Document
... is designated by R and the recessive wrinkled allele by r (Figure 4). ♦ The genotype of the true-breeding parental round line is RR indicating that it carries two copies of the round allele in each cell. ♦ Such pure lines are said to be homozygous (homo -meaning “identical”) for the round allele. ♦ ...
... is designated by R and the recessive wrinkled allele by r (Figure 4). ♦ The genotype of the true-breeding parental round line is RR indicating that it carries two copies of the round allele in each cell. ♦ Such pure lines are said to be homozygous (homo -meaning “identical”) for the round allele. ♦ ...
Chapter 3 -- The Nature and Nurture of Behavior
... Gender - in psychology, the characteristics, whether biologically or socially influenced, by which people define male and female. Gender differences in attitudes extend to differences in behavior. Casual hit-and-run sex is most frequent among males with traditional masculine attitudes (Pleck & other ...
... Gender - in psychology, the characteristics, whether biologically or socially influenced, by which people define male and female. Gender differences in attitudes extend to differences in behavior. Casual hit-and-run sex is most frequent among males with traditional masculine attitudes (Pleck & other ...
05 Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
... (genetic equilibrium) – Population allele and genotype frequencies remain constant from generation to generation unless they are acted upon by forces other than normal genetics (excluding mutations) ...
... (genetic equilibrium) – Population allele and genotype frequencies remain constant from generation to generation unless they are acted upon by forces other than normal genetics (excluding mutations) ...
IntGen pathway Design (2)
... A---, --BA 15 ratio includes at least one dominant allele for EITHER gene. A dominant allele at EITHER gene is REQUIRED to produce color in Wheat. 13:3 – Dominant suppression 13 No-Mal --B-, aabb NO MENU Dominant allele at gene A BLOCKS gene B, which requires dominant allele. 3 Malvidin A-bb A 3 rat ...
... A---, --BA 15 ratio includes at least one dominant allele for EITHER gene. A dominant allele at EITHER gene is REQUIRED to produce color in Wheat. 13:3 – Dominant suppression 13 No-Mal --B-, aabb NO MENU Dominant allele at gene A BLOCKS gene B, which requires dominant allele. 3 Malvidin A-bb A 3 rat ...
- ScholarSphere
... A case study of Huntington’s disease Alicia Mangin and Marla Gabriele American Society of Human Genetics, in order to diagnose Huntington’s disease, there must be more than 40 tandem repeats for the carrier of this mutation to be completely symptomatic. In these family studies, it found that CAG re ...
... A case study of Huntington’s disease Alicia Mangin and Marla Gabriele American Society of Human Genetics, in order to diagnose Huntington’s disease, there must be more than 40 tandem repeats for the carrier of this mutation to be completely symptomatic. In these family studies, it found that CAG re ...
STB 221 THEORY - Unesco
... genetic characteristic. We will enlarge this definition as we learn more about what genes are and how they function. Genes come in multiple forms called alleles- A gene that specifies a characteristic may exist in several forms, called alleles. For example, a gene for coat color in cats may exist in ...
... genetic characteristic. We will enlarge this definition as we learn more about what genes are and how they function. Genes come in multiple forms called alleles- A gene that specifies a characteristic may exist in several forms, called alleles. For example, a gene for coat color in cats may exist in ...
Independent evolution of overlapping polymerase and surface
... one of the two overlapping genes being subjected to positive selection (adaptive evolution), while the other one is subjected to purifying selection. Yet, for HBV to persist successfully, adaptive evolution of both the P and S genes is essential. We propose that HBV employs a mechanism that allows t ...
... one of the two overlapping genes being subjected to positive selection (adaptive evolution), while the other one is subjected to purifying selection. Yet, for HBV to persist successfully, adaptive evolution of both the P and S genes is essential. We propose that HBV employs a mechanism that allows t ...
Genetics Susceptibility to Infectious Diseases
... One gene – multiple phenotypes • AD STAT1 deficiency: dominant negative mutations susceptibility to mycobacterial and salmonella infections • AD STAT1 deficiency: gain-of-function mutations chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis • AR STAT1 deficiency: loss-of-function mutations susceptibility to s ...
... One gene – multiple phenotypes • AD STAT1 deficiency: dominant negative mutations susceptibility to mycobacterial and salmonella infections • AD STAT1 deficiency: gain-of-function mutations chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis • AR STAT1 deficiency: loss-of-function mutations susceptibility to s ...
NOTES ON STOCKS
... This is in agreement with predictions bored on the linkage doto, since the genetic mop for the parents in alI of these crosses shows that each intercross ...
... This is in agreement with predictions bored on the linkage doto, since the genetic mop for the parents in alI of these crosses shows that each intercross ...
Applied Biology Final Exam Review Sheet Exam: Friday (June 21st
... 3) Describe what homologous chromosomes are (be sure to explain where they come from and how they are similar). Also explain why the X and Y chromosomes are not homologous. 4) Describe the relationship between genes, chromosomes, and DNA. Describe what a trait is and what the relationship is between ...
... 3) Describe what homologous chromosomes are (be sure to explain where they come from and how they are similar). Also explain why the X and Y chromosomes are not homologous. 4) Describe the relationship between genes, chromosomes, and DNA. Describe what a trait is and what the relationship is between ...
Pair-rule genes
... model organism Drosophila melanogaster--Fruit fly • The fruit fly is small and easily grown in the laboratory. – It has a generation time of only two weeks and produces many offspring (up to 300). ...
... model organism Drosophila melanogaster--Fruit fly • The fruit fly is small and easily grown in the laboratory. – It has a generation time of only two weeks and produces many offspring (up to 300). ...
Should this dog be called Spot? Imagine this microscope drama. A
... 11. Does the female dog have curly hair? __________ 12. Does the male dog have curly hair? __________ 13. Define the term heterozygous ________________________________________________________ 14. For which traits is the puppy heterozygous? ____________________________________________ 15, Define the ...
... 11. Does the female dog have curly hair? __________ 12. Does the male dog have curly hair? __________ 13. Define the term heterozygous ________________________________________________________ 14. For which traits is the puppy heterozygous? ____________________________________________ 15, Define the ...
Genetically Effective Population Size
... The Effective Population Size (Ne) is the size of an idealized population that would lose genetic diversity, or become inbred, at the same rate as the actual population. In practice, the effective size of real populations is usually much smaller than the number of breeding individuals because real ...
... The Effective Population Size (Ne) is the size of an idealized population that would lose genetic diversity, or become inbred, at the same rate as the actual population. In practice, the effective size of real populations is usually much smaller than the number of breeding individuals because real ...
Section 2
... • Punnett squares show all possible offspring genotypes. • Probability can be used to describe possible outcomes in offspring and the likelihood of each ...
... • Punnett squares show all possible offspring genotypes. • Probability can be used to describe possible outcomes in offspring and the likelihood of each ...
Quia Quiz – After Unit 6 Which is true? Random scatter in the
... I. Random scatter in the residuals indicates a model with high predictive power. II. If two variables are very strongly associated, then the correlation between them will be near +1.0 or -1.0. III. The higher the correlation between two variables the more likely the association is based in cause and ...
... I. Random scatter in the residuals indicates a model with high predictive power. II. If two variables are very strongly associated, then the correlation between them will be near +1.0 or -1.0. III. The higher the correlation between two variables the more likely the association is based in cause and ...
Developmental buffering: how many genes?
... genes are involved in the control of morphological variation (Breuker et al. 2006). For these strains, the amounts of individual variation of the average shape of the left and right wings and fluctuating asymmetry of wing shape were correlated, suggesting a shared control of both levels of variabilit ...
... genes are involved in the control of morphological variation (Breuker et al. 2006). For these strains, the amounts of individual variation of the average shape of the left and right wings and fluctuating asymmetry of wing shape were correlated, suggesting a shared control of both levels of variabilit ...
A Genetic Analysis of Avian Personality Traits: Correlated
... Individuals in a range of species consistently differ in their behavior towards mild challenges, over age and time. Differences have been found for several personality traits in a range of species. In great tits these traits have a genetic basis and are phenotypically correlated. Estimates of genetic ...
... Individuals in a range of species consistently differ in their behavior towards mild challenges, over age and time. Differences have been found for several personality traits in a range of species. In great tits these traits have a genetic basis and are phenotypically correlated. Estimates of genetic ...
chapter14sganswersfall2008
... 1. Why did Mendel use pea plant as a model organism for his study of genetic inheritance? Peas are available in many varieties, and he could strictly control which plants mated with which. Many of the pea plant traits (flower color, height, etc.) varied in an “eitheror” manner. 2. Mendel tracked onl ...
... 1. Why did Mendel use pea plant as a model organism for his study of genetic inheritance? Peas are available in many varieties, and he could strictly control which plants mated with which. Many of the pea plant traits (flower color, height, etc.) varied in an “eitheror” manner. 2. Mendel tracked onl ...
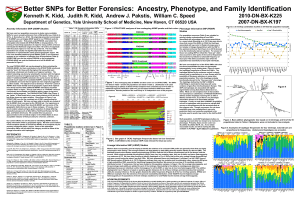
Better SNPs for Better Forensics
... are “better” in that South Asia is now clearly distinct at K=8 and K=9, but Africa shows no major variation. Also shown in Figure 1 are STRUCTURE runs for the combined set of SNPs representing the union of both panels. We have not been able to identify any subset of the 56 AISNPs that is as good as ...
... are “better” in that South Asia is now clearly distinct at K=8 and K=9, but Africa shows no major variation. Also shown in Figure 1 are STRUCTURE runs for the combined set of SNPs representing the union of both panels. We have not been able to identify any subset of the 56 AISNPs that is as good as ...
Neutrality: A Necessity for Self-Adaptation
... genotype encodes not only the information on the phenotype but also information on further explorations. One might state it like this: Although a non-injective genotype-phenotype mapping can be called redundant, the corresponding mapping from genotype to exploration distribution may in general be no ...
... genotype encodes not only the information on the phenotype but also information on further explorations. One might state it like this: Although a non-injective genotype-phenotype mapping can be called redundant, the corresponding mapping from genotype to exploration distribution may in general be no ...
lorenzo-genetics
... girl, the father’s X chromosome will contain instructions to the same parts of the body as the mother’s X chromosome. If the father’s allele is dominant for the characteristic, the recessive trait will not be expressed. This concept is particularly important for sex-linked genetic defects in male ch ...
... girl, the father’s X chromosome will contain instructions to the same parts of the body as the mother’s X chromosome. If the father’s allele is dominant for the characteristic, the recessive trait will not be expressed. This concept is particularly important for sex-linked genetic defects in male ch ...
Genetics of Skin Colour
... may have contributed to the development of skin colour variation over long periods of time. Two plausible hypotheses have been explored. Firstly, UV rays are also known to break down folate (vitamin B6) in the blood vessels just beneath the skin. Folate is essential for dividing cells and therefore ...
... may have contributed to the development of skin colour variation over long periods of time. Two plausible hypotheses have been explored. Firstly, UV rays are also known to break down folate (vitamin B6) in the blood vessels just beneath the skin. Folate is essential for dividing cells and therefore ...
Backcross Breeding
... • Choose DPs that differ greatly from RP to increase the likelihood of recovery of desired trait (earliness example) • Effect of environment on expression of trait can be a problem in BC quantitative traits ...
... • Choose DPs that differ greatly from RP to increase the likelihood of recovery of desired trait (earliness example) • Effect of environment on expression of trait can be a problem in BC quantitative traits ...