Full Text - BioTechniques
... Human ES and iPS cells have many properties similar to mouse cells, so perhaps we could develop technologies that would allow us to generate a resource of knockout human cells. The main challenge in working with human cells is that, in order to understand gene function, we have to knock out both gen ...
... Human ES and iPS cells have many properties similar to mouse cells, so perhaps we could develop technologies that would allow us to generate a resource of knockout human cells. The main challenge in working with human cells is that, in order to understand gene function, we have to knock out both gen ...
VII. DNA/ GENES/ AND GENETICS • Describe the relationship
... What mechanism do cells use to turn genes on and off? Give examples of emerging biotechnologies. What modern technologies are currently being implemented to determine evolutionary relationships among species? How are viruses used to treat disease? How can over exposure to sunlight cause skin cancer? ...
... What mechanism do cells use to turn genes on and off? Give examples of emerging biotechnologies. What modern technologies are currently being implemented to determine evolutionary relationships among species? How are viruses used to treat disease? How can over exposure to sunlight cause skin cancer? ...
Gene Expression - Pleasantville High School
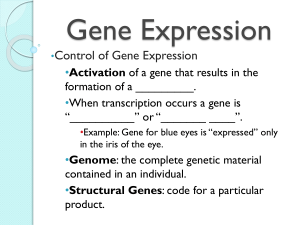
... •Example: Gene for blue eyes is “expressed” only in the iris of the eye. ...
... •Example: Gene for blue eyes is “expressed” only in the iris of the eye. ...
Biology 325: Genetics
... Prokaryotic Gene Regulation: To enable bacteria to respond to their environments, transcription initiation is turned on and off mainly by trans-acting proteins; gene expression is also regulated after initiation by cis- or transacting RNAs, or trans-acting proteins. Eukaryotic Gene Regulation: Multi ...
... Prokaryotic Gene Regulation: To enable bacteria to respond to their environments, transcription initiation is turned on and off mainly by trans-acting proteins; gene expression is also regulated after initiation by cis- or transacting RNAs, or trans-acting proteins. Eukaryotic Gene Regulation: Multi ...
Discovery and analysis of inflammatory disease-related
... the corresponding gene are shown in the layout. Some genes have more than one target element to guarantee specificity of signal. ...
... the corresponding gene are shown in the layout. Some genes have more than one target element to guarantee specificity of signal. ...
Resource - Chromosome Viewer (www
... Inside every one of our cells (except red blood cells) is a nucleus containing 23 pairs of chromosomes. These chromosomes are built from long strands of a ladder-shaped molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). The DNA molecule, in turn, is made up of many smaller components. These nucleotides, o ...
... Inside every one of our cells (except red blood cells) is a nucleus containing 23 pairs of chromosomes. These chromosomes are built from long strands of a ladder-shaped molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). The DNA molecule, in turn, is made up of many smaller components. These nucleotides, o ...
The Human Genome Project and Ectodermal Dysplasia March 2001
... There are about three thousand million base pairs of DNA in the human genome, distributed on the 24 different chromosomes visible under the microscope (the twentytwo pairs of autosomes, numbered 1-22, and the two sex chromosomes, X and Y). Buried and dispersed within this massive quantity of DNA are ...
... There are about three thousand million base pairs of DNA in the human genome, distributed on the 24 different chromosomes visible under the microscope (the twentytwo pairs of autosomes, numbered 1-22, and the two sex chromosomes, X and Y). Buried and dispersed within this massive quantity of DNA are ...
Genetic Engineering
... organisms, usually to express a protein’’. DNA taken from one organism and inserted (transformed) into another (transgenic) organism Heritable, directed alteration of an organism. Altering DNA or adding new DNA allows us to change the characteristics of a cell or cells. ...
... organisms, usually to express a protein’’. DNA taken from one organism and inserted (transformed) into another (transgenic) organism Heritable, directed alteration of an organism. Altering DNA or adding new DNA allows us to change the characteristics of a cell or cells. ...
Chapter 15 - Advances in Molecular Genetics
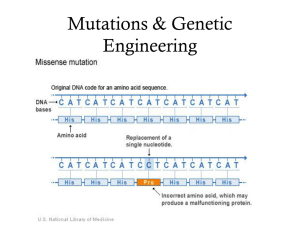
... mutation. Give examples of each (not the ones from the book) 27. What is a frameshift mutation? 28. What test is given to every child born in the US at birth? Why? What is the nature of the disorder being tested? 29.Describe three different chromosome arrangements and in the space below, draw repres ...
... mutation. Give examples of each (not the ones from the book) 27. What is a frameshift mutation? 28. What test is given to every child born in the US at birth? Why? What is the nature of the disorder being tested? 29.Describe three different chromosome arrangements and in the space below, draw repres ...
Wednesday, September 5
... simultaneously, thus providing a genome-wide view of which genes are expressed in different tissues, under particular conditions, or at different stages of development. ...
... simultaneously, thus providing a genome-wide view of which genes are expressed in different tissues, under particular conditions, or at different stages of development. ...
Review of relevant topics prior to “Linkage” lectures
... Review of relevant topics prior to “Linkage” lectures ...
... Review of relevant topics prior to “Linkage” lectures ...
What are multiple alleles
... nucleus of the organism to be cloned, and placing the egg cell with its new nucleus into a compatible or the same female for gestation. ...
... nucleus of the organism to be cloned, and placing the egg cell with its new nucleus into a compatible or the same female for gestation. ...
Genetics Quiz- Matching, Short answer
... 1. Explain the difference between dominant and recessive alleles. For example, if I have brown eyes what would the allele look like. ...
... 1. Explain the difference between dominant and recessive alleles. For example, if I have brown eyes what would the allele look like. ...
L3_Viral Vector and Non
... • Lentiviruses have a more complex genome; in addition to the gag, pol, and env genes, they encode two regulatory genes, tat and rev, essential for expression of the genome, and a variable set of accessory genes. • Spumaviruses also contain bel-1, an essential gene regulating expression of the geno ...
... • Lentiviruses have a more complex genome; in addition to the gag, pol, and env genes, they encode two regulatory genes, tat and rev, essential for expression of the genome, and a variable set of accessory genes. • Spumaviruses also contain bel-1, an essential gene regulating expression of the geno ...
Genetic engineering
... genetic constitutions of organisms by their selection of plants and animals in the new activity of agriculture .The breeding of domesticated species of plants and animals involves artificial selection and natural hybridization between related species and the doubling of whole sets of chromosomes to ...
... genetic constitutions of organisms by their selection of plants and animals in the new activity of agriculture .The breeding of domesticated species of plants and animals involves artificial selection and natural hybridization between related species and the doubling of whole sets of chromosomes to ...
Principles of Biology Lake Tahoe Community College
... 5. super coil. 6. DNA packing tends to prevent transcription and translation B. In female mammals, one x chromosome is inactivated in each cell 1. early in embryonic development. C. control of eukaryotic transcription 1. eukaryotes have transcription factors D. Eukaryotic RNA may be spliced in more ...
... 5. super coil. 6. DNA packing tends to prevent transcription and translation B. In female mammals, one x chromosome is inactivated in each cell 1. early in embryonic development. C. control of eukaryotic transcription 1. eukaryotes have transcription factors D. Eukaryotic RNA may be spliced in more ...
Concept Check Questions with answers
... simultaneously, thus providing a genome-wide view of which genes are expressed in different tissues, under particular conditions, or at different stages of development. ...
... simultaneously, thus providing a genome-wide view of which genes are expressed in different tissues, under particular conditions, or at different stages of development. ...
Slide 1
... culture of embryonic stem (ES) cells. Stem cells can give rise to a complete organism. The cells are then incorporated into an embryo at the blastocyst stage of development. ...
... culture of embryonic stem (ES) cells. Stem cells can give rise to a complete organism. The cells are then incorporated into an embryo at the blastocyst stage of development. ...
Site-specific recombinase technology

Nearly every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse (regardless of the fact that a minor set of orthologues had to follow species specific selection routes). This made the mouse the major model for elucidating the ways in which our genetic material encodes information. In the late 1980s gene targeting in murine embryonic stem (ES-)cells enabled the transmission of mutations into the mouse germ line and emerged as a novel option to study the genetic basis of regulatory networks as they exist in the genome. Still, classical gene targeting proved to be limited in several ways as gene functions became irreversibly destroyed by the marker gene that had to be introduced for selecting recombinant ES cells. These early steps led to animals in which the mutation was present in all cells of the body from the beginning leading to complex phenotypes and/or early lethality. There was a clear need for methods to restrict these mutations to specific points in development and specific cell types. This dream became reality when groups in the USA were able to introduce bacteriophage and yeast-derived site-specific recombination (SSR-) systems into mammalian cells as well as into the mouse