Genetics Part I
... Phenotype It is important to note that it is not possible to directly observe an individual's genotype. We can only observe the phenotype and infer the genotype. This learning activity is opposite to real life. However, we do it this way to learn how to decode genotypes. If we treat each allele inde ...
... Phenotype It is important to note that it is not possible to directly observe an individual's genotype. We can only observe the phenotype and infer the genotype. This learning activity is opposite to real life. However, we do it this way to learn how to decode genotypes. If we treat each allele inde ...
Diamond Blackfan Anemia, Genetics, and You
... DBA, because genetic mutations have not yet been found to explain more than half of the causes of the disorder. ...
... DBA, because genetic mutations have not yet been found to explain more than half of the causes of the disorder. ...
Genetic epidemiology: Systemic lupus erythematosus | Arthritis
... 1q41–42, using 43 families with 52 affected sibling pairs of mixed origin. Several additional linkage studies have been performed using sib-pairs and extended family pedigrees [15–19]. The parameters and test populations for each study as well as the genomic intervals detected in at least two mappin ...
... 1q41–42, using 43 families with 52 affected sibling pairs of mixed origin. Several additional linkage studies have been performed using sib-pairs and extended family pedigrees [15–19]. The parameters and test populations for each study as well as the genomic intervals detected in at least two mappin ...
Genetics Tutorial
... gene can hide another form of a gene. For example, the purple form of a gene would hide the white form of a gene. This now explained why some traits and diseases would skip generations. Click to see examples of traits that can skip generations ...
... gene can hide another form of a gene. For example, the purple form of a gene would hide the white form of a gene. This now explained why some traits and diseases would skip generations. Click to see examples of traits that can skip generations ...
Chapter. 15(Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance)
... • During meiosis I, nondisjunction can occur: pairs of homologous chromosomes do not separate normally during anaphase I. • As a result, one gamete receives two of the same type of chromosome, and another gamete receives no copy. ...
... • During meiosis I, nondisjunction can occur: pairs of homologous chromosomes do not separate normally during anaphase I. • As a result, one gamete receives two of the same type of chromosome, and another gamete receives no copy. ...
Genetics
... features like eye color, straight or curly hair, baldness, attached vs. free ear lobes, the ability to taste certain substances, and even whether you have dry or sticky earwax! Other genes may actually cause disease. Sickle cell anemia, muscular dystrophy, cystic fibrosis are each caused by a specif ...
... features like eye color, straight or curly hair, baldness, attached vs. free ear lobes, the ability to taste certain substances, and even whether you have dry or sticky earwax! Other genes may actually cause disease. Sickle cell anemia, muscular dystrophy, cystic fibrosis are each caused by a specif ...
In recent year there have been rapid progress made in mapping the
... model is fit to a subset of 100 genes. The estimates of random-effects may be examined to identify differentially expressed genes. An alternative overall model uses a hierarchical Bayesian model to analyze the entire data set using BUGS. This method was also applied to a subset of 100 genes. 1. Intr ...
... model is fit to a subset of 100 genes. The estimates of random-effects may be examined to identify differentially expressed genes. An alternative overall model uses a hierarchical Bayesian model to analyze the entire data set using BUGS. This method was also applied to a subset of 100 genes. 1. Intr ...
a historical view of social responsibility in genetics
... The recombinant DNA era and the Human Genome Project Although it is possible that the molecular biology of the 1950s and 1960s generated an environment in which reductionist approaches to a wide range of problems seemed appropriate, the breakthroughs in genetics in the 1970s have even more clearly c ...
... The recombinant DNA era and the Human Genome Project Although it is possible that the molecular biology of the 1950s and 1960s generated an environment in which reductionist approaches to a wide range of problems seemed appropriate, the breakthroughs in genetics in the 1970s have even more clearly c ...
Plumage Genes and Little Else Distinguish the Genomes of
... pigmentation or patterning in this or other systems. Correlations of variation at particular feather tracts and specific genetic variants imply even stronger associations between genotype and phenotype. For example, the black throat of golden-winged warblers, absent in blue-winged warblers and F1 hy ...
... pigmentation or patterning in this or other systems. Correlations of variation at particular feather tracts and specific genetic variants imply even stronger associations between genotype and phenotype. For example, the black throat of golden-winged warblers, absent in blue-winged warblers and F1 hy ...
Phenotype and gene ontology enrichment as guides for
... disease model in C. elegans would be to identify the phenologs of the disease to be studied in C. elegans by identifying disease-associated human genes in an unbiased manner through genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and identified candidate homolog genes in C. elegans. The orthologs can be used ...
... disease model in C. elegans would be to identify the phenologs of the disease to be studied in C. elegans by identifying disease-associated human genes in an unbiased manner through genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and identified candidate homolog genes in C. elegans. The orthologs can be used ...
Read the article
... The following are just a few simple examples of methods to identify the genetic information behind a trait. There are several more techniques already available and more will come since this research area is expanding rapidly. The traits an organism exhibit can be described as the response of the gen ...
... The following are just a few simple examples of methods to identify the genetic information behind a trait. There are several more techniques already available and more will come since this research area is expanding rapidly. The traits an organism exhibit can be described as the response of the gen ...
POPSIM: a general population simulation program.
... common prerequisite before embarking on a genome-wide linkage analysis in disorders where reasonable parametric estimates on the disease model exist. However, for complex genetic disorders like diabetes, arteriosclerosis, bipolar disorder or inflammatory bowel disease, the genotype to phenotype rela ...
... common prerequisite before embarking on a genome-wide linkage analysis in disorders where reasonable parametric estimates on the disease model exist. However, for complex genetic disorders like diabetes, arteriosclerosis, bipolar disorder or inflammatory bowel disease, the genotype to phenotype rela ...
Promoter Analysis for Intestinally
... i. Most of the hits in all 3 species are mostly TGATAA sites or some variation, but a few aren’t related to TGATAA at all ii. Hits vary hugely in length (due to the merging of overlapping motifsampler hits of the same length) iii. Each result set was extracted independently, so these hits overlap wi ...
... i. Most of the hits in all 3 species are mostly TGATAA sites or some variation, but a few aren’t related to TGATAA at all ii. Hits vary hugely in length (due to the merging of overlapping motifsampler hits of the same length) iii. Each result set was extracted independently, so these hits overlap wi ...
Color Inheritance in the Brittany
... puppies born with a certain trait, even the largest litter is a statistically small number. The patterns of inheritance of liver and roan work exactly the same. Orange however is recessive, as is the tri-color gene. So let’s look at that from a different angle. Tri-color is not so much a color gene ...
... puppies born with a certain trait, even the largest litter is a statistically small number. The patterns of inheritance of liver and roan work exactly the same. Orange however is recessive, as is the tri-color gene. So let’s look at that from a different angle. Tri-color is not so much a color gene ...
Punnett Squares 2
... woman (BB) with a heterozygous man (Bb). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes? 6. Draw a Punnett Square that crosses a heterozygous female (Bb) with a homozygous recessive male (bb). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes? ...
... woman (BB) with a heterozygous man (Bb). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes? 6. Draw a Punnett Square that crosses a heterozygous female (Bb) with a homozygous recessive male (bb). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes? ...
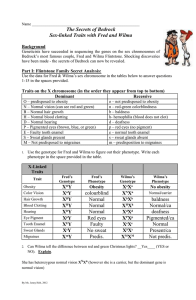
Part I: Flintstone Family Secret Analysis
... NO she does not. Her genotype is heterozygous (female offspring have 100% of inheriting a heterozygous genotype), meaning she is a carrier for baldness however she also has the dominant allele for normal hair, which means she will express normal hair ...
... NO she does not. Her genotype is heterozygous (female offspring have 100% of inheriting a heterozygous genotype), meaning she is a carrier for baldness however she also has the dominant allele for normal hair, which means she will express normal hair ...
Chapter 19 of Earth by Chernicoff
... Prevailing idea was that the characteristics of an organism were due to the blending of the traits from each parent (blending inheritance). Mendel proposed instead that an “element” determined a particular characteristic of an organism. Called particulate inheritance. The element (now called ‘gene’) ...
... Prevailing idea was that the characteristics of an organism were due to the blending of the traits from each parent (blending inheritance). Mendel proposed instead that an “element” determined a particular characteristic of an organism. Called particulate inheritance. The element (now called ‘gene’) ...
A de novo 16q24 - HAL
... suggests a possible role for COX4I1 in the paucity of observed adipose tissue. Moreover, a non-synonymous G to A transition is associated with a reduction in cytochrome oxidase activity and could be associated with Alzheimer's disease [18]. Finally, the MIR1910 (microRNA 1910) gene encodes microRNAs ...
... suggests a possible role for COX4I1 in the paucity of observed adipose tissue. Moreover, a non-synonymous G to A transition is associated with a reduction in cytochrome oxidase activity and could be associated with Alzheimer's disease [18]. Finally, the MIR1910 (microRNA 1910) gene encodes microRNAs ...
Genetics Questions Extra - Science-with
... Sickle cell anemia is caused by the sickle cell allele (HbS) of a gene that contributes to hemoglobin (Hb) production. The abnormal hemoglobin (hemoglobin-S) produced causes red blood cells to become deformed and block capillaries. Tissue damage results. Affected individuals homozygous for the sickl ...
... Sickle cell anemia is caused by the sickle cell allele (HbS) of a gene that contributes to hemoglobin (Hb) production. The abnormal hemoglobin (hemoglobin-S) produced causes red blood cells to become deformed and block capillaries. Tissue damage results. Affected individuals homozygous for the sickl ...
Gene Section IGH@ (Immunoglobulin Heavy) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... belonging to 7 subgroups, 9 IGHJ segments, and 11 IGHC genes. Eighty-two to 88 IGHV genes belong to 7 subgroups, whereas 41 pseudogenes, which are too divergent to be assigned to subgroups, have been assigned to 4 clans. Seven non-mapped IGHV genes have been described as insertion/deletion polymorph ...
... belonging to 7 subgroups, 9 IGHJ segments, and 11 IGHC genes. Eighty-two to 88 IGHV genes belong to 7 subgroups, whereas 41 pseudogenes, which are too divergent to be assigned to subgroups, have been assigned to 4 clans. Seven non-mapped IGHV genes have been described as insertion/deletion polymorph ...
Notes 16: More Mendelian Wrinkles
... • If you cross two Manx cats, you get two tailless kittens for every one tailed kitten. . . • The reason is that the TT genotype is embryonic lethal—it causes the embryo to fail to develop. TT embryos are never born. • Manx cats must therefore have the Tt genotype. • The Tt x Tt cross gives ...
... • If you cross two Manx cats, you get two tailless kittens for every one tailed kitten. . . • The reason is that the TT genotype is embryonic lethal—it causes the embryo to fail to develop. TT embryos are never born. • Manx cats must therefore have the Tt genotype. • The Tt x Tt cross gives ...
Pedigree Charts - Mrs. Meadows Science
... genetic history. Pedigrees are used to find out the probability of a child having a disorder in a particular family. To begin to interpret a pedigree, determine if the disease or condition is autosomal or Xlinked and dominant or recessive. ...
... genetic history. Pedigrees are used to find out the probability of a child having a disorder in a particular family. To begin to interpret a pedigree, determine if the disease or condition is autosomal or Xlinked and dominant or recessive. ...