sheet#10,by farah odeh
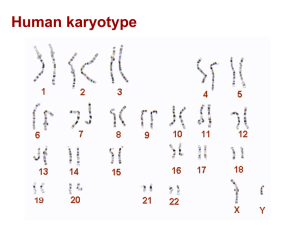
... Multifactorial diseases human diseases are caused by multiple causes genetic environmental or both. Some disease genetic predominate like Down syndrome and some environmental like infections (viruses). Most chronic diseases are caused by both (schizophrenia and diabetes ancongenetal malformation Gen ...
... Multifactorial diseases human diseases are caused by multiple causes genetic environmental or both. Some disease genetic predominate like Down syndrome and some environmental like infections (viruses). Most chronic diseases are caused by both (schizophrenia and diabetes ancongenetal malformation Gen ...
Study Guide for Genetics Test
... 15. A person who has one allele for a trait but does not exhibit the trait in their phenotype. Females can only be carriers because they have 2 X chromosomes, and if a male has one allele for the disease then they are not carriers, they actually have the disease. 16. A chart that tracks which member ...
... 15. A person who has one allele for a trait but does not exhibit the trait in their phenotype. Females can only be carriers because they have 2 X chromosomes, and if a male has one allele for the disease then they are not carriers, they actually have the disease. 16. A chart that tracks which member ...
2. Organism`s level of realization of hereditary information
... Different dominant non-allele's genes affect on one trait, making it more expressive. ...
... Different dominant non-allele's genes affect on one trait, making it more expressive. ...
Genetics Notes PDP - Lincoln Park High School
... o P (parental) generation: original true-breeding plants o F1 (1st filial) generation: offspring of P gen. o On your bellringer, predict the results in the offspring when Mendel crossed the following: Purple flowers X White flowers Tall plants X Short plants Results: F1 plants were all the sam ...
... o P (parental) generation: original true-breeding plants o F1 (1st filial) generation: offspring of P gen. o On your bellringer, predict the results in the offspring when Mendel crossed the following: Purple flowers X White flowers Tall plants X Short plants Results: F1 plants were all the sam ...
Slides - SFU.ca
... • The study of heritable changes in gene expression and function that cannot be explained by changes in DNA sequence. ...
... • The study of heritable changes in gene expression and function that cannot be explained by changes in DNA sequence. ...
(QTL) mapping for adaptive traits of tree growth in forests
... Commonly used to study the evolution of populations in response to environmental variations; QTL genes have allelic variants that make small, quantitative contributions to phenotype; Phenotype helps reveal the location of regulatory genes or other genomic regions affecting growth; Arabadopsis ...
... Commonly used to study the evolution of populations in response to environmental variations; QTL genes have allelic variants that make small, quantitative contributions to phenotype; Phenotype helps reveal the location of regulatory genes or other genomic regions affecting growth; Arabadopsis ...
Mendel and The Gene Idea
... • The independent segregation of each pair of alleles during gamete formation • In pea plants, flower color is independent of seed color, is independent of seedshape character, etc. • Monohybrid – heterozygous for one ...
... • The independent segregation of each pair of alleles during gamete formation • In pea plants, flower color is independent of seed color, is independent of seedshape character, etc. • Monohybrid – heterozygous for one ...
S-B-5-1_Vocabulary Worksheet and KEY Vocabulary Worksheet
... Directions: Write the correct vocabulary term for each definition in the blank. Select vocabulary words from the box below. ____________ Forms of genes responsible for controlling the same trait; different versions of the same gene ____________ An allele that is always expressed when it is present i ...
... Directions: Write the correct vocabulary term for each definition in the blank. Select vocabulary words from the box below. ____________ Forms of genes responsible for controlling the same trait; different versions of the same gene ____________ An allele that is always expressed when it is present i ...
Genetics - FAQ`s - El Camino College
... material. A chromosome is made up of one tightly coiled DNA molecule. Humans have 46 chromosomes, which occur in 23 pairs. WHAT IS A GENE? Even scientists disagree on how to define a gene. Generally, a gene is defined as a sequence of DNA that codes for a particular protein, or directs the cell’s fu ...
... material. A chromosome is made up of one tightly coiled DNA molecule. Humans have 46 chromosomes, which occur in 23 pairs. WHAT IS A GENE? Even scientists disagree on how to define a gene. Generally, a gene is defined as a sequence of DNA that codes for a particular protein, or directs the cell’s fu ...
Name - Valhalla High School
... 7. What is the difference between an allele and a gene? a. allele ...
... 7. What is the difference between an allele and a gene? a. allele ...
Detection of different genes heredity
... Some traits are controlled by a single gene with two alleles. Many human traits are also controlled by a single gene with one dominant allele and one recessive allele. These human traits have two distinctly different phenotypes. ...
... Some traits are controlled by a single gene with two alleles. Many human traits are also controlled by a single gene with one dominant allele and one recessive allele. These human traits have two distinctly different phenotypes. ...
genetic variation
... disturbance, geographical position, gene flow, population size, and founder effects (Lesica and Allendorf, 1995; Ohsawa et al., 2008). Studying of genetic variation can help us to identify the species, assess the distribution, examine the genetic structure, or probe the phenotype. Moreover, it was a ...
... disturbance, geographical position, gene flow, population size, and founder effects (Lesica and Allendorf, 1995; Ohsawa et al., 2008). Studying of genetic variation can help us to identify the species, assess the distribution, examine the genetic structure, or probe the phenotype. Moreover, it was a ...
File
... the cross of a known homozygous recessive with an unknown genotype to see if the offspring have any dominant traits ...
... the cross of a known homozygous recessive with an unknown genotype to see if the offspring have any dominant traits ...
Teacher - Application Genetics Notes Pre AP 13-14
... In humans, blood type is determined by 3 alleles – IA, IB and iO BUT genes come in pairs, so each human can only inherit 2 alleles ...
... In humans, blood type is determined by 3 alleles – IA, IB and iO BUT genes come in pairs, so each human can only inherit 2 alleles ...
PRE-AP BIOLOGY: GENETICS
... D) a triploid plant that results from breeding two very different plants. E) None of the choices are correct. 4. Which one of the following is false? A) The genetic makeup of an organism constitutes its genotype. B) An organism with two different alleles for a single trait is said to be heterozygous ...
... D) a triploid plant that results from breeding two very different plants. E) None of the choices are correct. 4. Which one of the following is false? A) The genetic makeup of an organism constitutes its genotype. B) An organism with two different alleles for a single trait is said to be heterozygous ...
Biology memory tricks
... Genotype – Rr, RR, rr (2 alleles per gene) Phenotype – tall or short – what you see! vocab - know it! allele, gene, hybrid, pure, trait, P1, F1, F2 4 step cross GASR working backwards - showing WORK! Dominance (RR, Rr – round, rr - wrinkled) Try to use letters that have different cases, Tt, Qq, etc. ...
... Genotype – Rr, RR, rr (2 alleles per gene) Phenotype – tall or short – what you see! vocab - know it! allele, gene, hybrid, pure, trait, P1, F1, F2 4 step cross GASR working backwards - showing WORK! Dominance (RR, Rr – round, rr - wrinkled) Try to use letters that have different cases, Tt, Qq, etc. ...
Genetic selection and variation
... Genetic selection and variation Genes A gene can be described as a linear piece of DNA that includes a regulatory sequence that determines when the gene will be transcribed: An initiation sequence; Exons that are the coding region; Introns that are non coding regions and are spliced out of the gene ...
... Genetic selection and variation Genes A gene can be described as a linear piece of DNA that includes a regulatory sequence that determines when the gene will be transcribed: An initiation sequence; Exons that are the coding region; Introns that are non coding regions and are spliced out of the gene ...
Evolution of Populations Scavenger Hunt
... *A gene pool typically contains ___________ or ____________ alleles for each inheritable trait. *The number of times an allele occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of times other alleles occur is known as ____________________ ________________________. Sources of Genetic Variation *The two ...
... *A gene pool typically contains ___________ or ____________ alleles for each inheritable trait. *The number of times an allele occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of times other alleles occur is known as ____________________ ________________________. Sources of Genetic Variation *The two ...
Biology - Genetics OEQs
... Genes exert their influence on organisms by being turned on and off in precise ways and at precise times. Disease can result when problems arise during this process of “gene regulation.” The first processes of gene regulation to be discovered involved molecular ‘switches’ that regulate transcription ...
... Genes exert their influence on organisms by being turned on and off in precise ways and at precise times. Disease can result when problems arise during this process of “gene regulation.” The first processes of gene regulation to be discovered involved molecular ‘switches’ that regulate transcription ...