x - Angelfire
... Place ion into cubic crystal environment with six Oxygen O2- neighbours: •Electrostatic field due to the neighbours; the crystal field. • Stark Effect: electric-field acting on ion. • Some of the 5-fold degeneracy is lifted. Cubic crystal: less symmetric than a spherical ion. → d orbitals split into ...
... Place ion into cubic crystal environment with six Oxygen O2- neighbours: •Electrostatic field due to the neighbours; the crystal field. • Stark Effect: electric-field acting on ion. • Some of the 5-fold degeneracy is lifted. Cubic crystal: less symmetric than a spherical ion. → d orbitals split into ...
download
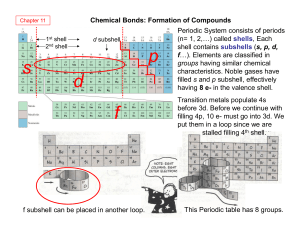
... When metal atoms bond, a metallic bond occurs. When an atom has a nearly full electron shell, it will try to find electrons from another atom so that it can fill its outer shell. These elements are usually described as nonmetals. The bond between two nonmetal atoms is usually a covalent bond. Where ...
... When metal atoms bond, a metallic bond occurs. When an atom has a nearly full electron shell, it will try to find electrons from another atom so that it can fill its outer shell. These elements are usually described as nonmetals. The bond between two nonmetal atoms is usually a covalent bond. Where ...
Tutorial 4 (PowerPoint)
... from the sample are exerted on it • The tip’s vibration amplitude must be much less than the distance between it and the sample to ensure linear operation – Like how a transistor amplifier is linear when the signal is much less than the supply voltage ...
... from the sample are exerted on it • The tip’s vibration amplitude must be much less than the distance between it and the sample to ensure linear operation – Like how a transistor amplifier is linear when the signal is much less than the supply voltage ...
Formation of a Surface–Sandwich Structure in Pd
... structure and composition. In particular, it is well-known that Pd is a metal with important existing and potential applications as a catalyst in heterogeneous catalysis. The use of Pd as a single active metal component in catalysis has received considerable attention on the basis of its remarkable ...
... structure and composition. In particular, it is well-known that Pd is a metal with important existing and potential applications as a catalyst in heterogeneous catalysis. The use of Pd as a single active metal component in catalysis has received considerable attention on the basis of its remarkable ...
(2) Gph 321- MECHANISM OF ELECTRICAL
... require other mechanisms than ion flow through connate water. c) Polarization of ions or sometimes electrons under the influence of an electrical field, they move a short distance then stop. Ex. Polarization of the dielectric in a condenser polarization ( electrical moment / unit ...
... require other mechanisms than ion flow through connate water. c) Polarization of ions or sometimes electrons under the influence of an electrical field, they move a short distance then stop. Ex. Polarization of the dielectric in a condenser polarization ( electrical moment / unit ...
Inductively-Coupled Plasma (ICP) Excitation Source
... waveguide or cavity. Microwaves produced from a magnetron (a microwave generator) fill the waveguide or cavity and cause the electrons in the plasma support gas to oscillate. The oscillating electons collide with other atoms in the flowing gas to create and maintain a hightemperature plasma. As in i ...
... waveguide or cavity. Microwaves produced from a magnetron (a microwave generator) fill the waveguide or cavity and cause the electrons in the plasma support gas to oscillate. The oscillating electons collide with other atoms in the flowing gas to create and maintain a hightemperature plasma. As in i ...
Click Here To File
... -There are 4 unpaired electrons. -Water is a weak ligand. Thus the hybridisation involved is sp3d2 (marks to be granted if hybridisation is depicted diagrammatically) (ii) The ionisation isomer is [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br. The IUPAC name is pentaamminesulphatocobalt(III)bromide. Chemical test to distinguish ...
... -There are 4 unpaired electrons. -Water is a weak ligand. Thus the hybridisation involved is sp3d2 (marks to be granted if hybridisation is depicted diagrammatically) (ii) The ionisation isomer is [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br. The IUPAC name is pentaamminesulphatocobalt(III)bromide. Chemical test to distinguish ...
Document
... never involved in the bond as they are too close to their own nucleus. 2 He atoms will never form a bond because Energy of He2 > 2 He. ...
... never involved in the bond as they are too close to their own nucleus. 2 He atoms will never form a bond because Energy of He2 > 2 He. ...
MISE - Physical Basis of Chemistry
... next mission was to “super-size” the atomic weight scale so that the listed atomic weights would prove useful for weighing things out on laboratory balances. Question: Can an atomic weight scale be developed - related in a simple way to the existing one - such that the listed numerical values can st ...
... next mission was to “super-size” the atomic weight scale so that the listed atomic weights would prove useful for weighing things out on laboratory balances. Question: Can an atomic weight scale be developed - related in a simple way to the existing one - such that the listed numerical values can st ...
File
... 2. Physical Change: a change in the size or form of a substance that does not change its composition eg. cutting, bending, changes in state: boiling, melting, condensing, and solidifying 3. Chemical Property: characteristic of matter that can be observed when matter undergoes a change in composition ...
... 2. Physical Change: a change in the size or form of a substance that does not change its composition eg. cutting, bending, changes in state: boiling, melting, condensing, and solidifying 3. Chemical Property: characteristic of matter that can be observed when matter undergoes a change in composition ...
“Step-induced defects in thin films and the properties”
... Many transition metal oxides show the electrical induced resistive switching effect and therefore have been proposed as the basis for future non-volatile memories. Non-volatile memories combine the advantages of Flash and (DRAM) while avoiding their typical disadvantages. The resistive switching eff ...
... Many transition metal oxides show the electrical induced resistive switching effect and therefore have been proposed as the basis for future non-volatile memories. Non-volatile memories combine the advantages of Flash and (DRAM) while avoiding their typical disadvantages. The resistive switching eff ...
Scanning Probe MicroScopy History of Scanning Probe Microscopy
... The plot obtained depends on the nature of the material (see sidebar); for semiconductors, the plot would look something like Figure 8. The measurements are carried out at an extremely low temperature to improve the resolution. AFM ...
... The plot obtained depends on the nature of the material (see sidebar); for semiconductors, the plot would look something like Figure 8. The measurements are carried out at an extremely low temperature to improve the resolution. AFM ...
29:28 – dielectric materials
... since the electrons from the hydrogen atoms spend more time near the oxygen atom then with the hydrogen atoms. This results in an effective and permanent charge separation. H+ ...
... since the electrons from the hydrogen atoms spend more time near the oxygen atom then with the hydrogen atoms. This results in an effective and permanent charge separation. H+ ...
Part V
... of the orbital of the outer valence electron for that atom.
• Similarly, the Ionic Radius of an ion can be crudely
thought of as the Mean Quantum Mechanical Radius
of the orbital of the outer valence electron for that ion.
• In quantum mechanics, could be calculated using the
wavefunctio ...
...
Topic 2
... Early in the 19th century John Dalton developed atomic theory. His theory explained the best available experimental data at that time. His theory has been modified since then with the discovery of other data, but his work was the initial ground ...
... Early in the 19th century John Dalton developed atomic theory. His theory explained the best available experimental data at that time. His theory has been modified since then with the discovery of other data, but his work was the initial ground ...
Atomic spectroscopy methods
... light absorption and emission of atoms in the gas phase. The goal is elemental analysis - identity and concentration • of a specific element in the sample; chemical and structural information are lost. The sample is destroyed. ...
... light absorption and emission of atoms in the gas phase. The goal is elemental analysis - identity and concentration • of a specific element in the sample; chemical and structural information are lost. The sample is destroyed. ...
Extrinsic Semiconductors, P-N Junctions and Transistors
... overlap, causing the material to become a metal ...
... overlap, causing the material to become a metal ...
How to Balance Chemical Equations
... involved are set and their formulas can not be altered. Hence, any change to the subscripts is NOT allowed. ONLY COEFFICIENTS ARE ALLOWED TO BE CHANGED!! ...
... involved are set and their formulas can not be altered. Hence, any change to the subscripts is NOT allowed. ONLY COEFFICIENTS ARE ALLOWED TO BE CHANGED!! ...
doc: Oxidation Numbers
... It is often useful to follow chemical reactions by looking at changes in the oxidation numbers of the atoms in each compound during the reaction. Oxidation numbers also play an important role in the naming of chemical compounds. By definition, the oxidation number of an atom is the charge that atom ...
... It is often useful to follow chemical reactions by looking at changes in the oxidation numbers of the atoms in each compound during the reaction. Oxidation numbers also play an important role in the naming of chemical compounds. By definition, the oxidation number of an atom is the charge that atom ...
Unit 1 PowerPoint Complete Notes
... following are hints to help determine the physical state. (s) – most metals, precipitates (l) – mercury, bromine, water (g) – noble gases, diatomic molecules (except bromine), ammonia (aq) – substance is in a water based solution (use solubility chart) ...
... following are hints to help determine the physical state. (s) – most metals, precipitates (l) – mercury, bromine, water (g) – noble gases, diatomic molecules (except bromine), ammonia (aq) – substance is in a water based solution (use solubility chart) ...
Defining the Atom - Central Lyon CSD
... together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. ...
... together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. ...
Spatial resolution in atom probe tomography
... The spatial resolution in atom probe tomography is highly anisotropic: the resolution in the direction of the analysis, the dimension that is built through the procedure described above, is often high enough to resolve atomic planes in the depth of the material (Warren, et al., 1998), as revealed in ...
... The spatial resolution in atom probe tomography is highly anisotropic: the resolution in the direction of the analysis, the dimension that is built through the procedure described above, is often high enough to resolve atomic planes in the depth of the material (Warren, et al., 1998), as revealed in ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions - Moodle @ FCT-UNL
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Atom probe

The atom probe was introduced at the 14th International Field Emission Symposium in 1967 by Erwin W. Müller and John Panitz. For the first time an instrument could “... determine the nature of one single atom seen on a metal surface and selected from neighboring atoms at the discretion of the observer”. Erwin Wilhelm Müller, J. A. Panitz, and S. Brooks McLane. The atom probe is closely related to the field ion microscope, the first microscopic instrument capable of atomic resolution, developed in 1951 by Erwin Wilhelm Müller.Atom probes are unlike conventional optical or electron microscopes, in that the magnification effect comes from the magnification provided by a highly curved electric field, rather than by the manipulation of radiation paths. The method is destructive in nature removing ions from a sample surface in order to image and identify them, generating magnifications sufficient to observe individual atoms as they are removed from the sample surface. Through coupling of this magnification method with time of flight mass spectrometry, ions evaporated by application of electric pulses can have their mass-to-charge ratio computed.Through successive evaporation of material, layers of atoms are removed from a specimen, allowing for probing not only of the surface, but also through the material itself. Computer methods are utilised to rebuild a three-dimensional view of the sample, prior to it being evaporated, providing atomic scale information on the structure of a sample, as well as providing the type atomic species information. The instrument allows the three-dimensional reconstruction of up to billions of atoms from a sharp tip (corresponding to specimen volumes of 10,000-10,000,000 nm3).