A Nucleotide Consists of what three parts?
... DNA GATAGCCGATTACGGATA Complimentary Strand CTATCGGCTAATGCCTAT RNA CUAUCGGCUAAUGCCUAU A Codon is: Three base pairs: CUA Codon = Amino Acid ...
... DNA GATAGCCGATTACGGATA Complimentary Strand CTATCGGCTAATGCCTAT RNA CUAUCGGCUAAUGCCUAU A Codon is: Three base pairs: CUA Codon = Amino Acid ...
Unit_biology_2_Genetic_variation
... d) An allele that controls the development of a characteristic when it is present on only one of the chromosomes is a dominant allele. e) An allele that controls the development of characteristics only if the dominant allele is not present is a recessive allele. f) Chromosomes are made up of large m ...
... d) An allele that controls the development of a characteristic when it is present on only one of the chromosomes is a dominant allele. e) An allele that controls the development of characteristics only if the dominant allele is not present is a recessive allele. f) Chromosomes are made up of large m ...
Regulation of Gene Expression – Part III
... • UV - if 2 thymine molecules next to one another, UV radiation may cause them to bind together…forming _______________. Result: kink in the DNA. They can sometimes be repaired/removed by ____________ ...
... • UV - if 2 thymine molecules next to one another, UV radiation may cause them to bind together…forming _______________. Result: kink in the DNA. They can sometimes be repaired/removed by ____________ ...
Genetic Engineering Activity Directions: Follow the steps below to
... cell, which could be a bacterium, an egg cell or a virus. In this activity, our host (target) cell will be a bacterium. The most commonly used vectors are viruses and plasmids. In this activity, the vector will be a plasmid. Remember, a plasmid is a circular form of DNA found in a bacteria cell. a. ...
... cell, which could be a bacterium, an egg cell or a virus. In this activity, our host (target) cell will be a bacterium. The most commonly used vectors are viruses and plasmids. In this activity, the vector will be a plasmid. Remember, a plasmid is a circular form of DNA found in a bacteria cell. a. ...
Name:
... Biotechnology v. DNA technology v. recombinant DNA technology Goals/uses of transformation & genetic engineering: o significance of plasmids, restriction enzymes & ligase, “sticky ends” GMOs: production, uses, controversy Animal cloning: process, controversy DNA technology o PCR o Electrop ...
... Biotechnology v. DNA technology v. recombinant DNA technology Goals/uses of transformation & genetic engineering: o significance of plasmids, restriction enzymes & ligase, “sticky ends” GMOs: production, uses, controversy Animal cloning: process, controversy DNA technology o PCR o Electrop ...
Genetics Webquest Name: What is DNA? http://learn.genetics.utah
... 18) The passing of traits from parents to a child is the basis of __________. 19) Every child receives _________of its chromosomes from his mother, and _________from his father. 20) When a sperm and egg join, they create a single cell called a _________. 21) Each child inherits a _________ set of ch ...
... 18) The passing of traits from parents to a child is the basis of __________. 19) Every child receives _________of its chromosomes from his mother, and _________from his father. 20) When a sperm and egg join, they create a single cell called a _________. 21) Each child inherits a _________ set of ch ...
Genetic Control of Metabolism
... • New strains are also produced by bacteria taking up DNA fragments from their environment. • Scientists try to produce new strains of useful bacteria by culturing existing strains together in conditions where horizontal transfer of DNA is most likely to occur. ...
... • New strains are also produced by bacteria taking up DNA fragments from their environment. • Scientists try to produce new strains of useful bacteria by culturing existing strains together in conditions where horizontal transfer of DNA is most likely to occur. ...
Combinatorial Control of Gene Activation and Coordinately
... • In eukaryotes, the precise control of transcription depends on the binding of activators to DNA control elements. • There are only about twelve nucleotide sequences that make up control elements and they appear over and over again. • Each enhancer-a group of control elements- contains about ten nu ...
... • In eukaryotes, the precise control of transcription depends on the binding of activators to DNA control elements. • There are only about twelve nucleotide sequences that make up control elements and they appear over and over again. • Each enhancer-a group of control elements- contains about ten nu ...
Punnetts 2
... • Because males have only one X chromosome, they show all the traitsgenes on that X. Females have two X’s, so they have two chances to get a gene that is good, and can show the good trait. Example: If females, have one gene on an X for colorblindness, and one gene on the other X for normal vision, s ...
... • Because males have only one X chromosome, they show all the traitsgenes on that X. Females have two X’s, so they have two chances to get a gene that is good, and can show the good trait. Example: If females, have one gene on an X for colorblindness, and one gene on the other X for normal vision, s ...
Launches RNAcomplete Allowing Co-Extraction
... specificity. The co-extracted DNA produced by RNAcomplete is suitable for whole exome sequencing with PGDx’s CancerXOMETM, which captures and analyzes the coding regions of more than 20,000 genes. The CancerXOME and RNAcomplete results together provide powerful information on both gene expression an ...
... specificity. The co-extracted DNA produced by RNAcomplete is suitable for whole exome sequencing with PGDx’s CancerXOMETM, which captures and analyzes the coding regions of more than 20,000 genes. The CancerXOME and RNAcomplete results together provide powerful information on both gene expression an ...
blumberg-lab.bio.uci.edu
... ● Same phenomena was observed when cells were treated with RNAi targeted at proapoptotic caspases, except in cells with coRNAi for CG15455 ● Demonstrated to researchers that CG11700 and D-IAP1 were likely involved in the same pathway ...
... ● Same phenomena was observed when cells were treated with RNAi targeted at proapoptotic caspases, except in cells with coRNAi for CG15455 ● Demonstrated to researchers that CG11700 and D-IAP1 were likely involved in the same pathway ...
How do the specific expressions of genes compare between
... The domesticated dogs have the most phenotypic diversity of all land mammals. For example, the average weight of Chihuahuas and English Mastiffs differs by 65-fold. Consequently the level of expression of a certain genes may differ across breeds. For example, it is noteworthy the levels of circulati ...
... The domesticated dogs have the most phenotypic diversity of all land mammals. For example, the average weight of Chihuahuas and English Mastiffs differs by 65-fold. Consequently the level of expression of a certain genes may differ across breeds. For example, it is noteworthy the levels of circulati ...
Safety - Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering
... 55,000,000 cells, or about 93,205 miles of DNA! As of 2005, 59% of Europeans believed that tomatoes, and for that sake plants in general, do not contain DNA. ...
... 55,000,000 cells, or about 93,205 miles of DNA! As of 2005, 59% of Europeans believed that tomatoes, and for that sake plants in general, do not contain DNA. ...
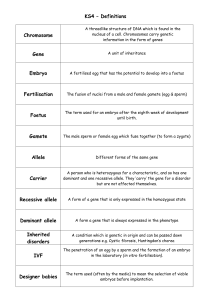
Definitions
... A threadlike structure of DNA which is found in the nucleus of a cell. Chromosomes carry genetic information in the form of genes ...
... A threadlike structure of DNA which is found in the nucleus of a cell. Chromosomes carry genetic information in the form of genes ...
Study Questions – Chapter 1
... “Diversity revealed: From atoms to traits: Charles Darwin saw that random variations in organisms provide fodder for evolution. Modern scientists are revealing how that diversity arises from changes to DNA and can add up to complex creatures or even cultures” by David M. Kingsley in Scientific Ameri ...
... “Diversity revealed: From atoms to traits: Charles Darwin saw that random variations in organisms provide fodder for evolution. Modern scientists are revealing how that diversity arises from changes to DNA and can add up to complex creatures or even cultures” by David M. Kingsley in Scientific Ameri ...
Genetic Mutation - Raymond Williams Foundation
... ‘ mutation – the raw material of evolution… fuel for the Darwinian factory’; ‘What is Life? – unlike, say a pebble, living beings store information and also develop it over time…’; attempted explanations of ‘enzymes, DNA, ‘the gene pool’, ‘randomness, and genetic drift…’ , ‘induced mutations’ , ‘dis ...
... ‘ mutation – the raw material of evolution… fuel for the Darwinian factory’; ‘What is Life? – unlike, say a pebble, living beings store information and also develop it over time…’; attempted explanations of ‘enzymes, DNA, ‘the gene pool’, ‘randomness, and genetic drift…’ , ‘induced mutations’ , ‘dis ...
No Slide Title
... • Enables the immune system to generate a diversity of protein antibodies from a limited set of genes • Enables viruses to integrate their genetic material into a host’s genome • Enables host organism to assort alleles (differing copies of same gene) into novel groups - favorable & unfavorable allel ...
... • Enables the immune system to generate a diversity of protein antibodies from a limited set of genes • Enables viruses to integrate their genetic material into a host’s genome • Enables host organism to assort alleles (differing copies of same gene) into novel groups - favorable & unfavorable allel ...
Gene Q
... Questions 9 and 10 pertain to the following. Six independently derived mutants are recovered in Neurospora that are all able to grow on compound Z. The mutants are then grown on minimal media supplemented with one of 6 chemicals all known to be precursors to compound Z. A summary of the ability of t ...
... Questions 9 and 10 pertain to the following. Six independently derived mutants are recovered in Neurospora that are all able to grow on compound Z. The mutants are then grown on minimal media supplemented with one of 6 chemicals all known to be precursors to compound Z. A summary of the ability of t ...
Mutation
... 2.) Deletions of large chromosomal regions, leading to loss of the genes 3.) Chromosomal inversions: reversing the orientation of a chromosomal segment. Gene P Gene Q ...
... 2.) Deletions of large chromosomal regions, leading to loss of the genes 3.) Chromosomal inversions: reversing the orientation of a chromosomal segment. Gene P Gene Q ...
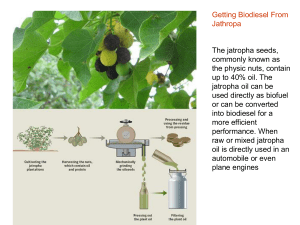
Jatropha genotyping In Gh Pu QR In Gh Pu QR 13 primer pairs
... • Results indicate very little variation between accessions from India, Ghana, Tanzania & Madagascar ...
... • Results indicate very little variation between accessions from India, Ghana, Tanzania & Madagascar ...
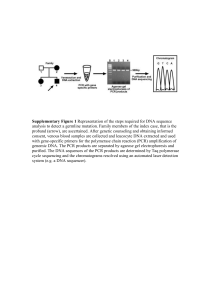
Figure 2 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
I. Multiple Choice: choose one best answer (2.5 points each, 80 points)
... B. The trait forms sterile progeny. C. Either the dominant or the recessive allele in its homozygous form is lethal. D. The trait causes semisterility in one of the parents. E. The recessive allele for the trait is lethal in its homozygous form. 126. Humans with the disorder PKU develop light colore ...
... B. The trait forms sterile progeny. C. Either the dominant or the recessive allele in its homozygous form is lethal. D. The trait causes semisterility in one of the parents. E. The recessive allele for the trait is lethal in its homozygous form. 126. Humans with the disorder PKU develop light colore ...
Site-specific recombinase technology

Nearly every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse (regardless of the fact that a minor set of orthologues had to follow species specific selection routes). This made the mouse the major model for elucidating the ways in which our genetic material encodes information. In the late 1980s gene targeting in murine embryonic stem (ES-)cells enabled the transmission of mutations into the mouse germ line and emerged as a novel option to study the genetic basis of regulatory networks as they exist in the genome. Still, classical gene targeting proved to be limited in several ways as gene functions became irreversibly destroyed by the marker gene that had to be introduced for selecting recombinant ES cells. These early steps led to animals in which the mutation was present in all cells of the body from the beginning leading to complex phenotypes and/or early lethality. There was a clear need for methods to restrict these mutations to specific points in development and specific cell types. This dream became reality when groups in the USA were able to introduce bacteriophage and yeast-derived site-specific recombination (SSR-) systems into mammalian cells as well as into the mouse