PROBABILITY
... cleft chin). For example, having free earlobes is the dominant form of the trait; so it will show up more often in a population. When there is at least one dominant gene in the pair, then the dominant allele masks, or covers up, the recessive allele. The only time the recessive form of the gene show ...
... cleft chin). For example, having free earlobes is the dominant form of the trait; so it will show up more often in a population. When there is at least one dominant gene in the pair, then the dominant allele masks, or covers up, the recessive allele. The only time the recessive form of the gene show ...
G - bellevuebiology
... Sources of genetic variation 1) SEXUAL REPRODUCTION A. Meiosis – one allele is passed on from each parent (recall that sperm and eggs are haploid cells, each containing half the necessary genetic information). B. Random fertilization – only one of the millions of sperm involved in mating will ferti ...
... Sources of genetic variation 1) SEXUAL REPRODUCTION A. Meiosis – one allele is passed on from each parent (recall that sperm and eggs are haploid cells, each containing half the necessary genetic information). B. Random fertilization – only one of the millions of sperm involved in mating will ferti ...
DNA & Heredity
... that the ribosome can hold it in place for the tRNA. The tRNA then comes and hooks onto the mRNA and bring the amino acid. When a bunch of amino acids are hooked together it makes something called a ...
... that the ribosome can hold it in place for the tRNA. The tRNA then comes and hooks onto the mRNA and bring the amino acid. When a bunch of amino acids are hooked together it makes something called a ...
The Principle Methods of Identifying Twins for Research
... But it isn’t the home environment that makes the difference. It is the environment shared by children (in) the same peer group. Judith Rich Harris, 1998 ...
... But it isn’t the home environment that makes the difference. It is the environment shared by children (in) the same peer group. Judith Rich Harris, 1998 ...
V p
... Phenotype Hypothetical: Three loci determine plant’s height; each with two alleles; • A+; B+; C+ are producing growth hormone • A-; B-; C- are not producing growth hormone • For A the possible genotypes are • A+A+; A+A-; A-A- ...
... Phenotype Hypothetical: Three loci determine plant’s height; each with two alleles; • A+; B+; C+ are producing growth hormone • A-; B-; C- are not producing growth hormone • For A the possible genotypes are • A+A+; A+A-; A-A- ...
S1-1-11 - Single Trait Inheritance
... experiential/evidential plane by using the students’ experiences of uniqueness to explain genetics. In this lesson, they are learning about single trait inheritance. These are the genes that have usually either/or results, and have only one gene affecting phenotype. By using the activity on the “act ...
... experiential/evidential plane by using the students’ experiences of uniqueness to explain genetics. In this lesson, they are learning about single trait inheritance. These are the genes that have usually either/or results, and have only one gene affecting phenotype. By using the activity on the “act ...
Notes - marric
... –Gene Mapping Tracking crossing over helps determine where genes are located on the chromosome –Genes that are far apart have a ______________chance of crossing over –Genes that are closer have a _________________________ chance of crossing over •Genes that stay together are said to be _____________ ...
... –Gene Mapping Tracking crossing over helps determine where genes are located on the chromosome –Genes that are far apart have a ______________chance of crossing over –Genes that are closer have a _________________________ chance of crossing over •Genes that stay together are said to be _____________ ...
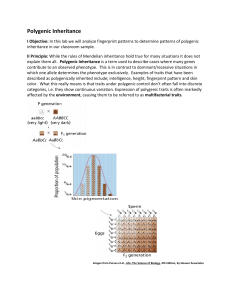
Polygenic Inheritance
... II Principle: While the rules of Mendelian inheritance hold true for many situations it does not explain them all. Polygenic Inheritance is a term used to describe cases where many genes contribute ...
... II Principle: While the rules of Mendelian inheritance hold true for many situations it does not explain them all. Polygenic Inheritance is a term used to describe cases where many genes contribute ...
Mendel and the Gene Idea
... Is an example of codominance The M, N, and MN blood groups of humans presence of two specific molecules on the surface of red blood cells Both the M & N molecules are expressed in the heterozygous individual People of group M (genotype MM) have one type of molecule on their red blood cells, people ...
... Is an example of codominance The M, N, and MN blood groups of humans presence of two specific molecules on the surface of red blood cells Both the M & N molecules are expressed in the heterozygous individual People of group M (genotype MM) have one type of molecule on their red blood cells, people ...
Genetics and Reproduction Quiz
... 2. A species has 52 chromosomes. How many chromosomes would be in a sperm cell of this species? A) 16 B) 26 C) 32 D) 8 3.Which statement is MOST accurate? a. Organisms produced by asexual reproduction are genetically identical to the parent. b. In sexual reproduction, offspring get genes from only o ...
... 2. A species has 52 chromosomes. How many chromosomes would be in a sperm cell of this species? A) 16 B) 26 C) 32 D) 8 3.Which statement is MOST accurate? a. Organisms produced by asexual reproduction are genetically identical to the parent. b. In sexual reproduction, offspring get genes from only o ...
Unit 3: Genetics
... Dominant Allele: an allele that hides a recessive trait; usually characterized by a capital letter. Recessive Allele: an allele that can be “masked” or hidden by a dominant allele; usually characterized by a lower-case letter ...
... Dominant Allele: an allele that hides a recessive trait; usually characterized by a capital letter. Recessive Allele: an allele that can be “masked” or hidden by a dominant allele; usually characterized by a lower-case letter ...
2015 Test 3 study guide Bio 105
... • What a test is cross: what would the phenotype ratio be for a monohybrid test cross: and what would be the phenotype ratio for a dihybrid cross? • For dihybrid cross BbDd x BbDd what phenotype ratio would you get? • 5.14 Pedigrees • Pedigrees are useful to look at genetic diseases cause by a singl ...
... • What a test is cross: what would the phenotype ratio be for a monohybrid test cross: and what would be the phenotype ratio for a dihybrid cross? • For dihybrid cross BbDd x BbDd what phenotype ratio would you get? • 5.14 Pedigrees • Pedigrees are useful to look at genetic diseases cause by a singl ...
Genetic variation
... DNA to any one of the two parents. The offspring may inherit certain traits from the parents, but will have a different genotype and therefore a different phenotype. ...
... DNA to any one of the two parents. The offspring may inherit certain traits from the parents, but will have a different genotype and therefore a different phenotype. ...
Presentation
... He also noticed that the pea plants inherited two forms of each gene; one from each parent plant. ...
... He also noticed that the pea plants inherited two forms of each gene; one from each parent plant. ...
A trait - Images
... Full-shaded circle represents a female with the trait Full-shaded square represents a male with the trait ...
... Full-shaded circle represents a female with the trait Full-shaded square represents a male with the trait ...
Genetics Vocabulary
... The chemical factors in your DNA that determine your traits Genes for things give us codons which we use to make proteins and proteins help us express those traits! ...
... The chemical factors in your DNA that determine your traits Genes for things give us codons which we use to make proteins and proteins help us express those traits! ...
Untitled
... 1. More males that females affected 2. Affected sons are usually born to unaffected mothers, zig-zag pattern – from grandfather to grandson through an unaffected female. 3. Approximately 50% of a carrier female are affected 4. It is never passed from father to son 5. All daughters of affected father ...
... 1. More males that females affected 2. Affected sons are usually born to unaffected mothers, zig-zag pattern – from grandfather to grandson through an unaffected female. 3. Approximately 50% of a carrier female are affected 4. It is never passed from father to son 5. All daughters of affected father ...
6.2 Human Genetic Disorders
... and intestines, making it hard for the person to breathe. Caused by a recessive allele on one chromosome – result of a mutation. ...
... and intestines, making it hard for the person to breathe. Caused by a recessive allele on one chromosome – result of a mutation. ...
Document
... blocked • Genotype - Homozygous recessive at the gene locus that codes for tyrosinase, an enzyme in the melaninsynthesizing pathway ...
... blocked • Genotype - Homozygous recessive at the gene locus that codes for tyrosinase, an enzyme in the melaninsynthesizing pathway ...