File
... Activity 2.1.1: Student Response Sheet Part I: Genetic Testing Pre-Survey Before we begin our study of genetic disorders and genetic testing, think about each of the following scenarios. Circle true or false in each case and explain why you chose this option. ...
... Activity 2.1.1: Student Response Sheet Part I: Genetic Testing Pre-Survey Before we begin our study of genetic disorders and genetic testing, think about each of the following scenarios. Circle true or false in each case and explain why you chose this option. ...
Evolution of Populations
... Genetics Joins Evolutionary Theory Darwin’s original ideas can now be understood in genetic terms. ▶ Researchers discovered that traits are controlled by genes and that many genes have at least two forms, or alleles. The combination of different alleles is an individual’s genotype. Natural selection ...
... Genetics Joins Evolutionary Theory Darwin’s original ideas can now be understood in genetic terms. ▶ Researchers discovered that traits are controlled by genes and that many genes have at least two forms, or alleles. The combination of different alleles is an individual’s genotype. Natural selection ...
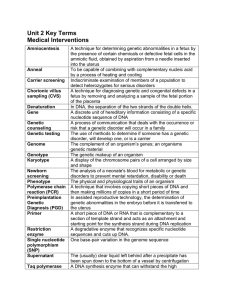
Unit 2 Terms
... measurement of internal body structures and the detection of bodily abnormalities Using a somatic or body cell from a multicellular organism to make one or more genetically identical individuals The alteration of the genes of a person afflicted with a genetic disease A procedure in which gametes are ...
... measurement of internal body structures and the detection of bodily abnormalities Using a somatic or body cell from a multicellular organism to make one or more genetically identical individuals The alteration of the genes of a person afflicted with a genetic disease A procedure in which gametes are ...
Mechansisms for Evolution 2015
... Microevolution is evolution on the smallest scale that cause generation-to-generation changes in allele frequency within populations. •Population: a group of interbreeding organisms present in a specific location at a specific time. •Allele frequency: the frequency of a particular allele in the popu ...
... Microevolution is evolution on the smallest scale that cause generation-to-generation changes in allele frequency within populations. •Population: a group of interbreeding organisms present in a specific location at a specific time. •Allele frequency: the frequency of a particular allele in the popu ...
What to review for the Genetics Test: Be able to compare and
... 9. Identify and use a punett square to compare inherited traits. 10. Vocabulary to know: genetics, phenotype, genotype, natural selection, evolution, homozygous, heterozygous, adaptation, inherited trait, acquired trait, sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. What to review for the Genetics T ...
... 9. Identify and use a punett square to compare inherited traits. 10. Vocabulary to know: genetics, phenotype, genotype, natural selection, evolution, homozygous, heterozygous, adaptation, inherited trait, acquired trait, sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. What to review for the Genetics T ...
SEMINAR CANCELED- Rescheduled to January 28, 2016
... Rim101, and genes characteristic of invasive hyphal cells. The late phase includes responses related to phagocytosis by macrophages. Transcription factor gene expression also reflects early and late phases. Transcription factor genes that are required for virulence or proliferation in vivo are enric ...
... Rim101, and genes characteristic of invasive hyphal cells. The late phase includes responses related to phagocytosis by macrophages. Transcription factor gene expression also reflects early and late phases. Transcription factor genes that are required for virulence or proliferation in vivo are enric ...
Summary Gene regulatory factors in the evolutionary history of
... among other 218 gene ontology terms. Using the classification of DNA-binding GRFs (Wingender et al. 2015), we were able to group 1521 GRF genes (~46%) into 41 different GRF classes. This GRF catalog allowed us to initially explore and discuss how some GRF genes have ...
... among other 218 gene ontology terms. Using the classification of DNA-binding GRFs (Wingender et al. 2015), we were able to group 1521 GRF genes (~46%) into 41 different GRF classes. This GRF catalog allowed us to initially explore and discuss how some GRF genes have ...
TOC - Genes | Genomes | Genetics
... In clonally propagated crops, like cassava (Manihot esculenta), non-additive genetic effects (i.e. dominance and epistasis) are exploited by selecting superior genetic individuals as varieties. We quantified the amount and nature of non-additive genetic variation for key traits in a breeding populati ...
... In clonally propagated crops, like cassava (Manihot esculenta), non-additive genetic effects (i.e. dominance and epistasis) are exploited by selecting superior genetic individuals as varieties. We quantified the amount and nature of non-additive genetic variation for key traits in a breeding populati ...
Genetics Case Study: The Royal Family
... • Had body guard with him at all times to prevent accidents. ...
... • Had body guard with him at all times to prevent accidents. ...
Chapter 11 Study Guide
... Distinguish between the terms gene, allele, character, and trait. Distinguish between a dominant and a recessive allele. Distinguish between phenotype and genotype. Distinguish between complete dominance, incomplete dominance, and codominance, A. Using the character of fur color in tigers (blue is d ...
... Distinguish between the terms gene, allele, character, and trait. Distinguish between a dominant and a recessive allele. Distinguish between phenotype and genotype. Distinguish between complete dominance, incomplete dominance, and codominance, A. Using the character of fur color in tigers (blue is d ...
Genetics Case Study: The Royal Family
... • Had body guard with him at all times to prevent accidents. ...
... • Had body guard with him at all times to prevent accidents. ...
Nature vs nurture article
... apart. But a number of studies show that they are never exactly alike, even though they are remarkably similar in most respects. So, was the way we behave engrained in us before we were born? Or has it developed over time in response to our experiences? Researchers on all sides of the nature vs nurt ...
... apart. But a number of studies show that they are never exactly alike, even though they are remarkably similar in most respects. So, was the way we behave engrained in us before we were born? Or has it developed over time in response to our experiences? Researchers on all sides of the nature vs nurt ...
17 - Genetic Mutation
... single gene disorder is sickle-cell anemia. A mutation causes blood cells to look like a sickle rather than the normal doughnut-without-a-hole shape of a blood cell. Cystic fibrosis and Huntington’s disease are also single gene disorders. Multifactorial Disorders Multifactorial disorders result from ...
... single gene disorder is sickle-cell anemia. A mutation causes blood cells to look like a sickle rather than the normal doughnut-without-a-hole shape of a blood cell. Cystic fibrosis and Huntington’s disease are also single gene disorders. Multifactorial Disorders Multifactorial disorders result from ...
Genetic Modification Regulations and Procedures
... Genes located on a sex chromosome are called sex-linked genes. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Genes located on a sex chromosome are called sex-linked genes. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Genetics Notes
... receives from its parents. 2. Genes carry the instructions responsible for the expression of traits. 3. A pair of inherited genes controls a trait. 4. One member of the pair comes from each parent. 5. Alternative versions of genes are known as alleles. ...
... receives from its parents. 2. Genes carry the instructions responsible for the expression of traits. 3. A pair of inherited genes controls a trait. 4. One member of the pair comes from each parent. 5. Alternative versions of genes are known as alleles. ...
Linkage and Chromosome Mapping in Eukaryotes
... Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic Gene Mapping Genes on the same chromosome are physically and genetically linked They are in the same linkage group Since chromosomes segregate as a unit, linked genes should segregate as a unit Of course, there is recombination (crossing over) that will cha ...
... Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic Gene Mapping Genes on the same chromosome are physically and genetically linked They are in the same linkage group Since chromosomes segregate as a unit, linked genes should segregate as a unit Of course, there is recombination (crossing over) that will cha ...
non-Mendelian inheritance
... • Note: Most mitochondrial proteins are encoded by genes in the nucleus – These proteins are made in the cytoplasm, then transported into the ...
... • Note: Most mitochondrial proteins are encoded by genes in the nucleus – These proteins are made in the cytoplasm, then transported into the ...
Evolution Populations 17.2
... The Hardy-Weinberg Principle states that allele frequencies in a population should remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change. These factors include: non-random mating, small population size, immigration or emigration, mutations, and natural selection. Populations a ...
... The Hardy-Weinberg Principle states that allele frequencies in a population should remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change. These factors include: non-random mating, small population size, immigration or emigration, mutations, and natural selection. Populations a ...
Gene: Usually, a section of DNA long enough to code for a protein
... one allele may code for brown eyes, the other for blue. Because blue is recessive, your phenotype would be brown. Phenotype: Describes the effect of a gene. White fur is a phenotype. Genotype: Describes the genes an organism has inherited. In class a genotype might be written as BB. Homozygous: The ...
... one allele may code for brown eyes, the other for blue. Because blue is recessive, your phenotype would be brown. Phenotype: Describes the effect of a gene. White fur is a phenotype. Genotype: Describes the genes an organism has inherited. In class a genotype might be written as BB. Homozygous: The ...
Handout 25-27 - U of L Class Index
... Since neither A nor B is dominant over the other and they are both dominant over O they are said to be codominant. Many genes have more than two alleles (even though any one diploid individual can only have at most two alleles for any gene), such as the ABO blood groups in humans, which are an examp ...
... Since neither A nor B is dominant over the other and they are both dominant over O they are said to be codominant. Many genes have more than two alleles (even though any one diploid individual can only have at most two alleles for any gene), such as the ABO blood groups in humans, which are an examp ...
Study Guide for Chapter 4
... 19) What is the expected ratio of purple to white flowers when you breed first generation hybrids to each other? Why? 20) What were Mendel’s conclusions about inheritance? (reread page 179) 21) What are genes? What are alleles? 22) What is the difference between genotype and phenotype? 23) What does ...
... 19) What is the expected ratio of purple to white flowers when you breed first generation hybrids to each other? Why? 20) What were Mendel’s conclusions about inheritance? (reread page 179) 21) What are genes? What are alleles? 22) What is the difference between genotype and phenotype? 23) What does ...
PreAssessment - Boone County Schools
... Some plants reproduce this way Requires two different parent (sex) cells. DNA of the offspring is different than that of both parents. Each time offspring are formed, a new combination of traits is passed. Advantage- variation among offspring allows for adaptations and natural selection to occur. A ...
... Some plants reproduce this way Requires two different parent (sex) cells. DNA of the offspring is different than that of both parents. Each time offspring are formed, a new combination of traits is passed. Advantage- variation among offspring allows for adaptations and natural selection to occur. A ...
Pedigree - Turner
... Helps scientists separate genetic contributions from environmental contributions Traits that appear frequently in identical twins are at least partially controlled by heredity. Traits expressed differently in identical twins are strongly influenced by environment. ...
... Helps scientists separate genetic contributions from environmental contributions Traits that appear frequently in identical twins are at least partially controlled by heredity. Traits expressed differently in identical twins are strongly influenced by environment. ...
XYZW as nature`s language of love?
... may evolve more easily in species such as birds and butterflies with ZW sex determination than in species with the more familiar XY system. So, how convincing is the above explanation for the phylogenetic differences in how sexual selection is manifested? We cannot truthfully know – the evolutionary ...
... may evolve more easily in species such as birds and butterflies with ZW sex determination than in species with the more familiar XY system. So, how convincing is the above explanation for the phylogenetic differences in how sexual selection is manifested? We cannot truthfully know – the evolutionary ...