AP Psychology - Coshocton High School
... Besides the functioning of the endocrine and nervous system, genetics is another biological factor that affects human behavior and thought • Behavioral Genetics – Genetic and environmental contributions to personality and behavior • Human traits are usually caused by genes acting together (not usual ...
... Besides the functioning of the endocrine and nervous system, genetics is another biological factor that affects human behavior and thought • Behavioral Genetics – Genetic and environmental contributions to personality and behavior • Human traits are usually caused by genes acting together (not usual ...
Bacterial Transformation with (pGLO Plasmid)
... Bacterial Transformation with (pGLO Plasmid) Lab #6: Molecular Biology ...
... Bacterial Transformation with (pGLO Plasmid) Lab #6: Molecular Biology ...
Genetics Mark Schedule 2010
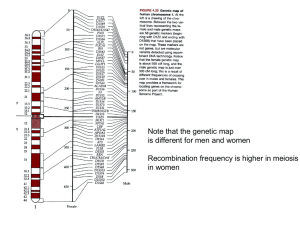
... is an exchange of alleles, called genetic recombination/ Without recombination, all alleles for those genes found together on the same chromosome would be inherited together/ Recombination shuffles the allele content between sister chromatids/ makes gametes unique. Somatic and gametic mutations (bot ...
... is an exchange of alleles, called genetic recombination/ Without recombination, all alleles for those genes found together on the same chromosome would be inherited together/ Recombination shuffles the allele content between sister chromatids/ makes gametes unique. Somatic and gametic mutations (bot ...
Key concepts_Regulation of transcription in
... Distal DNA regulatory elements include enhancers, silencers, insulators, and locus control regions. Each of these elements acts through its own mechanisms. Eukaryotic transcription factors are molecular complexes that bind to DNA regulatory elements. Typically, they contain both DNA-binding and acti ...
... Distal DNA regulatory elements include enhancers, silencers, insulators, and locus control regions. Each of these elements acts through its own mechanisms. Eukaryotic transcription factors are molecular complexes that bind to DNA regulatory elements. Typically, they contain both DNA-binding and acti ...
Microbiology Exam II - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... Essay Questions: Use the provided space to answer each of the following questions. 36. Name the three types of RNA and describe their functions. (6 points) ...
... Essay Questions: Use the provided space to answer each of the following questions. 36. Name the three types of RNA and describe their functions. (6 points) ...
“IPMATC” Activity Directions: Use complete, meaning
... What are the phases of mitosis? Use page 131 to draw and label a chromosome. What happens to the amount of DNA during “Replication” phase of interphase? Where in the cell is the chromatin during interphase? In what phase are the chromosomes completely separated in their own nuclear envelope? How doe ...
... What are the phases of mitosis? Use page 131 to draw and label a chromosome. What happens to the amount of DNA during “Replication” phase of interphase? Where in the cell is the chromatin during interphase? In what phase are the chromosomes completely separated in their own nuclear envelope? How doe ...
NedGeneticsCompRecomb12 51 KB
... Complementation tests allow you to see if two mutations affect the same gene or affect two different genes in a pathway. Pathway Models: -The three models of epistasis we discussed all involve pathways. -Interactions we looked at in plants control pigment formation. What is the advantage to controll ...
... Complementation tests allow you to see if two mutations affect the same gene or affect two different genes in a pathway. Pathway Models: -The three models of epistasis we discussed all involve pathways. -Interactions we looked at in plants control pigment formation. What is the advantage to controll ...
Lecture 3 Human Genetics
... • The CEPH families were instrumental in constructing the map • But our goal is to map human diseases •You rarely get large multi-generational highly informative families • How do we get to a lod score of 3 with small families? ...
... • The CEPH families were instrumental in constructing the map • But our goal is to map human diseases •You rarely get large multi-generational highly informative families • How do we get to a lod score of 3 with small families? ...
Slide 1
... that the mutations must be mapped and correlated with genomic sequence, a process that can take months or years. Another disadvantage is that mutations are limited by the screening criteria, meaning that all the mutations isolated will result in a particular phenotype. Another mutagenesis approach t ...
... that the mutations must be mapped and correlated with genomic sequence, a process that can take months or years. Another disadvantage is that mutations are limited by the screening criteria, meaning that all the mutations isolated will result in a particular phenotype. Another mutagenesis approach t ...
Biotechnology in Agriculture
... http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_reading_frame#/media/File:Sampleorf.png ...
... http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open_reading_frame#/media/File:Sampleorf.png ...
Module 1 poster
... We can insert correct genes to replace faulty ones. A carrier molecule called a vector is used to deliver the gene. Normally this is in the form of a virus which has been modified to insert specific genes into its host’s DNA. We can selectively switch certain genes on or off to regulate the function ...
... We can insert correct genes to replace faulty ones. A carrier molecule called a vector is used to deliver the gene. Normally this is in the form of a virus which has been modified to insert specific genes into its host’s DNA. We can selectively switch certain genes on or off to regulate the function ...
Chapter 13 Genetic Engineering - Mrs. Moyer
... can synthesize a DNA strand and connect it to a circular DNA molecule known as a plasmid… which can be found naturally in bacteria. This bacteria can then be injected into a plant, and will insert its DNA into the plant. ► If transformation is successful, the recombinant DNA is integrated into one o ...
... can synthesize a DNA strand and connect it to a circular DNA molecule known as a plasmid… which can be found naturally in bacteria. This bacteria can then be injected into a plant, and will insert its DNA into the plant. ► If transformation is successful, the recombinant DNA is integrated into one o ...
Public data and tool repositories Section 2 Survey of
... 1. Integrates feature identity information with whole genome view 2. Allows one to view and search an organism's complete genome 3. Displays chromosome maps 4. User can zoom into progressively greater levels of detail, down to the sequence data for a region of interest. 5. Focus more on individual s ...
... 1. Integrates feature identity information with whole genome view 2. Allows one to view and search an organism's complete genome 3. Displays chromosome maps 4. User can zoom into progressively greater levels of detail, down to the sequence data for a region of interest. 5. Focus more on individual s ...
Transcription and Translation Exercise
... 5. If a protein has 150 amino acids, how many DNA nucleotides would make up the coding region of the gene? ...
... 5. If a protein has 150 amino acids, how many DNA nucleotides would make up the coding region of the gene? ...
Introduction o Except for identical twins, have the same DNA. o
... The Function and Structure of DNA Human DNA consists of about ________________ bases, and more than _____________________ of those bases are the same in all people. The order, or ______________, of these bases determines the information available for building and maintaining an organism, similar to ...
... The Function and Structure of DNA Human DNA consists of about ________________ bases, and more than _____________________ of those bases are the same in all people. The order, or ______________, of these bases determines the information available for building and maintaining an organism, similar to ...
Genes and health
... • Fill in your information on the appropriate slides. You may need to copy some of the slides to include all your information: go to ‘Insert’ and choose ‘Insert duplicate slide’. • Make sure you link the starting slide for each topic back to the Index and that the topic is included in the Index. ...
... • Fill in your information on the appropriate slides. You may need to copy some of the slides to include all your information: go to ‘Insert’ and choose ‘Insert duplicate slide’. • Make sure you link the starting slide for each topic back to the Index and that the topic is included in the Index. ...
View or print this bulletin in its original format.
... nucleotide polymorphisms, i.e., single variations in genes) in genetic material from 2,692 family members, including 1,595 people with MS (The American Journal of Human Genetics 77:454-467, 2005). There are millions of SNPs in the genome, but if some of these slight variations can be identified as o ...
... nucleotide polymorphisms, i.e., single variations in genes) in genetic material from 2,692 family members, including 1,595 people with MS (The American Journal of Human Genetics 77:454-467, 2005). There are millions of SNPs in the genome, but if some of these slight variations can be identified as o ...
Lecture 17 - The Eukaryotic Genome
... • The genome was broken into overlapping fragments called “contigs” • Contigs were sequenced, then their overlapping ends matched up with each other to produce the whole sequence ...
... • The genome was broken into overlapping fragments called “contigs” • Contigs were sequenced, then their overlapping ends matched up with each other to produce the whole sequence ...
Site-specific recombinase technology

Nearly every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse (regardless of the fact that a minor set of orthologues had to follow species specific selection routes). This made the mouse the major model for elucidating the ways in which our genetic material encodes information. In the late 1980s gene targeting in murine embryonic stem (ES-)cells enabled the transmission of mutations into the mouse germ line and emerged as a novel option to study the genetic basis of regulatory networks as they exist in the genome. Still, classical gene targeting proved to be limited in several ways as gene functions became irreversibly destroyed by the marker gene that had to be introduced for selecting recombinant ES cells. These early steps led to animals in which the mutation was present in all cells of the body from the beginning leading to complex phenotypes and/or early lethality. There was a clear need for methods to restrict these mutations to specific points in development and specific cell types. This dream became reality when groups in the USA were able to introduce bacteriophage and yeast-derived site-specific recombination (SSR-) systems into mammalian cells as well as into the mouse