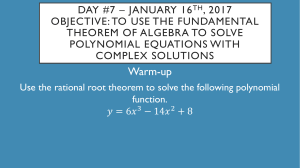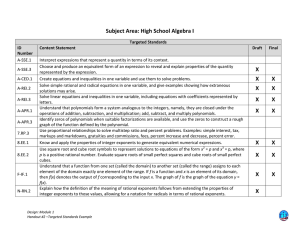
A-APR.A.1
... This definition for highly-leveraged standards was adapted from the website of Millis Public Schools, K-12, in Massachusetts, USA. http://www.millis.k12.ma.us/services/curriculum_assessment/brochures Specifically for mathematics, the Highly-Leveraged Standards are the Major Content/Clusters as defin ...
... This definition for highly-leveraged standards was adapted from the website of Millis Public Schools, K-12, in Massachusetts, USA. http://www.millis.k12.ma.us/services/curriculum_assessment/brochures Specifically for mathematics, the Highly-Leveraged Standards are the Major Content/Clusters as defin ...
Automatic Geometric Theorem Proving: Turning Euclidean
... Theorem: (Hilbert’s Nullstellensatz) Let k be an algebraically closed field. For any ideal J ⊂ k[x1, . . . , xn], ...
... Theorem: (Hilbert’s Nullstellensatz) Let k be an algebraically closed field. For any ideal J ⊂ k[x1, . . . , xn], ...