Interactions between freestream turbulence and boundary layers
... Note that the form of u(x) in {M}, derived from (2.12) differs from that in {U}, being negative and having two minima. In the surface zone {S}, viscous effects induce velocity profiles with inflexion points and may trigger instability there. These results change as the travel time T increases so as ...
... Note that the form of u(x) in {M}, derived from (2.12) differs from that in {U}, being negative and having two minima. In the surface zone {S}, viscous effects induce velocity profiles with inflexion points and may trigger instability there. These results change as the travel time T increases so as ...
Deep fluid flow – melt interaction and problems of granite
... the processes of crystallization and emanative differentiation of granitic magma. In case of large and unique pegmatite rare-metal deposits, the most complicated issue in terms of this concept is to identify the mode of strong concentrating and transport of huge amounts of rare elements into local c ...
... the processes of crystallization and emanative differentiation of granitic magma. In case of large and unique pegmatite rare-metal deposits, the most complicated issue in terms of this concept is to identify the mode of strong concentrating and transport of huge amounts of rare elements into local c ...
Introduction to the immersed boundary method
... condition. A local force density is introduced to modify the flow field. When applied correctly, this can be used to realize deformable or rigid objects in the flow. The advantage of this approach is that complex geometries can be easily implemented. For this reason, it is worthwhile to separate the ...
... condition. A local force density is introduced to modify the flow field. When applied correctly, this can be used to realize deformable or rigid objects in the flow. The advantage of this approach is that complex geometries can be easily implemented. For this reason, it is worthwhile to separate the ...
Flow Measurement
... rings. In the case of viscous liquids, the upstream edge of the bore can be rounded. The shape of the opening and its location do vary widely, and this is dependent on the material being measured. Standard orifice meters are primarily used to measure gas and vapor flow. Measurement is relatively acc ...
... rings. In the case of viscous liquids, the upstream edge of the bore can be rounded. The shape of the opening and its location do vary widely, and this is dependent on the material being measured. Standard orifice meters are primarily used to measure gas and vapor flow. Measurement is relatively acc ...
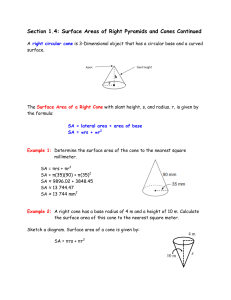
Section 1.4: Surface Areas of Right Pyramids and Cones Continued
... Finding Missing unknowns given the surface area of a Right Pyramid, Cone, Prism or cylinder. (Major topic—study for LA) Example 1: The surface area of a right cone is 125 in.2 and its radius is 4.7 in. What is the slant height of the right cone? Step 1: Sketch a diagram. Step 2: Use the formula for ...
... Finding Missing unknowns given the surface area of a Right Pyramid, Cone, Prism or cylinder. (Major topic—study for LA) Example 1: The surface area of a right cone is 125 in.2 and its radius is 4.7 in. What is the slant height of the right cone? Step 1: Sketch a diagram. Step 2: Use the formula for ...
Physical Principles - Thayer School of Engineering
... A couple of remarks are in order. First, as intimated in Chapter 1, stratification is an essential ingredient of environmental fluid mechanics, and this implies that density variations, although small, can have significant dynamical effects. The astute student can then legitimately ask whether the n ...
... A couple of remarks are in order. First, as intimated in Chapter 1, stratification is an essential ingredient of environmental fluid mechanics, and this implies that density variations, although small, can have significant dynamical effects. The astute student can then legitimately ask whether the n ...
Document
... of the “flow” or penetration of the field vectors through an imaginary fixed surface in the field. • Flux is the rate at which field lines passes through the surface area. ...
... of the “flow” or penetration of the field vectors through an imaginary fixed surface in the field. • Flux is the rate at which field lines passes through the surface area. ...
Fluid thread breakup
Fluid thread breakup is the process by which a single mass of fluid breaks into several smaller fluid masses. The process is characterized by the elongation of the fluid mass forming thin, thread-like regions between larger nodules of fluid. The thread-like regions continue to thin until they break, forming individual droplets of fluid.Thread breakup occurs where two fluids or a fluid in a vacuum form a free surface with surface energy. If more surface area is present than the minimum required to contain the volume of fluid, the system has an excess of surface energy. A system not at the minimum energy state will attempt to rearrange so as to move toward the lower energy state, leading to the breakup of the fluid into smaller masses to minimize the system surface energy by reducing the surface area. The exact outcome of the thread breakup process is dependent on the surface tension, viscosity, density, and diameter of the thread undergoing breakup.