two metal rails graduated accurately in millimeters. The bench is provided with the three metal uprights which can slide along the rails and their p ...
... plate of glass by suitable grinding and polishing, the obtuse angle of the prism (which is only slightly less than 1800). The optical bench consists of two metal rails graduated accurately in millimeters. The bench is provided with the three metal uprights which can slide along the rails and their p ...
Concave Lenses and Mirrors
... In this part of the experimental tutorial you will determine the focal length of a converging lens then observe the change when the same lens is used in conjunction with a diverging lens. Measuring this change accurately will enable you to calculate the focal length of the diverging lens. Select a ...
... In this part of the experimental tutorial you will determine the focal length of a converging lens then observe the change when the same lens is used in conjunction with a diverging lens. Measuring this change accurately will enable you to calculate the focal length of the diverging lens. Select a ...
Chapter 34 – Geometric Optics and Optical Instruments
... index 1.50. The right half of the sphere is coated with a reflecting material. Where, what size, and what orientation is the final image? ...
... index 1.50. The right half of the sphere is coated with a reflecting material. Where, what size, and what orientation is the final image? ...
unit 9: imaging
... 1. The object is placed just outside the objective lens’ focal point in order to form a real image for the eyepiece lens. 2. A real, inverted, larger image is formed more than twice the objective lens’ focal length away on the other side of this lens. 3. The eyepiece lens is placed so that it acts a ...
... 1. The object is placed just outside the objective lens’ focal point in order to form a real image for the eyepiece lens. 2. A real, inverted, larger image is formed more than twice the objective lens’ focal length away on the other side of this lens. 3. The eyepiece lens is placed so that it acts a ...
Geometric optics
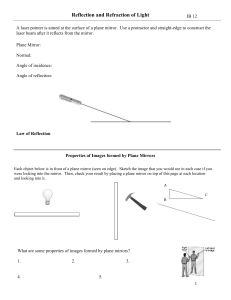
... Figure for use in showing how to find answer (I would draw this on the board) ...
... Figure for use in showing how to find answer (I would draw this on the board) ...
Experiment #6 Optics
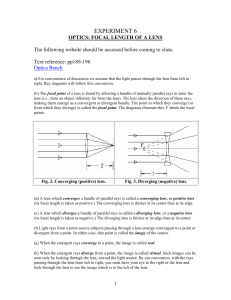
... (its focal length is taken as positive.) The converging lens is thicker at its center than at its edge. (e) A lens which diverges a bundle of parallel rays is called a diverging lens, or a negative lens (its focal length is taken as negative.) The diverging lens is thicker at its edge than at its ce ...
... (its focal length is taken as positive.) The converging lens is thicker at its center than at its edge. (e) A lens which diverges a bundle of parallel rays is called a diverging lens, or a negative lens (its focal length is taken as negative.) The diverging lens is thicker at its edge than at its ce ...
Lab 5. Spherical Mirrors and Lenses
... 1/si+l/so=l/f to calculate the focal length. Please fill your data into the table below. Lens ...
... 1/si+l/so=l/f to calculate the focal length. Please fill your data into the table below. Lens ...
Handout Building the demonstration refractor tube
... telescope tube. The inner tube at most moves into the outer tube enough so that the negative eyepiece lens will focus. At most it moves out far enough so the positive eyepiece lens will come into focus. Both the negative and positive eyepieces are positioned relative to the focal length of the big o ...
... telescope tube. The inner tube at most moves into the outer tube enough so that the negative eyepiece lens will focus. At most it moves out far enough so the positive eyepiece lens will come into focus. Both the negative and positive eyepieces are positioned relative to the focal length of the big o ...
Eyepiece

An eyepiece, or ocular lens, is a type of lens that is attached to a variety of optical devices such as telescopes and microscopes. It is so named because it is usually the lens that is closest to the eye when someone looks through the device. The objective lens or mirror collects light and brings it to focus creating an image. The eyepiece is placed near the focal point of the objective to magnify this image. The amount of magnification depends on the focal length of the eyepiece.An eyepiece consists of several ""lens elements"" in a housing, with a ""barrel"" on one end. The barrel is shaped to fit in a special opening of the instrument to which it is attached. The image can be focused by moving the eyepiece nearer and further from the objective. Most instruments have a focusing mechanism to allow movement of the shaft in which the eyepiece is mounted, without needing to manipulate the eyepiece directly.The eyepieces of binoculars are usually permanently mounted in the binoculars, causing them to have a pre-determined magnification and field of view. With telescopes and microscopes, however, eyepieces are usually interchangeable. By switching the eyepiece, the user can adjust what is viewed. For instance, eyepieces will often be interchanged to increase or decrease the magnification of a telescope. Eyepieces also offer varying fields of view, and differing degrees of eye relief for the person who looks through them.