TECHNICAL NOTE 4.1
... When viewed under the microscope, each human cell has the same general structure, a round ball that is filled with various particles (called organelles), and a smaller ball, somewhere in the middle, called the nucleus. The nucleus houses all of the “programming code” for the organism. The code for o ...
... When viewed under the microscope, each human cell has the same general structure, a round ball that is filled with various particles (called organelles), and a smaller ball, somewhere in the middle, called the nucleus. The nucleus houses all of the “programming code” for the organism. The code for o ...
Identification of ORC1/CDC6-interacting factors in
... -You work in teams of two, presenting groups are randomly chosen at each data* - Introductions (given in red letters) are presented by volunteers (who don´t have to prepare the paper seminars) - The group that presented one paper will not be presenting another on the same day - Imagine you did the s ...
... -You work in teams of two, presenting groups are randomly chosen at each data* - Introductions (given in red letters) are presented by volunteers (who don´t have to prepare the paper seminars) - The group that presented one paper will not be presenting another on the same day - Imagine you did the s ...
View PDF
... - A prophage picks up a few adjacent genes as it leaves and transfers to a new host. - Transfer only of adjacent genes. ...
... - A prophage picks up a few adjacent genes as it leaves and transfers to a new host. - Transfer only of adjacent genes. ...
Diapositiva 1
... factors genes, that have more duplications than in the ancestral. MEF2 myocyte enhancer factor 2 is responsible of the contractile proteins. Vertebrates have 4 copies of the gene. Loss of function no contractile proteins and right ventricle. ...
... factors genes, that have more duplications than in the ancestral. MEF2 myocyte enhancer factor 2 is responsible of the contractile proteins. Vertebrates have 4 copies of the gene. Loss of function no contractile proteins and right ventricle. ...
Genetics Objectives 20
... protects against this by adding base pairs back to telomers after cellular division, thus protecting cancerous cells from severe DNA damage that would ultimately result in cell death. ...
... protects against this by adding base pairs back to telomers after cellular division, thus protecting cancerous cells from severe DNA damage that would ultimately result in cell death. ...
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
... • Ranks all genes on array based on their differential expression • Identifies gene sets whose member genes are clustered either towards top or bottom of the ranked list (i.e. up- or down regulated) • Enrichment score calculated for each category • Permutation test to identify significantly enriched ...
... • Ranks all genes on array based on their differential expression • Identifies gene sets whose member genes are clustered either towards top or bottom of the ranked list (i.e. up- or down regulated) • Enrichment score calculated for each category • Permutation test to identify significantly enriched ...
Chapter 15
... The Hardy Weinberg Law: Under certain conditions the relative frequencies of alleles for a given trait in a population do not change. For this to be true: 1) The population must be large 2) Individuals must not migrate into or out of the population. 3) Mutations must not occur 4) Reproduction must b ...
... The Hardy Weinberg Law: Under certain conditions the relative frequencies of alleles for a given trait in a population do not change. For this to be true: 1) The population must be large 2) Individuals must not migrate into or out of the population. 3) Mutations must not occur 4) Reproduction must b ...
Of Genes and Genomes.
... carries two bits of information; in other words, approximately 12 billion bits of information needed to be stored. In those days, the capacity of a computer was measured in 8-bit units called bytes; but we had need for 750 million bytes (750 megabytes). Joseph Goldstein spoke of the invention of the ...
... carries two bits of information; in other words, approximately 12 billion bits of information needed to be stored. In those days, the capacity of a computer was measured in 8-bit units called bytes; but we had need for 750 million bytes (750 megabytes). Joseph Goldstein spoke of the invention of the ...
Figure 13-1
... True or False? Correct the false statement. A = TRUE; B = False 20. ___________________ In bacteria, a promoter is cluster of related genes plus its control sequences to turn on or off transcription. 21. ___________________ A protein produced by a transgenic bacteria is different from the same prot ...
... True or False? Correct the false statement. A = TRUE; B = False 20. ___________________ In bacteria, a promoter is cluster of related genes plus its control sequences to turn on or off transcription. 21. ___________________ A protein produced by a transgenic bacteria is different from the same prot ...
Genetics - Region 11 Math And Science Teacher Partnership
... possible to house large numbers in a laboratory setting. The total number of somatic cells in an adult worm is about 959 cells comparing to human's trillions of cells. Its life cycle/span is short (about 3 days/weeks respectively). This shortens the amount of time needed for each experiment and incr ...
... possible to house large numbers in a laboratory setting. The total number of somatic cells in an adult worm is about 959 cells comparing to human's trillions of cells. Its life cycle/span is short (about 3 days/weeks respectively). This shortens the amount of time needed for each experiment and incr ...
Fact sheet (PDF, 58.54 KB) (opens in a new window)
... This same siRNA technology can also be used to increase gene transcription. siRNA to increase gene transcription siRNAs are typically used to knock-down gene expression. Scientists at UWS have now devised a simple siRNA method to increase gene transcription. This new siRNA technology has many import ...
... This same siRNA technology can also be used to increase gene transcription. siRNA to increase gene transcription siRNAs are typically used to knock-down gene expression. Scientists at UWS have now devised a simple siRNA method to increase gene transcription. This new siRNA technology has many import ...
Causes of Evolution
... Types of Natural Selection 1. STABILIZING Selection = favors average individuals in a population • reduces variation in organisms Ex: lizards – large captured easily & small cannot run fast enough 2. DIRECTIONAL Selection = favors one of the extreme variations of a trait • can lead to rapid evolutio ...
... Types of Natural Selection 1. STABILIZING Selection = favors average individuals in a population • reduces variation in organisms Ex: lizards – large captured easily & small cannot run fast enough 2. DIRECTIONAL Selection = favors one of the extreme variations of a trait • can lead to rapid evolutio ...
epigenetics
... consequence of parental imprinting is that imprinted genes are expressed as if they were hemizygous*, even though there are two copies of each of these autosomal genes in each cell. Furthermore, when these genes are examined at the molecular level, no changes in their DNA sequences are observed. Rat ...
... consequence of parental imprinting is that imprinted genes are expressed as if they were hemizygous*, even though there are two copies of each of these autosomal genes in each cell. Furthermore, when these genes are examined at the molecular level, no changes in their DNA sequences are observed. Rat ...
Oxygen (O 2 ) - Mona Shores Blogs
... This occurs when a molecule other than the substrate stops the function of an enzyme by attaching to the active site ...
... This occurs when a molecule other than the substrate stops the function of an enzyme by attaching to the active site ...
Biology 101 Section 6
... Some final notes on probability Mendel's crosses and rules reflect chance, not certainty. Genetic crosses show only the odds of getting a particular genotype at any one time, not what must be. Genes, Natural Selection and Adaptation Some mutations are good. Mutations, genetic recombination and cross ...
... Some final notes on probability Mendel's crosses and rules reflect chance, not certainty. Genetic crosses show only the odds of getting a particular genotype at any one time, not what must be. Genes, Natural Selection and Adaptation Some mutations are good. Mutations, genetic recombination and cross ...
In situ - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... – mapping of restriction sites – sequence-tagged sites (STSs) ...
... – mapping of restriction sites – sequence-tagged sites (STSs) ...
Human Genome Project Gene Therapy
... Proof they had CF gene one gene identified that is expressed differently in CF patients than in normal patients. Mutation found in every CF gene patients studied- not found in normal patients (looked at many patients) Chloride transport – deficient in secretory cells from CF patients. Cultured ...
... Proof they had CF gene one gene identified that is expressed differently in CF patients than in normal patients. Mutation found in every CF gene patients studied- not found in normal patients (looked at many patients) Chloride transport – deficient in secretory cells from CF patients. Cultured ...
In situ - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... – mapping of restriction sites – sequence-tagged sites (STSs) ...
... – mapping of restriction sites – sequence-tagged sites (STSs) ...
Cloning and PCR File
... 1. In isolation, an enzyme (called a restriction enzyme) is used to break DNA at a specific base sequence. This is done to isolate a gene. 2. During ligation, the enzyme DNA ligase combines the isolated gene with plasmid DNA from bacteria. (A plasmid is circular DNA that is not part of a chromosome ...
... 1. In isolation, an enzyme (called a restriction enzyme) is used to break DNA at a specific base sequence. This is done to isolate a gene. 2. During ligation, the enzyme DNA ligase combines the isolated gene with plasmid DNA from bacteria. (A plasmid is circular DNA that is not part of a chromosome ...
Genes & Chromosomes
... states: That genes are located on the chromosome and each gene occupies a specific place on that chromosome. Each chromosome contains just one allele for each of its genes. ...
... states: That genes are located on the chromosome and each gene occupies a specific place on that chromosome. Each chromosome contains just one allele for each of its genes. ...
APOC1 gene rs4420638 SNP
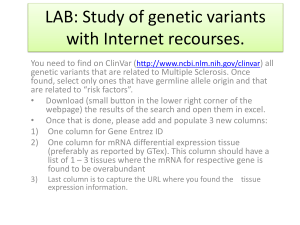
... LAB: Study of genetic variants with Internet recourses. You need to find on ClinVar (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar) all genetic variants that are related to Multiple Sclerosis. Once found, select only ones that have germline allele origin and that are related to “risk factors”. • Download (sma ...
... LAB: Study of genetic variants with Internet recourses. You need to find on ClinVar (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar) all genetic variants that are related to Multiple Sclerosis. Once found, select only ones that have germline allele origin and that are related to “risk factors”. • Download (sma ...
Pleiotropy - MACscience
... Definition • The ability of a gene to affect more than one characteristic. A ...
... Definition • The ability of a gene to affect more than one characteristic. A ...
Site-specific recombinase technology

Nearly every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse (regardless of the fact that a minor set of orthologues had to follow species specific selection routes). This made the mouse the major model for elucidating the ways in which our genetic material encodes information. In the late 1980s gene targeting in murine embryonic stem (ES-)cells enabled the transmission of mutations into the mouse germ line and emerged as a novel option to study the genetic basis of regulatory networks as they exist in the genome. Still, classical gene targeting proved to be limited in several ways as gene functions became irreversibly destroyed by the marker gene that had to be introduced for selecting recombinant ES cells. These early steps led to animals in which the mutation was present in all cells of the body from the beginning leading to complex phenotypes and/or early lethality. There was a clear need for methods to restrict these mutations to specific points in development and specific cell types. This dream became reality when groups in the USA were able to introduce bacteriophage and yeast-derived site-specific recombination (SSR-) systems into mammalian cells as well as into the mouse